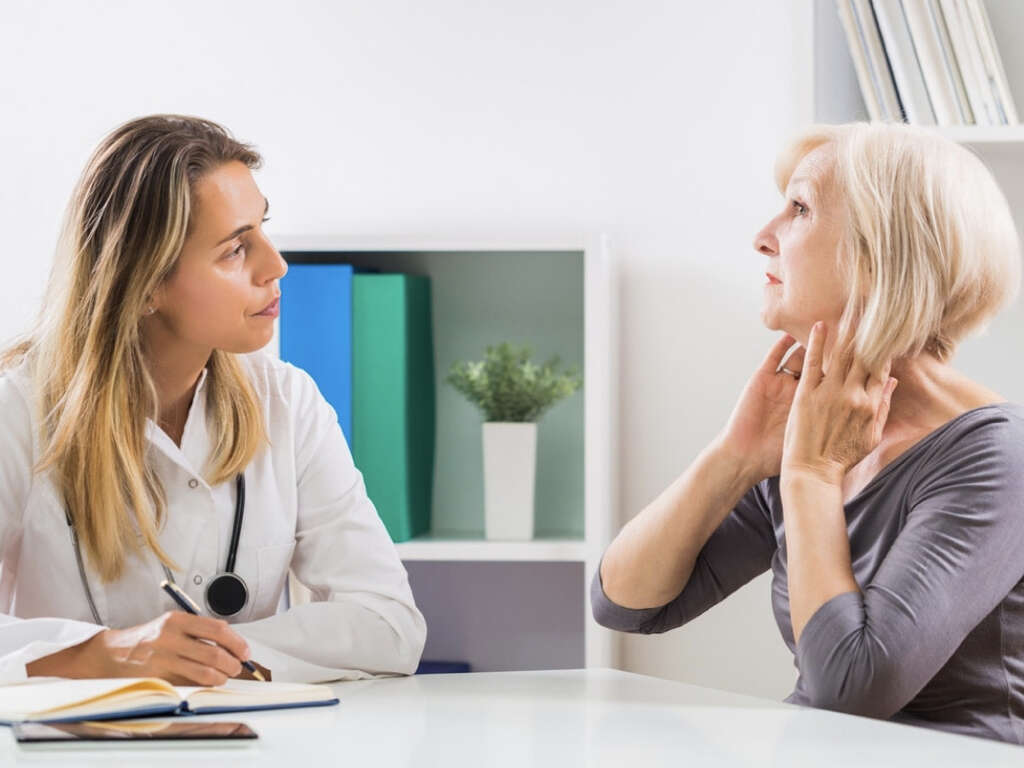
10 Causes of Swollen Lymph Nodes
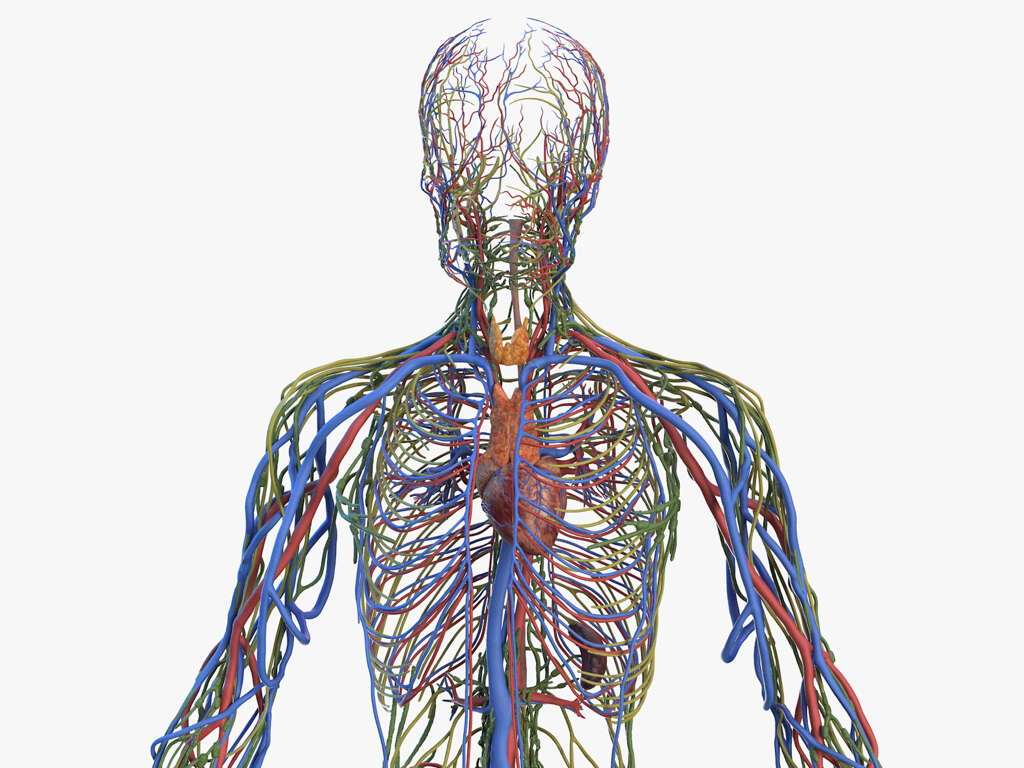
Swollen lymph nodes, also called lymphadenopathy or swollen glands, is a condition in which the small lymph nodes that span the lymph system enlarge significantly. When this happens, the white blood cells filled nodes become prominent and they can easily be felt by touching. In some instances, and depending on its location, you may be able to see the swelling.
