10 Causes of Necrotizing Fasciitis
Necrotizing fasciitis, also known as flesh-eating disease, occurs due to an infection that leads to death in parts of the body’s soft tissue. It is a severe disease that begins suddenly and spreads rapidly. Patients with necrotizing fasciitis will experience fever, severe pain, vomiting, and purplish-red skin in the affected area.
The most common sites that are affected are the perineum and limbs. The infection usually begins when the pathogen enters the body through a wound or cut. The risk of necrotizing fasciitis is higher if the individual has poor immune function due to cancer or diabetes, intravenous drug use, peripheral vascular disease, and alcoholism. It does not usually spread between people. This disease can be divided into four types based on the organism responsible for the infection. It has been estimated that 55 to 80 percent of cases involves more than one bacterium. Approximately 33 percent of cases involve methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
Prevention includes handwashing and proper wound care. Treatment involves surgery to remove infected tissue and intravenous antibiotics. Combinations of antibiotics such as vancomycin, penicillin G, gentamicin, and clindamycin can be used. When surgery is delayed, it has been associated with a higher risk of death. Despite quality treatment, the risk of death from necrotizing fasciitis has been estimated to be between 25 to 35 percent. It occurs in approximately 0.4 per 100,000 individuals in the United States. While both sexes are equally affected, it is more common among older individuals and rarely seen in children. This article discusses 10 causes of necrotizing fasciitis.

Cause #1: Chemotherapy or Radiotherapy
Chemotherapy is a treatment for cancer. Chemotherapeutic agents are given with an aim to cure, reduce symptoms, or prolong life. Generally, chemotherapy can be thought of as a method to damage cells, which can result in cell death. Radiotherapy refers to therapy given using ionizing radiation. It is most often used for cancer treatment to kill or control malignant cells. It can be used with an aim to cure or as part of adjuvant therapy.
Both chemotherapy and radiotherapy weaken the immune system and patients will have a higher risk of various infections such as from the naturally occurring microorganisms in the gastrointestinal tract. It also increases the likelihood of necrotizing fasciitis.
Cause #2: Diabetes
Diabetes is a group of metabolic disorders that results in hyperglycemia for a prolonged duration. Patients with diabetes will experience increased thirst, frequent urination, and increased hunger. Diabetes can lead to complications such as diabetic ketoacidosis, chronic kidney disease, heart disease, foot ulcers, stroke, and eye damage.
Diabetes occurs when there is decreased insulin sensitivity or if the pancreas is not producing enough insulin. It can be divided into type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes. Patients with diabetes are also known to have a weaker immune system, which causes infections such as necrotizing fasciitis to be more likely.
Cause #3: Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are a class of medications (steroid hormones) that are also produced in the adrenal cortex. Corticosteroids can be divided into mineralocorticoids and glucocorticoids. They are involved in various physiological processes such as the immune response, stress response, carbohydrate metabolism, blood electrolyte levels, protein catabolism, and inflammation.
Corticosteroids can be used in various diseases such as brain tumors, skin diseases, allergies, interstitial lung disease, Addison’s disease, congenital adrenal hyperplasia, and ulcerative colitis. However, long-term corticosteroids suppress the immune system and can lead to infections such as necrotizing fasciitis.
Cause #4: HIV or AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection or acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) refer to a spectrum of conditions that occur because of infection in an individual due to HIV. Initial stages of infection are usually asymptomatic, or they may experience influenza-like illness.
There can be a prolonged period without any symptoms. As the infection progresses, it increases the likelihood of other infections such as tuberculosis, tumors (that rarely affect individuals with normal immune systems), and necrotizing fasciitis.

