Dysphonia Causes, Remedies & More
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. 'Hoarse Voice (Dysphonia).' Hoarse Voice (Dysphonia): Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention, www.nationwidechildrens.org/conditions/hoarse-voice-dysphonia.
- 2. 'Vocal Cord Nodules, Polyps, and Cysts: Condition: UT Southwestern Medical Center.' Condition | UT Southwestern Medical Center, utswmed.org/conditions-treatments/vocal-cord-nodules-polyps-and-cysts/.
- 3. 'Botulinum Neurotoxin Injections.' National Spasmodic Dysphonia Association, dysphonia.org/about-sd/treatment-for-sd/botulinum-toxin-injections/.
- 4. 'Onset and Diagnosis of SD.' National Spasmodic Dysphonia Association, dysphonia.org/about-sd/what-is-spasmodic-dysphonia/onset-diagnosis-sd/.
- 5. 'Muscle Tension Dysphonia.' Johns Hopkins Medicine, www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/muscle-tension-dysphonia.
- 6. 'Why You Shouldn't Whisper With a Hoarse Voice: Keck Medicine of USC.' Keck Medicine of USC , Keck Medicine of USC, 20 Dec. 2019, www.keckmedicine.org/why-you-shouldnt-whisper-with-a-hoarse-voice/.
Dysphonia is a medical issue where an individual has an abnormally hoarse, breathy, raspy or husky voice. Dysphonia can manifest in a number of ways in a patient and may be due to many different causes. If an individual notices any change in their voice that lasts for longer than a week or two, they should seek medical care to diagnose the cause.
Dysphonia can occur in people of any age. It can last for weeks, months or decades, depending on the cause. Usually, it is treatable, but treatment methods vary widely and can include prescription medications, vocal therapy, injections and surgery.2‘Vocal Cord Nodules, Polyps, and Cysts: Condition: UT Southwestern Medical Center.’ Condition | UT Southwestern Medical Center, utswmed.org/conditions-treatments/vocal-cord-nodules-polyps-and-cysts/.
1. Overuse & Illness
Dysphonia is commonly caused by overuse of the voice, which can lead to laryngitis, or inflammation of the voice box (larynx). Excessive overuse can cause scarring, which can permanently damage the voice box. Usually, vocal rest resolves short-term laryngitis.
Another cause of laryngitis is a viral respiratory illness, which can irritate both the vocal folds and the voice box. The voice box can also become inflamed due to an allergic reaction. Coughing and post-nasal drip can cause substantial irritation of the throat, which may lead to hoarseness. Another cause of dysphonia is laryngopharyngeal reflux, which occurs when acid from the stomach causes throat irritation.1‘Hoarse Voice (Dysphonia).’ Hoarse Voice (Dysphonia): Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention, www.nationwidechildrens.org/conditions/hoarse-voice-dysphonia.

2. Vocal Cord Growths
Growths on the vocal cords are another cause of dysphonia, and there are several types. Nodules are growths that appear on the folds due to injury or extended overuse of the voice.1‘Hoarse Voice (Dysphonia).’ Hoarse Voice (Dysphonia): Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention, www.nationwidechildrens.org/conditions/hoarse-voice-dysphonia. Polyps are small clumps of cells caused by vocal abuse.
Cysts are a rarer vocal cord growth. They may be caused by mucus glands in the vocal folds becoming clogged, which can occur due to overuse.2‘Vocal Cord Nodules, Polyps, and Cysts: Condition: UT Southwestern Medical Center.’ Condition | UT Southwestern Medical Center, utswmed.org/conditions-treatments/vocal-cord-nodules-polyps-and-cysts/. Human papillomavirus (HPV) can also cause warts on the vocal cords, which can induce dysphonia.

3. Nerves & Muscle Tension
Problems with the nervous system are another cause of dysphonia, particularly spasmodic dysphonia, which is a lifelong condition. A nerve injury can also lead to vocal issues, but the cause of the nerve problems that lead to spasmodic dysphonia is unknown.
Additionally, vocal paralysis can occur in people due to a birth defect or nerve injury. This can cause an inability to speak or a permanently weak speaking voice. Muscle tension in the area surrounding the larynx can also lead to dysphonia.5‘Muscle Tension Dysphonia.’ Johns Hopkins Medicine, www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/muscle-tension-dysphonia.