Lymph nodes are present all through the body. They are part of the lymph system, which is a component of the immune system. When lymph node swelling occurs, it signifies that there is a problem such as an infection within the body. Swelling is most noticeable in the neck, the armpits, and the groin, where there are clusters of nodes.
Many types of infections can cause lymph node swelling. This article looks at some of the top 10 causes of swollen lymph nodes.
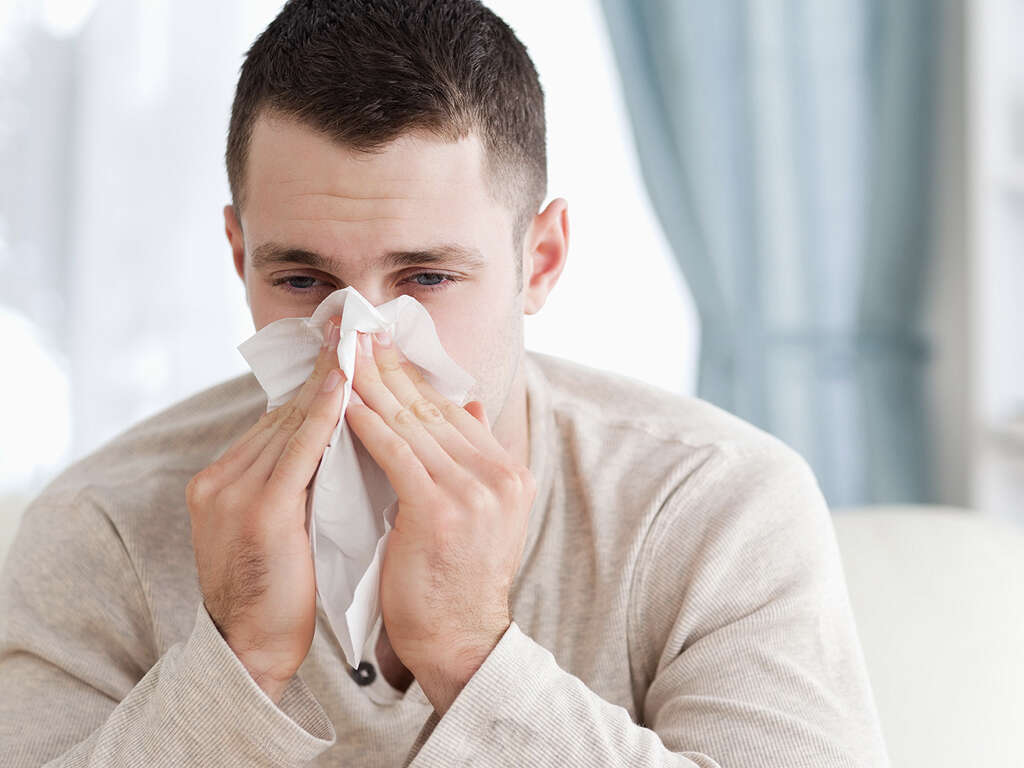

