10 Causes of Joint Pain
Joint pain, or arthralgia, is often a symptom seen in infection, injury, illness, or as a side effect of medication. Joint pain occurs due to destructive and degenerative processes and can originate from any part of the joint, such as the tendons, muscles, ligaments, cartilage, and bone.
The diagnosis of joint pain involves interviewing and examining the patient in collaboration with various tests. The treatment of joint pain depends on the underlying cause and usually involves treatment of that cause. Therapeutic options include immunosuppressants if there is dysfunction of the immune system, antibiotics if there is an infection, discontinuation of medication that causes joint pain, and surgery.
One goal of treatment is pain management, which can involve pain medication, physical therapy, heat therapy, capsaicin, and more. Although joint pain is rarely an emergency, patients should seek professional medical opinion if there is joint swelling, redness, warmth, tenderness, deformity, and inability to use the joint.

Cause #1: Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disease that mostly affects the joints. Patients who suffer from it usually experience painful, swollen, and warm joints. There may also be pain and stiffness that worsens after periods of rest.
Affected joints are often symmetrical, mostly pertaining to the hands and wrists. While the effects of the disease are most pronounced on the joints, rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic condition resulting in inflammation around the lungs, heart, and anemia. Rheumatoid arthritis is believed to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.

Cause #2: Rheumatic Fever
Rheumatic fever is an inflammatory condition affecting the joints, skin, heart, and brain. It usually develops two to four weeks after an episode of streptococcal throat infection. Symptoms of rheumatic fever include painful joints, fever, erythema marginatum, involuntary muscle movements, and more.
In approximately 50 percent of the cases, the heart is also involved. If the heart valves are damaged, the condition is called rheumatic heart disease. Rheumatic fever affects approximately 325,000 children annually.

Cause #3: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease causing a variety of symptoms. The symptoms vary from mild to severe and can include fever, painful joints, joint swelling, swollen lymph nodes, hair loss, chest pain, tiredness, facial rash, and more.
The cause of SLE is thought to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. The treatment and management of SLE is based on the use of medications such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), immunosuppressants, corticosteroids, hydroxychloroquine, and methotrexate.
Cause #4: Gonococcal Arthritis
Gonococcal arthritis is caused by gonorrhea which is a sexually transmitted infection caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Symptoms include dysuria, testicular pain, discharge from the genitalia, pelvic pain, and more. If left untreated in the early stages, the infection can reach the heart valves and joints.
This infection spreads via any form of sexual encounter, and from mother to child during birth. Prevention includes the use of condoms. Gonococcal arthritis can be treated with oral azithromycin and ceftriaxone by injection. It has been estimated to affect about 0.8 percent of women and 0.6 percent of men.

