10 Neuropathy Symptoms
There are many types of neuropathies such as peripheral neuropathy, diabetic neuropathy, metabolic neuropathy, and autonomic neuropathy. Neuropathy refers to the disease of the nerves. The term peripheral neuropathy refers to disease or injury that causes dysfunction of the peripheral nerves. The peripheral nerves describe the peripheral nervous system comprising of 43 pairs of motor and sensory nerves that interconnects the spinal cords and brain to the entire body. It controls sensation, motor coordination, and movement. Diabetic neuropathy is a common complication of diabetes mellitus and can affect as many as 50% of patients with diabetes, regardless of whether it is type 1 or type 2 diabetes. It can severely decrease the quality of life in patients that are affected. While the factors are not fully understood it has been deemed to be a multifactorial process.
Some of the risk factors that are associated with it are poor blood glucose control, increasing age, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, alcohol consumption, and more. In the United States, it has been estimated that there are as many as 47% of diabetics suffering from neuropathy. Autonomic neuropathies affect the autonomic neurons, both sympathetic and parasympathetic. It can either be hereditary or acquired. It can be seen in individuals of all races or ages but happens predominantly in males.

Symptom #1: Numbness or Tingling
Neuropathy means that there is some degree of damage or injury to the nerves. This causes the nerves to become numb and affected individuals may experience sensations of tingling in certain parts of the body.
Since nerves function to relay messages of sensation or impulses back to the central nervous system, damage or injury to the nerves reduces the sensitivity of the nerves to touch, temperature, pain and more. The affected nerves are no longer functioning properly. Neuropathy most commonly affects the peripheral nerves which are located furthest away from the central nervous system and heart. As there is an increasing loss of perception of stimuli in the affected area, numbness ensues.
Symptom #2: Pain
Some individuals affected with peripheral neuropathy can sometimes experience pain that can be described as sharp and shooting in nature. It most commonly occurs in the legs. Some even experience pain from stimulus that normally should not cause pain (such as a light touch). Neuropathic pain does not start suddenly or resolve quickly and the intensity of pain can often wax and wane throughout the entire course of the day.
Patients at risk of neuropathic pain include those with diabetes, cancer, vitamin deficiencies, stroke, human immunodeficiency virus infection, multiple sclerosis, cancer treatments, and shingles. Neuropathic pain can be described as sharp, hot, cold, dull, itchy, stinging, burning, or deep.
Symptom #3: Allodynia and Hyperalgesia
Allodynia is a medical term that refers to sensitivity to pain that occurs without non-painful stimulation. Allodynia can be aggravated by stimuli such as temperature or physical stimuli and can provoke a burning sensation. It is different from hyperalgesia which is an exaggerated response to a stimulus that can be painful.
Hyperalgesia is the increased sensitivity to pain that may occur due to the damage of receptors or peripheral nerves. There are two types of hyperalgesia, where the primary form refers to pain occurring in damaged tissues while the secondary form refers to pain that happens in surrounding undamaged tissues. Both are seen in neuropathy and affect 15 to 50% of patients affected by it.

Symptom #4: Loss of Balance
Individuals with peripheral neuropathy can often lose their balance due to lack of coordination in several different parts of their body. In the body, there are proprioceptors that are a type of receptors in subcutaneous tissue that function to respond accordingly to stimuli that are occurring in the body.
Another contributing factor to loss of balance might be due to muscle weakness which can lead to patients requiring the enlistment of help from other individuals to cope with their daily routines. The injuries sustained from falls and other injuries can further contribute to prolonged periods of rest which can lead to muscular atrophy and weakness that once again, contributes to loss of balance and coordination.

Symptom #5: Issues with Gait
In patients with diabetic neuropathy, these patients experience impaired vibration and protective sensation (loss of sensation), reduced strength in the lower extremities, and alterations in the central nervous system that can all contribute to the issues of gait in diabetic patients. It has been found that patients with diabetic neuropathy have a higher risk of falling especially during movement suggesting that there may be difficulty maintaining stability during walking.
It has also been observed that these patients have a greater shift in their central mass when using the stairs. The study has also reported that diabetics take additional steps when they walk in a linear path and during turns that indicate their additional instability.
Symptom #6: Cramps
As previously established, there are many types of neuropathy. Patients who suffer from neuropathy often report experiencing muscle cramps. A muscle cramp is an involuntary and rapid contraction of the muscles. While it is generally harmless, it can cause severe pain and result in a temporary loss of muscle function until it resolves.
While it is a non-specific symptom that can be associated with any other disease such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (or better known as Lou Gehrig’s disease), it can occur with low calcium levels and neuropathy. If you are constantly experiencing muscle cramps, you should make an appointment with your doctor to determine the underlying cause of the condition.
Symptom #7: Weakness
If sensory nerves are affected the sensation such as touch, pain, and vibration are affected. If motor nerves are affected, it can result in weakness or paralysis. Other symptoms such as muscle twitching, cramping, spasms, tiredness, and other factors can also contribute to further muscle weakness as the muscles start to atrophy.
The pain can also cause the patient to be unwilling to move which further contributes to muscular weakness. Management, such as physical rehabilitation, might be beneficial. In elderly patients, the symptoms of weakness can often be mistaken as part of the aging process.