Cause #1: Cold or Flu
A cold is usually a viral infection. When the body catches an infection, its immune system reacts and produces antibodies to fight the infection. The lymph nodes are part of the immune system and they produce fighter cells whose function is to fight the invading microorganisms.
This is what happens when you catch a cold. Your lymph nodes become enlarged due to inflammation arising from the increased activities. This should not worry you because the lymph nodes will go back to normal once the cold infection heals in 5 to 7 days. However, if your lymph nodes remain enlarged after the cold is gone, you probably need to see your doctor and get checked to find out if you have a more serious problem.

Cause #2: Ear Infections
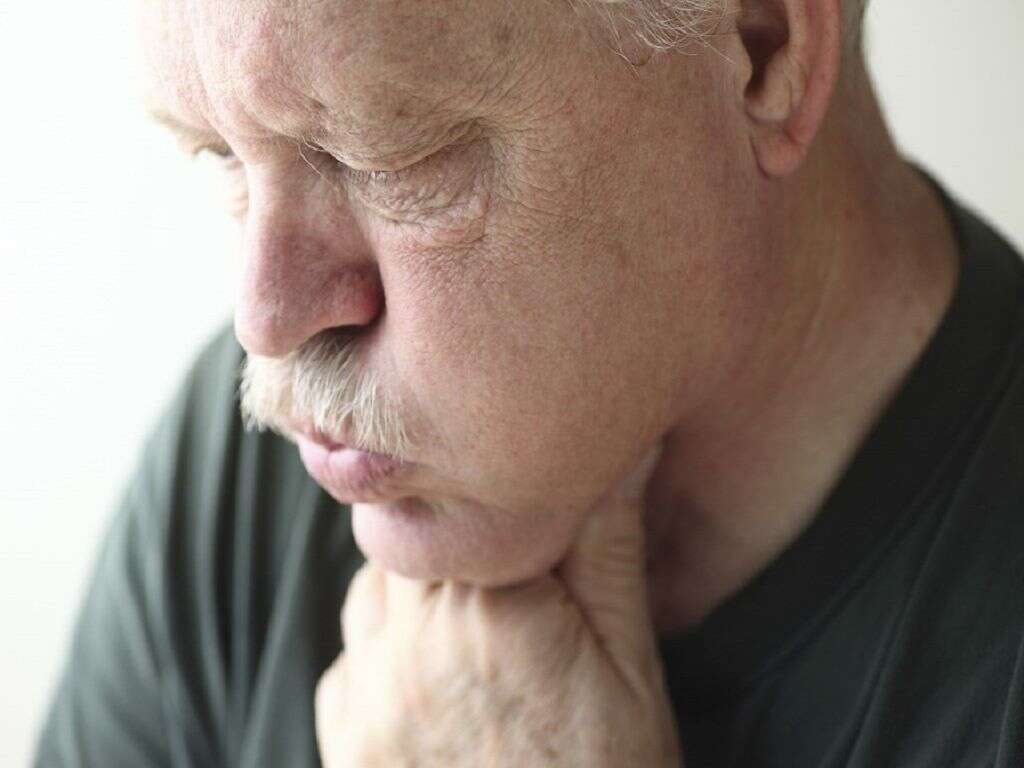
There are three symptoms that have a close association: sore throats, swollen lymph nodes, and ear infections. Ear infections can be the cause of the other two symptoms. If the source of infection is inside your ear and you left it untreated for a while, it will spread to your lymph nodes and make them swell.
The pain in your ears and lymph nodes may radiate and reach your throat and mouth, causing a sore throat. The most common lymph nodes affected by ear infections are those behind the ear and in the neck. They make it hard to move the neck around without feeling pain and dizziness.
Cause #3: Tooth Infection
If you suffer from acute dental pain, perhaps the infection has reached your root canal and affected your pulp and nerve. If a dental infection is not treated, it can spread to the surrounding tissues. In the longer term, it may spread through the bloodstream to other regions of the body and cause serious medical problems.
A dental infection that has spread to the nearby lymph nodes such as the cervical and submandibular lymph nodes causes them to swell. However, if the infection gets into the bloodstream and spreads to other parts of the body and, in effect, lymph nodes in those areas, it can cause widespread swelling of lymph nodes. Basic oral hygiene is required to prevent the spread of infection.
Cause #4: Strep Throat
Strep throat is one of the diseases that have been studied widely to determine the symptoms that confirm that an infection is actually strep throat. Swollen lymph nodes are among the main symptoms of strep throat.
Upon touching the lymph nodes, you will feel that besides swelling, they hurt. Some people can even see the swollen nodes by looking in the mirror. Usually, swollen lymph nodes are associated with a painful throat without cough, fever, or tonsillitis. If you have these symptoms, you need to see a doctor for treatment.