Cause #5: Lyme Disease
Lyme disease is an infectious disease spread by ticks. It is caused by a bacterium known as Borrelia. The most common sign of infection is erythema migrans, observed in 70 to 80 percent of those infected.
Other associated symptoms include headache, fever, tiredness, and may eventually progress to joint pain, severe headaches, neck stiffness, heart palpitations, and the loss of ability to move one or both sides of the face. Despite treatment, about 10 to 20 percent of individuals continue to experience joint pains, tiredness, and memory issues for about 6 months.
Cause #6: Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a type of joint disorder characterized by breakdown of the joint cartilage and underlying bone. Patients with osteoarthritis usually experience joint stiffness, joint pain, swelling of the joints, and decreased range of motion.
Severe cases of osteoarthritis can be debilitating as the condition negatively impacts daily activities such as work, walking, and more. The risk of osteoarthritis is greatest among individuals who are overweight or have jobs that cause high levels of joint stress. Treatment includes physical therapy, pain medications, and support groups.
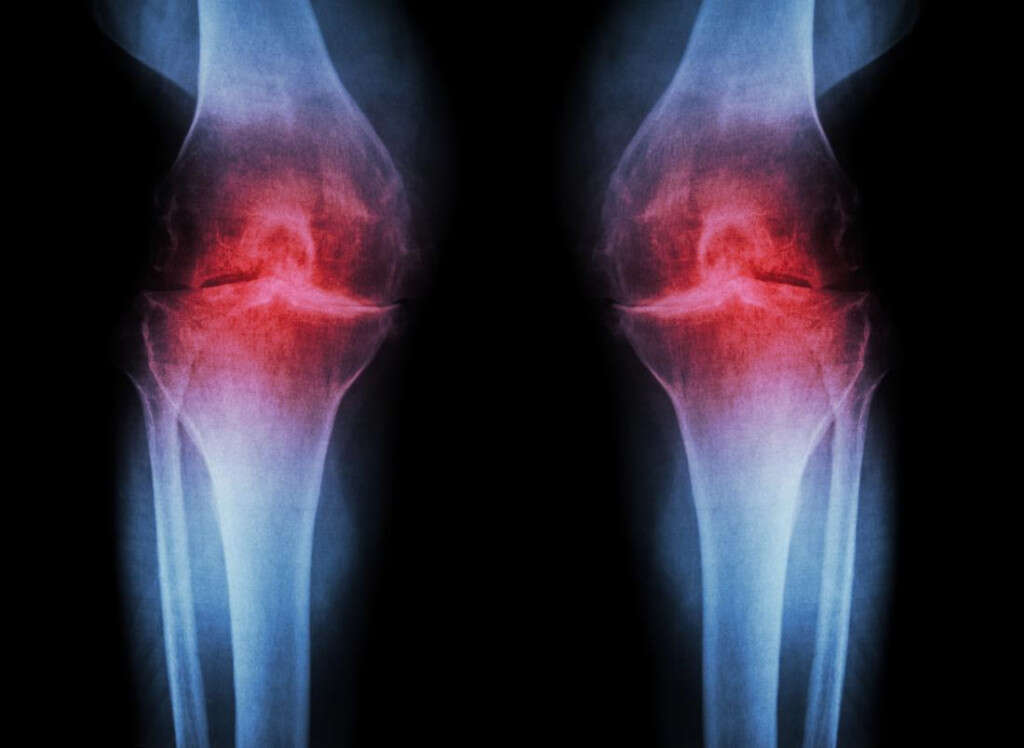
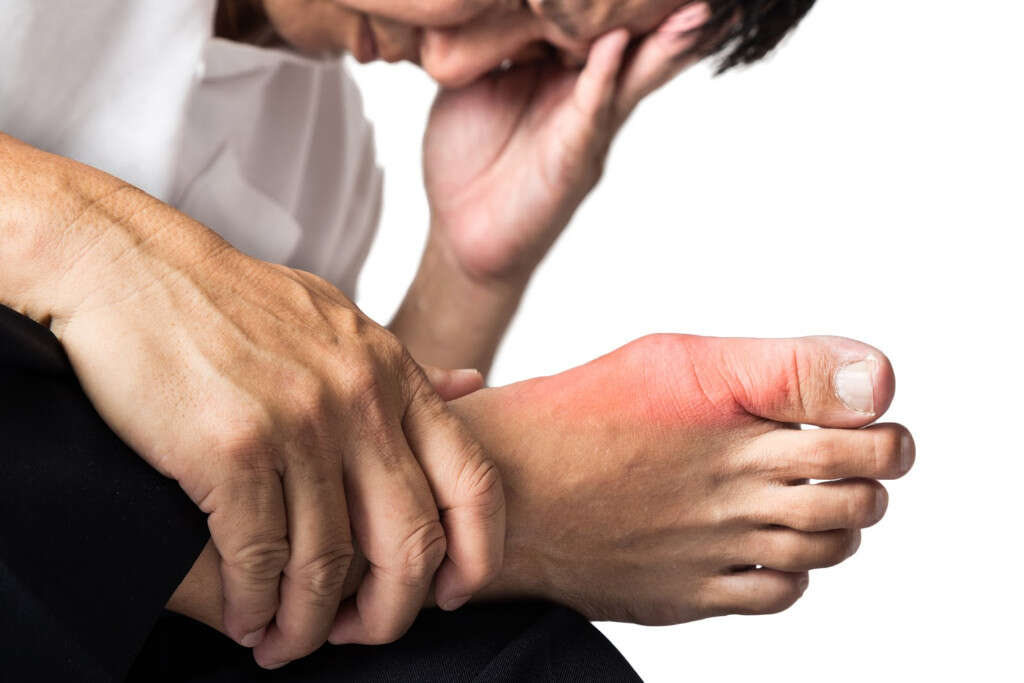
Cause #7: Gout Attack
Gout is a joint inflammation resulting in a painful, tender, red, hot, and swollen joint. The pain usually begins suddenly and quickly reaches maximal intensity. The most commonly affected joint is the one at the base of the big toe. Gout also causes kidney stones, urate nephropathy, and tophi.
Gout occurs when there is a persistently high level of uric acid in the blood. The uric acid crystallizes and gets deposited in the tendons, joints, and the surrounding tissues leading to a gout attack. Treatment involves the use of NSAIDs and colchicine, and steroids during the acute stage.
Cause #8: Reactive Arthritis
Reactive arthritis is an inflammatory condition that develops due to a separate infection that has occurred in a different part of the body. Contact with the bacteria that causes the infection can trigger the development of reactive arthritis.
The classic triad of symptoms include inflammation of the eyes where there is uveitis or conjunctivitis, inflammatory arthritis of the large joints, and cervicitis or urethritis in women or men. Other possible associated symptoms include mucocutaneous lesions. The most common triggers are Chlamydia trachomatis, Shigella, Salmonella, and Campylobacter.
Cause #9: Septic Arthritis
Septic arthritis occurs when an outside infectious agent travels throughout the body via the bloodstream and enters the joint causing inflammation. Infectious agents include fungus, parasite, bacterium, or virus. The symptoms of septic arthritis include joint pain, redness, warmth, and decreased range of motion. Other associated symptoms of septic arthritis are weakness, headache, fever, and more.
Diagnosis can be achieved through aspiration of the joint fluid. Patients are initially treated with antibiotics such as ceftazidime, vancomycin, and ceftriaxone. Surgery is also an option.
Cause #10: Dengue Fever
Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne tropical disease caused by the dengue virus. The symptoms of dengue fever include high fever, skin rash, headache, muscle pain, joint pain, vomiting, and more. The recovery from dengue fever usually takes 2 to 7 days.
In cases of dengue hemorrhagic fever, the disease can become life-threatening due to low levels of platelets, blood plasma leakage, and bleeding. A vaccine has been approved and is available in several countries. Other prevention methods include using mosquito repellants and reducing exposure to mosquito habitats.