4. Symptoms Include Voice Changes
A change in the voice is the main symptom of dysphonia, and it can result in the voice becoming higher or lower in pitch. Placement of the voice can also be affected, with a voice sounding more nasally or weaker than before.1‘Hoarse Voice (Dysphonia).’ Hoarse Voice (Dysphonia): Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention, www.nationwidechildrens.org/conditions/hoarse-voice-dysphonia.
Vocal rasp is another symptom, with the voice sounding gravelly, hoarse or weak. Words can drop off during speech, and talking can feel more difficult to manage. Vocal tremors, a lack of breath and voice breaks are also common symptoms.4‘Onset and Diagnosis of SD.’ National Spasmodic Dysphonia Association, dysphonia.org/about-sd/what-is-spasmodic-dysphonia/onset-diagnosis-sd/.

5. Pain When Speaking
Symptoms of dysphonia caused by a respiratory illness or overuse can include pain when speaking or swallowing, which can vary in severity. Pain can also occur with nodules or polyps on the vocal folds.2‘Vocal Cord Nodules, Polyps, and Cysts: Condition: UT Southwestern Medical Center.’ Condition | UT Southwestern Medical Center, utswmed.org/conditions-treatments/vocal-cord-nodules-polyps-and-cysts/.
Whenever an individual experiences pain when speaking, they should practice vocal rest to prevent further damage to the vocal folds. Scarring caused by overuse can require surgery to fix, and it may still cause permanent vocal issues that inhibit a person's ability to sing or speak normally.
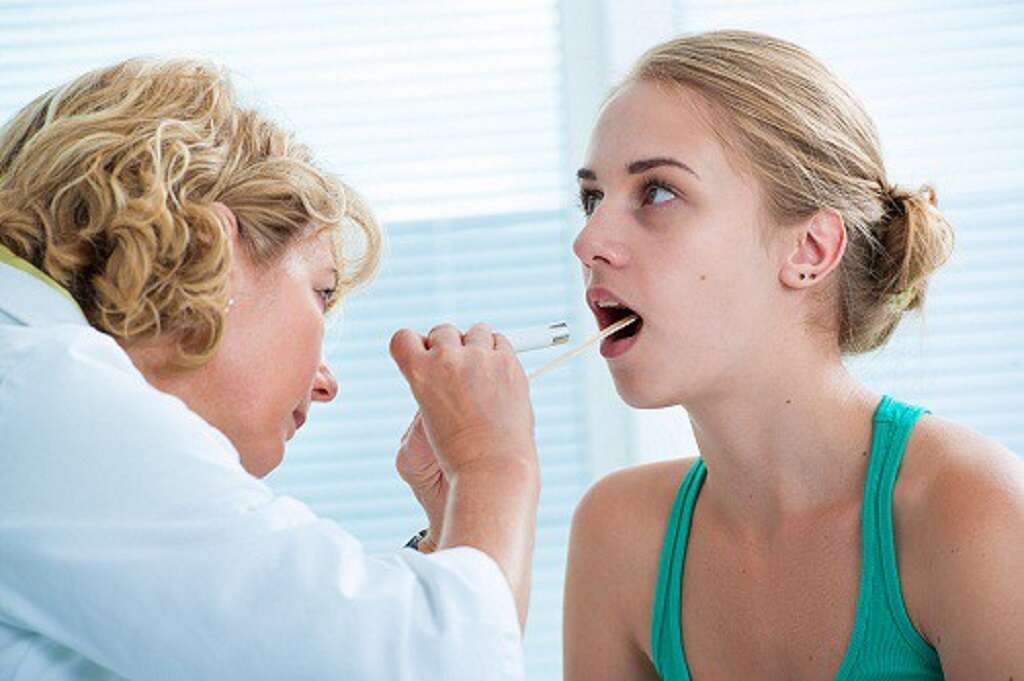
6. Diagnosis
Diagnosing the cause of dysphonia can require an appointment with an ENT specialist. A simple discussion of symptoms and a physical inspection of the vocal folds can help diagnosis. In some cases, a camera is placed through the nose to examine the vocal folds for the presence of polyps, cysts or nodules.2‘Vocal Cord Nodules, Polyps, and Cysts: Condition: UT Southwestern Medical Center.’ Condition | UT Southwestern Medical Center, utswmed.org/conditions-treatments/vocal-cord-nodules-polyps-and-cysts/.
Another test used is sound analysis, which identifies abnormalities in a voice to help pinpoint the cause. Spasmodic dysphonia can be difficult to diagnose, as there is no obvious anatomical cause.4‘Onset and Diagnosis of SD.’ National Spasmodic Dysphonia Association, dysphonia.org/about-sd/what-is-spasmodic-dysphonia/onset-diagnosis-sd/.