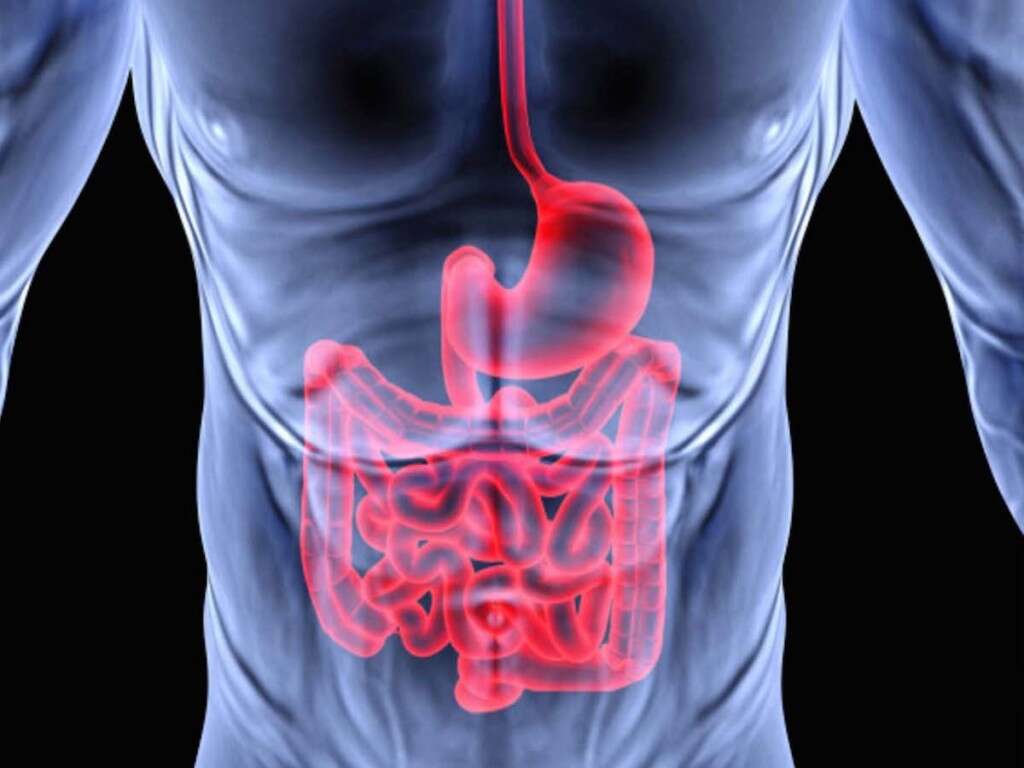
Symptom #8: Gastrointestinal Problems
Autonomic neuropathy seen in patients with diabetes is important as it affects a significant population of diabetics regardless if it is type 1 or 2 diabetes. Some of the gastrointestinal problems affecting those with neuropathy are gastroparesis (a condition where the muscles or nerves in the stomach stop working leading to poor emptying of food from the stomach into the intestine), and general signs of dysfunction of the bowels (such as diarrhea, constipation, and abdominal pain).
All these issues can be treated with both pharmacological and non-pharmacological options. Other issues can include bloating, indigestion, and flatulence. Many of these symptoms are treated symptomatically and healthcare professionals can sometimes overlook the association of neuropathy and gastrointestinal issues.
Symptom #9: Low Blood Pressure
In some cases of neuropathy where the autonomic nerves are affected, it can cause low blood pressure that leads to dizziness and fainting.
Usually, patients develop a condition called Orthostatic Hypotension, which means that their blood pressure falls after standing up.

Symptom #10: Bell’s Palsy
Another form of neuropathy is known as cranial neuropathy. The cranial nerves originate from the brain or brainstem and affect important areas such as the face and eyes. When cranial neuropathies occur, one of the conditions that can result is Bell’s palsy.
In Bell’s palsy, there is temporary weakness of the facial muscles causing one side of the face to droop. This also means that any emotions that you express will only be reflected on one side. Bell’s palsy occurs when the facial nerve (seventh cranial nerve) becomes affected.