What Is BPH?
2. Mechanism
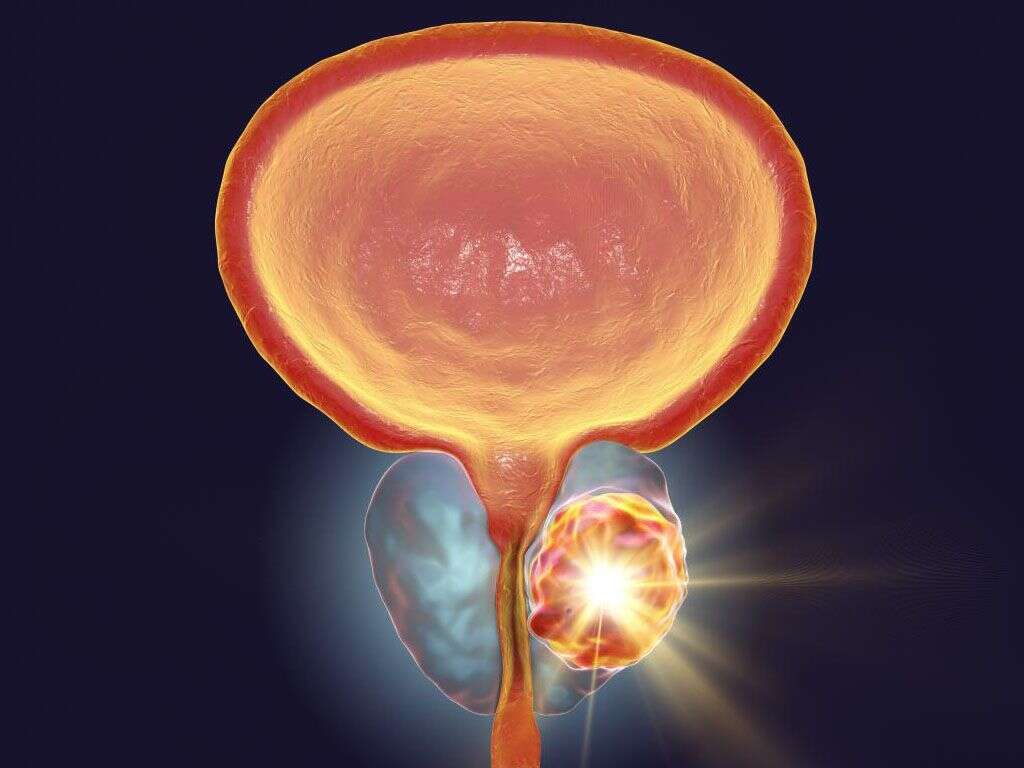
Prostatic enlargement occurs due to the actions of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) hormone, along with other unknown etiologic factors. Circulating testosterone is metabolized into DHT, by a prostatic enzyme known as 5-alpha-reductase. Subsequently, DHT acts on the nucleus of prostatic cells, possibly causing BPH.
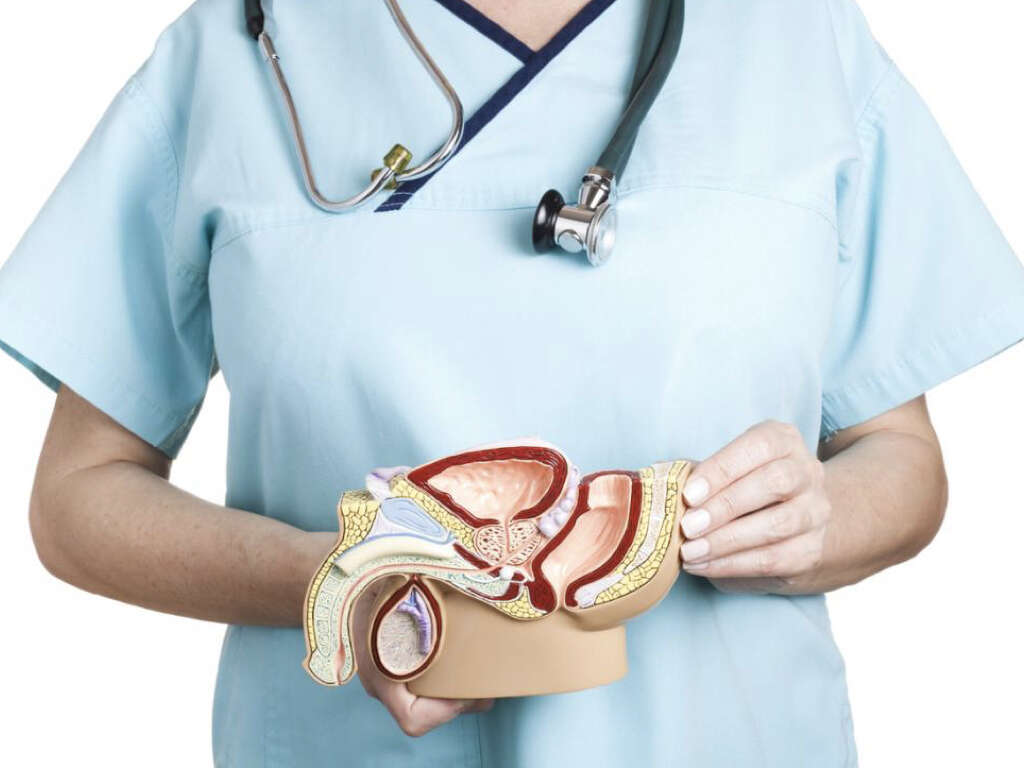
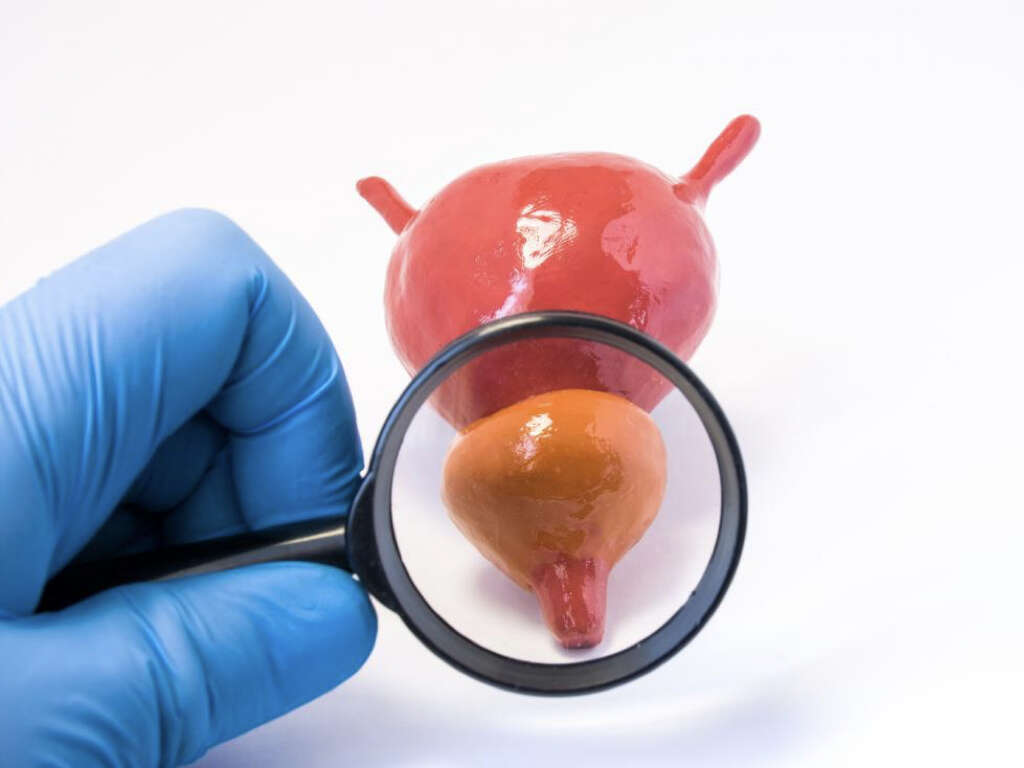
In BPH, the median and lateral lobes are generally enlarged due to their high glandular composition. Most of the growth occurs in the transition zone of the prostate. As mentioned before, the enlargement of the prostate gland may cause urinary symptoms as it restricts the urinary flow through the urethra. Additionally, in BPH, the bladder wall can become thickened and weak, losing its ability to empty completely. Thus, the amount of urine left in the bladder after urination may increase (residual urine volume), possibly leading to the inability to voluntarily pass urine (acute or chronic urinary retention).
Advertisement