What Is Bullous Pemphigoid?
Bullous Pemphigoid is a rare autoimmune disorder that occurs when the immune system attacks the thin layer of tissue below the upper layer of the skin. It is characterized by skin rashes and blistering. Though the condition can affect any person of any age, it most commonly affects the elderly.
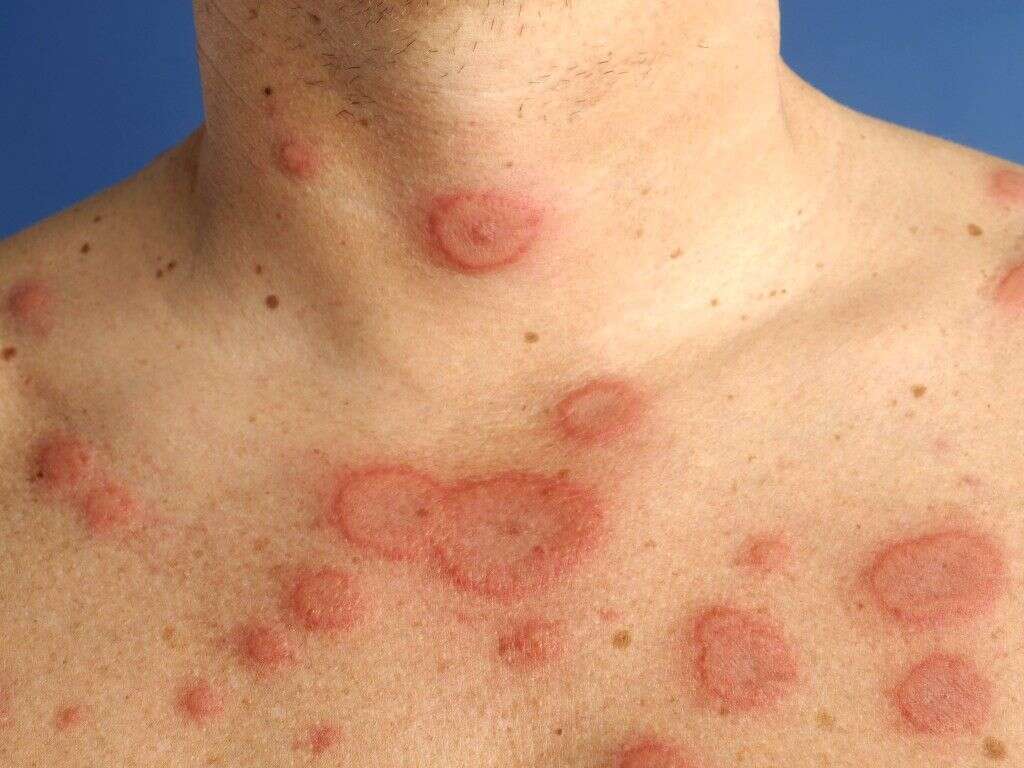
There are several presentations of this disease. For instance, the most common type of bullous pemphigoid is the generalized bullous form, where tense fluid-filled sacs (bullae) can arise in any part of the skin surface. Moreover, other less common forms involve the presence of groups of tiny vesicles or itchy hive-like lesions that may or may not evolve into bullae.
1. What Are the Symptoms of Bullous Pemphigoid?
The most common form of bullous pemphigoid usually presents with skin lesions known as bullae, which are tense fluid-filled sacs. These can involve any portion of the skin surface, but they often appear along creases or folds in the skin. Typical locations for bullous pemphigoid include the lower abdomen, upper thighs, or armpits. Rarely, the involvement of the oral and ocular surfaces occurs.
The skin around the blisters sometimes remains clear, but it can also develop a red hue. Itchiness is also common. On occasions, especially in the elderly, itching may be the only sign of disease. In other forms of bullous pemphigoid, bullae may or may not arise after persistent hive-like lesions.
2. What Causes Bullous Pemphigoid?
Pemphigoid is the result of a malfunctioning immune system. When the immune system is in good working order, it fights off potentially harmful foreign substances, such as viruses and bacteria. However, when it malfunctions, it may mistake certain parts of your body, such as tissue, for a harmful foreign substance.
In this condition, the immune system develops immune proteins (autoantibodies) that mistakenly attack skin structures that connect the epidermis (outer layer of the skin) with the dermis (inner layer). As a result, an inflammatory process of the skin takes place and the skin lesions of bullous pemphigoid appear.
3. What Are the Risk Factors for Bullous Pemphigoid?
The most common risk factor for bullous pemphigoid is age. The majority of individuals who develop the condition are over the age of 60. That said, research indicates certain factors may trigger the condition in prone individuals.
Exposure to certain medications can precipitate the condition (i.e. furosemide, captopril, ibuprofen, penicillin). Also, light and radiation therapies, such as those used to treat certain skin conditions and cancer, may trigger the disorder. Finally, certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, psoriasis, lichen planus, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis, may precipitate the disease.