Cause #5: Sinus Infection
A sinus infection is one of the main causes of enlarged lymph nodes. Sinus infections also present with a stuffy nose. The lymph nodes will usually swell on the affected side, be noticeable by touch, and moveable. These swollen nodes are usually painless.
Each lymph node group is responsible for draining a certain area of the body. If the infection is left untreated, it spreads to other areas of the body and causes other lymph nodes to swell. Most people neglect their sinus problems for a long time. This can lead to swollen lymph nodes in many other parts of the body in addition to the submandibular region.
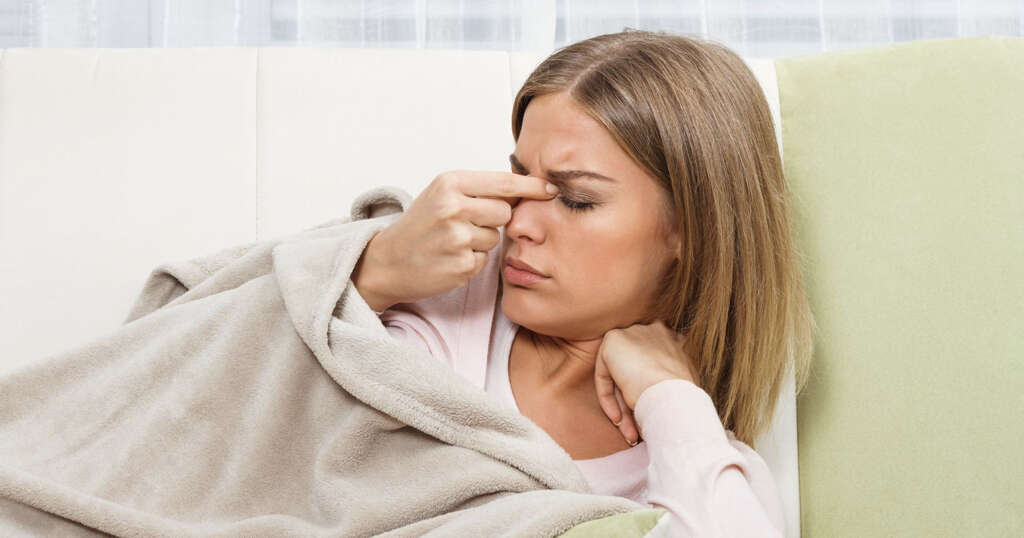

Cause #6: Measles
Measles is one of the highly-contagious infections of the respiratory tract. The infection is caused by a virus of the Paramyxovirus family and is spread through droplets of respiratory fluids. Enlarged lymph nodes are among the common symptoms of measles.
This condition usually causes generalized lymphadenopathy (multiple lymph nodes affected throughout the body). Swollen lymph nodes are normally accompanied by fever and a skin rash.

Cause #7: Syphilis
Syphilis is one of the most serious health conditions there is. A sexually transmitted disease, its symptoms are divided into 4 stages with each being slightly different. Swollen lymph nodes appear in the secondary stage.
The secondary stage usually appears after 6 weeks to 6 months from exposure to the infection and it lasts for between 1 and 3 months. Swelling of the lymph nodes can last for weeks or even months if the disease remains untreated. It starts with cervical and tonsillar lymph nodes then progresses to the rest of the body. Other symptoms include a skin rash, fever, loss of appetite, hair loss, and genital warts among others.
Cause #8: Lymphoma
Lymphoma, or cancer of the cells of the lymph system, can cause many different signs and symptoms depending on its type and its location in the body. In some cases, it doesn’t cause any symptoms until it becomes large enough.
Lymphomas, especially non-Hodgkin lymphoma, can cause enlarged lymph nodes. The affected lymph nodes are usually those that are close to the skin. The most commonly affected lymph nodes are those on the sides of the neck, in the groin, in the armpits, and above the collar bone. The swellings are usually visible and can be felt by touching. However, these swellings are usually painless. The lymph nodes usually enlarge because of infections that may occur and not because of the lymphoma itself.

Cause #9: Tuberculosis
There are two main types of tuberculosis (TB); pulmonary and extra-pulmonary. Swollen lymph nodes are a common sign of extra-pulmonary TB, which is more common in kids and women, especially in developing countries.
Extra-pulmonary tuberculosis normally causes swelling of the superficial lymph nodes located just beneath the skin, and more so, the posterior and anterior cervical lymph nodes. However, submandibular, periauricular, inguinal, and axillary lymph nodes may also be affected. TB also affects intrathoracic and abdominal lymph nodes. Swollen lymph nodes in many parts of the body may, therefore, indicate that you might be infected with this type of tuberculosis. Visit a medical care facility without delay for testing and treatment.

Cause #10: HIV
Viral and bacterial infections, including HIV, can lead to swelling of the lymph nodes. The infection spreads throughout the body. Once it gets into the lymph fluid, it ends up in the lymph nodes. An HIV infection is most likely to cause swelling of the lymph nodes around the neck, in the armpits, and the groin. As the disease progresses, other lymph nodes may be affected.
In some people, the swelling appears within days after infection while others may go on for months or even years without experiencing any HIV symptoms. If you have visible lymph nodes, you probably need to go for a checkup.