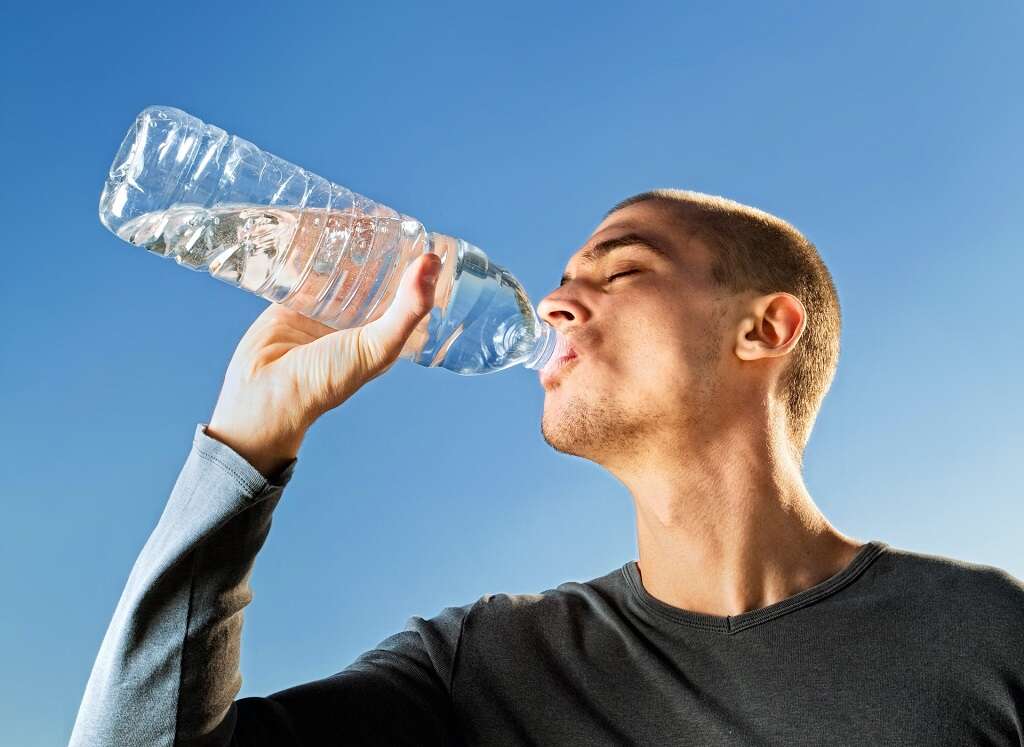
7. Treat With Vocal Rest & Hydration
The usual treatment for temporary dysphonia is vocal rest. If dysphonia is caused by an infection, a doctor may recommend antimicrobial agents. Resting the voice means no talking, including whispering. In fact, whispering with a lost or hoarse voice can lead to further damage, as whispering actually puts more strain on a person's vocal cords than speaking normally.6‘Why You Shouldn’t Whisper With a Hoarse Voice: Keck Medicine of USC.’ Keck Medicine of USC , Keck Medicine of USC, 20 Dec. 2019, www.keckmedicine.org/why-you-shouldnt-whisper-with-a-hoarse-voice/.
Other remedies for a lost voice include drinking lots of hydrating fluids, which means no coffee, which can dehydrate the throat and irritate the vocal folds.

8. Therapy & Medication Treatment
Treating growths on the vocal cords can prove to be a difficult process, which is why protecting the voice is so important for people with jobs that involve singing, shouting or constant speech. The cessation of smoking and drinking caffeine are often helpful to prevent further irritation and damage.2‘Vocal Cord Nodules, Polyps, and Cysts: Condition: UT Southwestern Medical Center.’ Condition | UT Southwestern Medical Center, utswmed.org/conditions-treatments/vocal-cord-nodules-polyps-and-cysts/.
Steroids are sometimes used to counteract inflammation. Speech therapy can also be used to alter speaking and singing patterns to prevent future damage, as nodules and polyps often occur due to improper singing/speaking techniques.

9. Surgical Intervention
For some forms of dysphonia, microsurgery and laser surgery can restructure the vocal folds and larynx and remove cysts and other growths. Surgery can also be used to remove scarring from the vocal folds.
For sufferers of spasmodic dysphonia, botox is sometimes injected to block the neurotransmitter that causes muscle contractions in the neck. If effective, this treatment will need to be administered indefinitely, as it usually only lasts for several months before another injection is required.3‘Botulinum Neurotoxin Injections.’ National Spasmodic Dysphonia Association, dysphonia.org/about-sd/treatment-for-sd/botulinum-toxin-injections/.
10. Living With Dysphonia
While there is still no cure for some forms of dysphonia, there are plenty of treatment options that can improve and alleviate symptoms; however, people with more permanent or long-lasting forms of dysphonia may experience lifelong symptoms.
While causes such as muscle tension dysphonia can be treated with vocal therapy and surgery, there's no guarantee treatment will be successful. The same goes for those with spasmodic dysphonia, which can lead to embarrassment in social situations and a reluctance to participate in group discussions.