4. How Is Bullous Pemphigoid Diagnosed?
Typically, it takes little more than a physical examination and a Q&A session for your doctor to diagnose bullous pemphigoid. Upon seeing your blisters, your doctor may ask you about when your symptoms began, associated symptoms, and whether you’ve been on any new medications or treatments.
If your doctor suspects bullous pemphigoid, he or she may order blood tests to confirm the condition. Most importantly, the physician will surely take a small sample from the affected area (biopsy) and send it to the lab for testing. If your doctor does not feel comfortable making a diagnosis, you may be referred to a specialist (dermatologist).

5. How Can You Help Your Doctor Make a Diagnosis?
There are a few steps you can take to help your doctor make a correct diagnosis. Before your appointment, make a list of any symptoms, in addition to the rash and blisters, you’ve experienced. Write down the name of any vitamins, supplements, and medications you’ve been taking.
Show up with a list of questions for your doctor as well. One of the best questions to ask is if there is possibly an alternate cause for your symptoms. Request tests if your doctor does not order any, ask how long the skin changes will last, and inquire about possible side effects of all treatment options.

6. How Is Bullous Pemphigoid Treated?
The goal of the treatment of pemphigoid is to manage the symptoms, relieve the itching, and accelerate the healing process. For this purpose, your doctor may prescribe a corticosteroid or immunosuppressant (i.e. azathioprine, methotrexate).
Because the aforementioned drugs weaken the immune system, they are not ideal for long-term use. To reduce the side effects of either, your doctor may prescribe topical therapies for local disease.

7. Can Self-Care Strategies Help?
In addition to taking any prescription medications, there are steps you can take at home to manage the condition and increase your comfort. First and foremost, take care of the wounds already present. This must be done according to the instructions given by a specialist.
To avoid aggravating the lesions, you may need to limit your activities until they are under control. If you do go out, make sure the affected skin is covered, as sun exposure can worsen symptoms. Additionally, wear loose-fitting clothing that does not rest heavily on the blisters or rash.
8. Is Bullous Pemphigoid Contagious?
Bullous pemphigoid is the result of a malfunctioning immune system. Instead of attacking germs, it attacks the body itself. Though the reasons behind this response are unclear the condition is not contagious, and close contact does not result in transmission.
Moreover, bullous pemphigoid is not caused by an allergy. While it can be triggered by some medications, these factors alone are not the cause. Pemphigoid is not affected by lifestyle or diet, meaning it is not preventable.
9. What Is the Outlook for Bullous Pemphigoid?
Most people who develop bullous pemphigoid do not live with it forever. The disease may have periods of exacerbations and spontaneous remissions. With proper treatment, that can last up to 60 months, many individuals can regain full health and go on without signs and symptoms within a few months or years.
That said, sometimes the immune system continues to attack the skin tissue once a person stops taking medication. If this is the case for you, work with your doctor to develop a treatment plan that consists of options that are safe for you long-term.

10. Can Bullous Pemphigoid Result in Complications?
Though rare, bullous pemphigoid can result in complications. This is especially true in cases in which a person does not seek treatment or refuses to take medication. In cases in which the disease is widespread or resistant to medication, it can be particularly dangerous.
The most common complications of bullous pemphigoid include infections with sepsis and adverse effects of treatment. Pemphigoid may also aggravate associated or underlying diseases. Unfortunately, bullous pemphigoid can be fatal in a minority of patients.