Uterine Polyps Symptoms, Causes and More
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. 'Uterine Polyps.' Mayo Clinic, Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research, 17 Dec. 2020, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/uterine-polyps/symptoms-causes/syc-20378709.
- 2. 'Uterine Polyps: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment.' Cleveland Clinic, my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/14683-uterine-polyps#symptoms-and-causes.
- 3. Nijkang, Njume Peter, et al. 'Endometrial Polyps: Pathogenesis, Sequelae and Treatment.' SAGE Open Medicine, SAGE Publications, 2 May 2019, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6501471/.
Uterine polyps develop from an overgrowth of endometrial tissue. Also known as endometrial polyps, they can cause irregular, heavy menstrual cycles and may even lead to infertility. Hormones play a role in the growth of the polyps. There are a few risk factors, including hypertension and obesity, that may also cause uterine overgrowth.1‘Uterine Polyps.’ Mayo Clinic, Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research, 17 Dec. 2020, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/uterine-polyps/symptoms-causes/syc-20378709.
There are both noninvasive and invasive treatment options for the condition. Although polyps can be cancerous, most endometrial overgrowth is noncancerous. Women with symptoms of uterine polyps should see a doctor to confirm the diagnosis and start treatment.2‘Uterine Polyps: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment.’ Cleveland Clinic, my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/14683-uterine-polyps#symptoms-and-causes.

1. What Are Uterine Polyps?
Uterine polyps form in the endometrium. These abnormal growths contain glands, blood vessels, and stroma and can vary from a few millimeters to several centimeters in size. Women may experience one or more round or oval polyps between the size of a sesame seed and a golf ball, which are attached to the uterine wall by a stalk or base. Some describe the overgrowth as having a finger-like appearance.3Nijkang, Njume Peter, et al. ‘Endometrial Polyps: Pathogenesis, Sequelae and Treatment.’ SAGE Open Medicine, SAGE Publications, 2 May 2019, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6501471/.
Most endometrial polyps are noncancerous. They're most often found inside the uterus. But sometimes, the growths can occur at the cervix's opening.

2. Symptoms
Some women have no symptoms of uterine polyps. Individuals with adverse responses may experience menstrual bleeding between periods, irregular periods, or heavy bleeding. Women past menopause might have vaginal bleeding.
Additionally, endometrial polyps can interfere with fertility. Some women may have trouble getting pregnant and have miscarriages. This condition is more likely to develop to those aged 40 or older, and it rarely occurs in women under the age of 20.
3. Causes
Medical experts don't know the exact cause of uterine polyps. However, research shows this type of overgrowth occurs in estrogen-dependent tissues, such as the uterus. Estrogen also causes the endometrium to thicken between menstrual cycles.
Additionally, studies indicate women with endometrial polyps have a higher concentration of progesterone receptors and estrogen receptors. These are some potential causes of overgrowth. A physician can help patients determine their risk factors for uterine polyps to help prevent future growth.

4. When to Call the Doctor
Women should seek medical care for unexplained changes in their menstrual cycle, such as heavier bleeding, longer periods, and bleeding between cycles. Postmenopausal women experiencing vaginal bleeding should contact their gynecologist.
Additionally, anyone experiencing trouble getting or staying pregnant should schedule an appointment with a specialist to rule out complications from uterine polyps in the uterus. The provider may conduct tests to check for polyps and related conditions that can cause fertility issues.