Cause #5: Organ Transplant
Organ transplant refers to the procedure where an organ is removed from a donor and placed in another individual as a replacement. Both the donor and recipient can be at the same place or organs can also be transported to another location for transplant.
Organ transplant can involve the heart, liver, kidneys, lungs, intestine, thymus, tendons, bones, heart valves, cornea, skin, veins, nerves, and bone marrow, among others. One key area after transplant is to ensure that transplant rejection does not occur. This means that patients will have to use immunosuppressant drugs after the procedure. The immunosuppressant drugs weaken the immune system and predisposes the patient to various infections such as necrotizing fasciitis.
Cause #6: Malignancies
The term “malignancy” refers to the tendency of the condition to progressively worsen. It is a term most commonly used in cancer where a malignant tumor is capable of invasion and metastasis while a benign tumor does not.
There are certain cancers that cause the patient to be immunocompromised. One good example is chronic lymphocytic leukemia where patients become susceptible to encapsulated bacteria. Other examples of malignancies causing immunocompromise include multiple myeloma, hairy cell leukemia, and Hodgkin disease. Since these patients are immunocompromised, it increases the likelihood of infections such as pneumonia and necrotizing fasciitis.

Cause #7: Alcohol Use Disorder
Alcohol use disorder is a major concern as it causes a considerable burden of disease. In 2014, the World Health Organization reported that 5.9 percent of deaths worldwide can be attributed to alcohol. Some diseases that can be attributed to alcohol include breast cancer, esophageal cancer, oropharyngeal cancer, colorectal cancer, diabetes, and heart disease.
The prevalence of necrotizing fasciitis has also been reported to be higher among individuals with alcohol use disorder. One study found that alcohol use disorder is an independent and significant risk factor for necrotizing fasciitis.

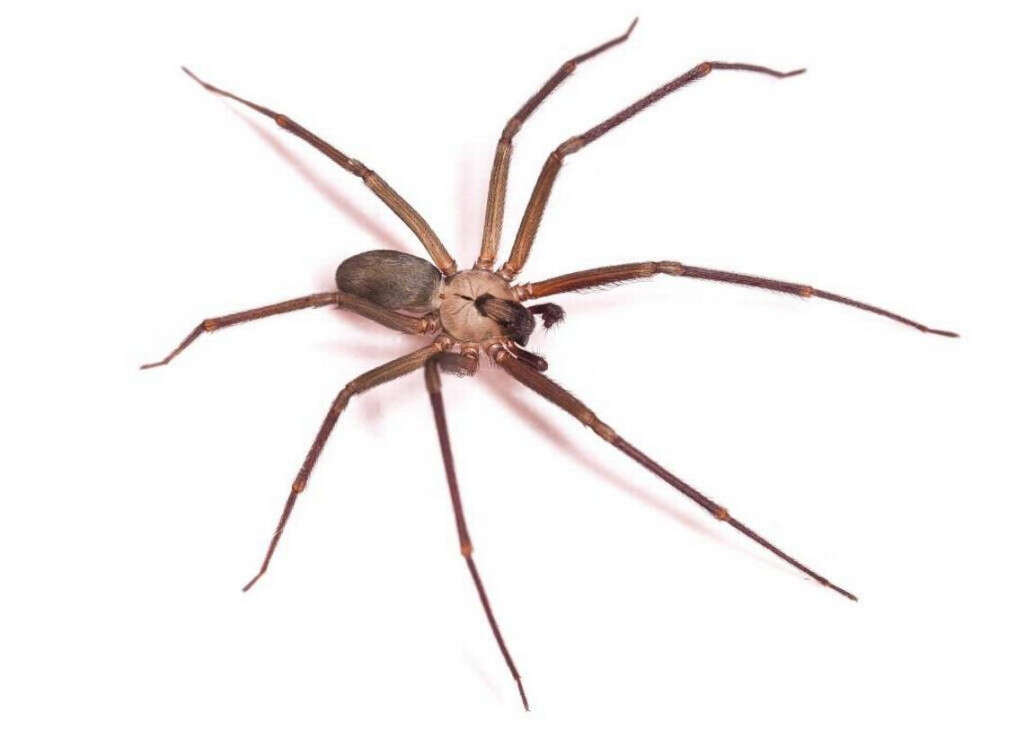
Cause #8: Bites
One study analyzed 31 cases of necrotizing fasciitis patients over a period of 20 years. This study found that 2 out of 31 patients had necrotizing fasciitis due to a brown recluse spider bite. Both these patients delayed in seeking medical treatment, resulting in secondary infection of necrotic tissue. Diagnosis was achieved via frozen section biopsy and clinical examination. Both patients underwent immediate aggressive operative debridement and survived with functional limbs.
The study concluded that necrotizing fasciitis can be caused by secondary infection due to a brown recluse spider bite. It is important for patients with necrotizing fasciitis to be diagnosed early and undergo immediate surgical debridement as it can improve prognosis and reduce complications.

