Gestational Diabetes Diet Overview, Foods & More
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. 'Gestational Diabetes.' Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 30 May 2019, www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/gestational.html
- 2. NHS Choices, NHS, www.nhs.uk/conditions/gestational-diabetes/treatment/.
- 3. 'Gestational Diabetes Treatment Plan: Yale Health.' Gestational Diabetes Treatment Plan | Yale Health, yalehealth.yale.edu/gestational-diabetes-treatment-plan.
- 4. UCSF Health. 'Dietary Recommendations for Gestational Diabetes.' Ucsfhealth.org, UCSF Health, 6 Oct. 2020, www.ucsfhealth.org/education/dietary-recommendations-for-gestational-diabetes.
- 5. NHS Choices, NHS, www.nhs.uk/common-health-questions/food-and-diet/what-is-the-glycaemic-index-gi/.
- 6. Evieosullivan. 'What Can I Eat with Gestational Diabetes?' Diabetes UK, Diabetes UK, www.diabetes.org.uk/guide-to-diabetes/enjoy-food/eating-with-diabetes/i-have-gestational-diabetes.
- 7. NHS Choices, NHS, www.nhs.uk/pregnancy/keeping-well/foods-to-avoid/.
- 8. Pistollato, Francesca, et al. 'Plant-Based and Plant-Rich Diet Patterns during Gestation: Beneficial Effects and Possible Shortcomings.' Advances in Nutrition (Bethesda, Md.), American Society for Nutrition, 15 Sept. 2015, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4561836/.
10. After Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes usually goes away soon after delivering the baby. The doctor will generally test for signs of type 2 diabetes six to twelve weeks after delivery and every one to three years after that. About half of all people who’ve had gestational diabetes develop type 2 diabetes later in life, and future pregnancies are likely to include gestational diabetes.
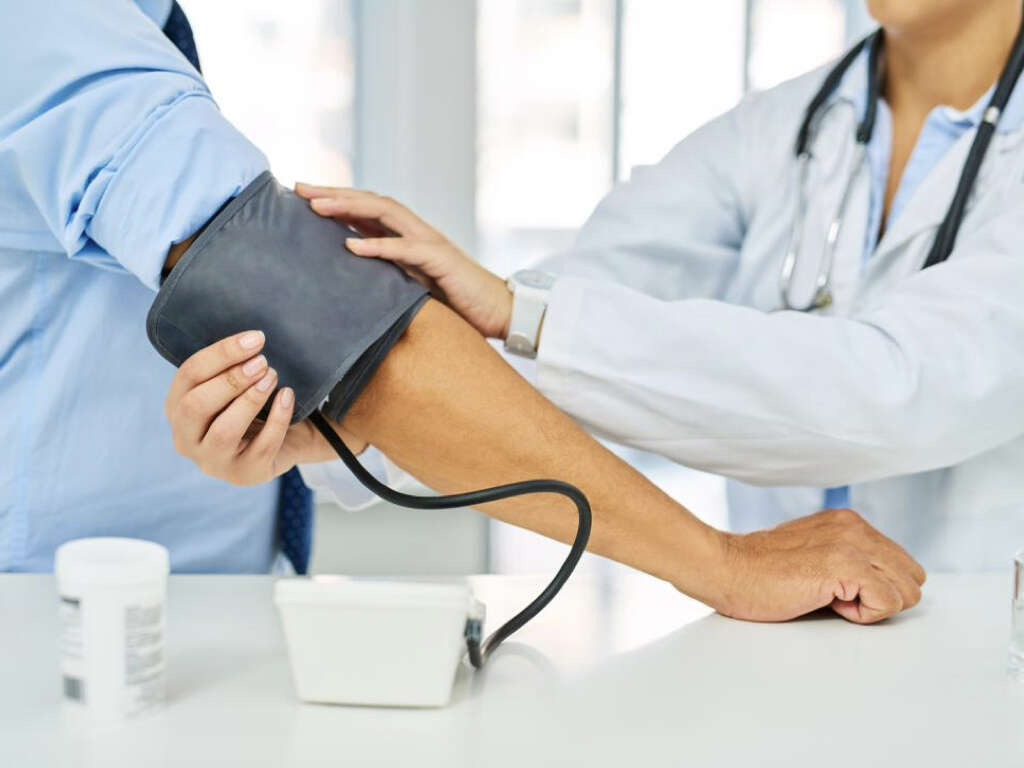
Regularly checking blood sugar in later life can help those who’ve had gestational diabetes stay healthy.1‘Gestational Diabetes.’ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 30 May 2019, www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/gestational.html
Advertisement