5. Diagnosis
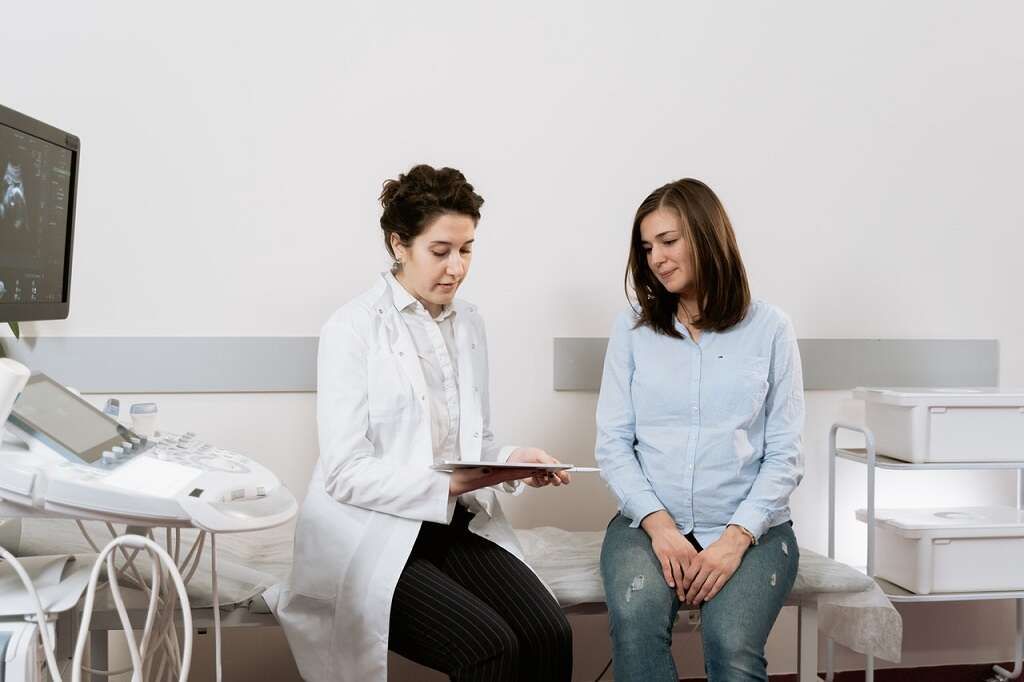
A diagnosis requires specific tests to verify the presence of polyps. Several options are available that vary in invasiveness. A common procedure is a transvaginal ultrasound, which involves inserting the device into the vagina. This test uses sound waves to produce an image of the uterus's interior.
Another option is a sonohysterography, which uses a catheter to expand the uterus for a clearer image of the area. Also, a hysteroscopy may be used to identify uterine polyps and remove smaller ones.

6. Risk Factors
Doctors don't know the exact cause of endometrial polyps, but they do know the condition's risk factors. Women who are obese have a greater chance of developing polyps. Also, women receiving Tamoxifen, a breast cancer treatment, have an increased risk.
Another possible medication-related cause is hormone replacement therapy. Women taking these drugs may be advised of the increased chances of uterine polyps. Individuals with a family history of Lynch syndrome or Cowden syndrome may also be more likely to develop polyps.

7. Treatment
Endometrial polyps may become cancerous in some rare cases. Most providers prefer to eliminate the slight risk of cancer through a minimally invasive outpatient treatment method, by removing the polyps with a hysteroscopy. This treatment also involves examining the polyps in a lab to check for precancerous and cancerous cells.
Sometimes, a medical professional prefers to test the lining around the polyp. A dilation and curettage procedure allows them to take a biopsy sample.

8. Prognosis
The prognosis is good for patients after uterine polyp removal. Only 1 percent of polyps become cancerous. After extracting the growths with the hysteroscopic polypectomy, the pregnancy rates for patients experiencing infertility increase, and the miscarriage percentage goes down.
Additionally, patients' periods typically return to normal, and all other symptoms stop. Endometrial polyps rarely return after they're removed. Women experiencing symptoms after a polypectomy should consult with their gynecologist to rule out other conditions.

9. Complications
Several complications of uterine polyps can develop. Although rare, they can develop into cancer. Women who've gone through menopause have a higher risk of precancerous and cancerous polyps.
This condition may prevent women from getting pregnant. Also, it may lead to a miscarriage, which can occur when one or more polyps make it difficult for the fertilized egg to attach to the uterus. They may also block the fallopian tubes and cervix. Research shows that after removal, women may avoid these complications.

10. Prevention
There is no proven method of preventing uterine polyps. However, women can take proactive measures to reduce the chances of developing endometrial overgrowth in the uterus.
Regular gynecological checkups can help diagnose and treat endometrial polyps. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight and keeping blood pressure low may reduce a woman's chances of developing the condition. Women who think they may have uterine polyps should seek medical care as soon as possible for treatment.