Cause #9: Infected Wounds
Necrotizing fasciitis can occur if individuals with injured skin expose themselves to water contaminated by bacteria that can cause this disease.
Vibrio vulnificus is a bacterium that can enter the body when an individual with wounds wade or swim in infected waters. It can also occur if they cut themselves on rocks, pebbles, or spines of fishes.

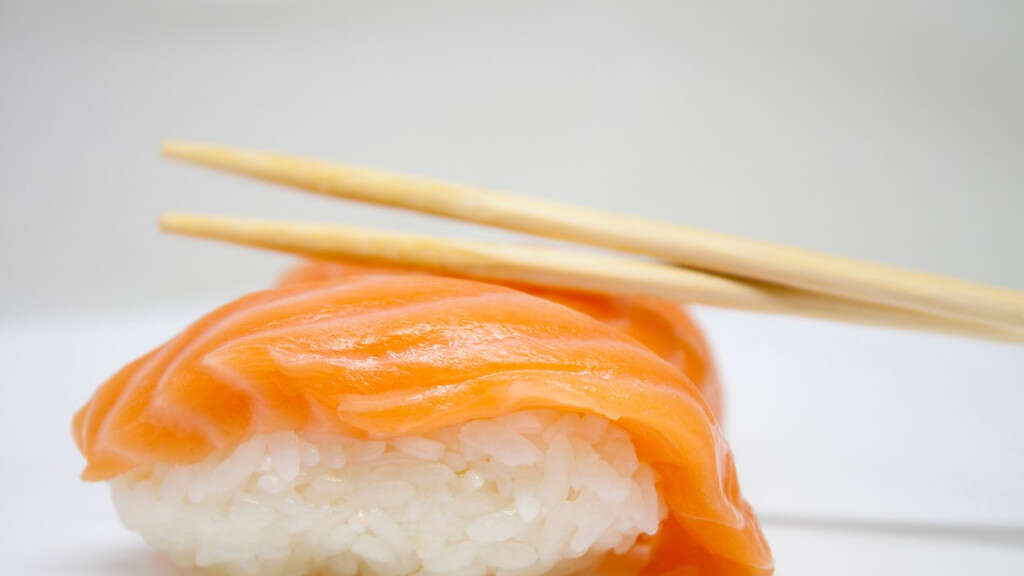
Cause #10: Ingestion of Raw or Undercooked Seafood
There have also been associations made between necrotizing fasciitis and ingestion of raw or undercooked seafood. It has been attributed to Vibrio vulnificus that is naturally found in warm seawaters. It is also thought that there may be high levels of this bacterium in bivalve mollusks such as oysters because of their filter feeding activity.
This bacterium is even more of a threat to those with underlying chronic diseases such as HIV or AIDS, liver disease, and diabetes. With an incubation period of 12 hours to several days, it can lead to symptoms such as diarrhea, fever, abdominal pain, and vomiting. Severe cases result in septicemia. Some organizations have claimed that ingestion of raw or undercooked seafood can result in necrotizing fasciitis. However, it has been thought that the handling of seafood during consumption could have resulted in cutaneous injury that was not noticed.

Related Articles
-
What Is Necrotizing Fasciitis?
10FAQ
-
What Is Flesh Eating Bacteria?
10FAQ
-
Nursing Degree: A Gateway To A Rewarding Career
10FAQ
-
Understanding LASIK Surgery for Improved Vision
10FAQ
-
Cheap Dental Implants: A Cost-Effective Solution For Your Dental Needs
10FAQ
-
Gallbladder Polyps Causes, Symptoms and More
10FAQ



