10 HPV Symptoms
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is the most common sexually transmitted infection. As many as 79 million Americans are infected with HPV, most of whom are in their late teens or early adulthood. There are many types of HPV and each different strain causes different issues such as genital warts, cervical cancer, and more. HPV is spread through sexual contact: vaginal, oral, or anal sex. It can be transmitted even when the affected individual shows no signs or symptoms. Symptoms sometimes take years to develop, making it hard for you to determine when you were first infected. In most cases of HPV infection, it resolves on its own without causing any health issues.
However, some subtypes (i.e. 16, 18) are considered high- risk, because they can cause precancerous lesions that can progress to carcinomas (i.e. cervical or anal carcinoma). To lower cancer risk caused by HPV, vaccination is recommended, specially before 13 years of age. The WHO (World Health Organization) recommends vaccination against HPV subtypes 16 and 18. Moreover, screening for cervical lesions is recommended for women ages 21 to 65 years. Other methods of prevention include having protected intercourse and limiting the number of sexual partners.
Symptom #1: Genital warts
The most common sign of HPV infection are genital warts. This is caused by certain strains of HPV. These warts can look like raised cauliflower-like bumps or flat lesions on the skin around your genitals. In women, it is most commonly found around the vulva, vagina and anus.
In men, the most common sites are the penis, scrotum, and anus. While these warts may not be painful, some may be itchy. Most individuals acquire HPV infections at one point in life and globally about 12% of women are infected (although higher prevalence can be noted in specific regions).

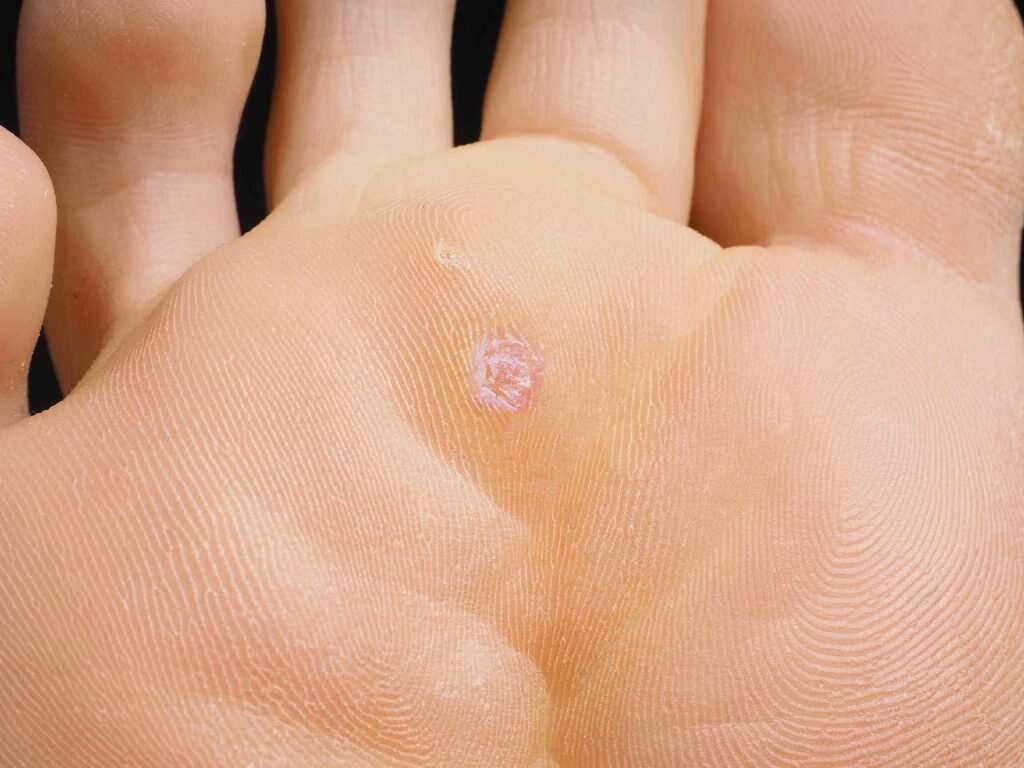
Symptom #2: Common Warts
Cutaneous infection by HPV is very common. HPV infection of the skin causes noncancerous skin growths known as warts or medically, verrucae. These warts occur when the outer layer of the skin has a rapid growth of cells.
Warts have been described since the time of ancient Greece, but the viral etiology was not discovered until the year 1907. Skin warts are very common in childhood and usually resolve on their own after several weeks to months. Approximately 10% of adults also suffer from skin warts.
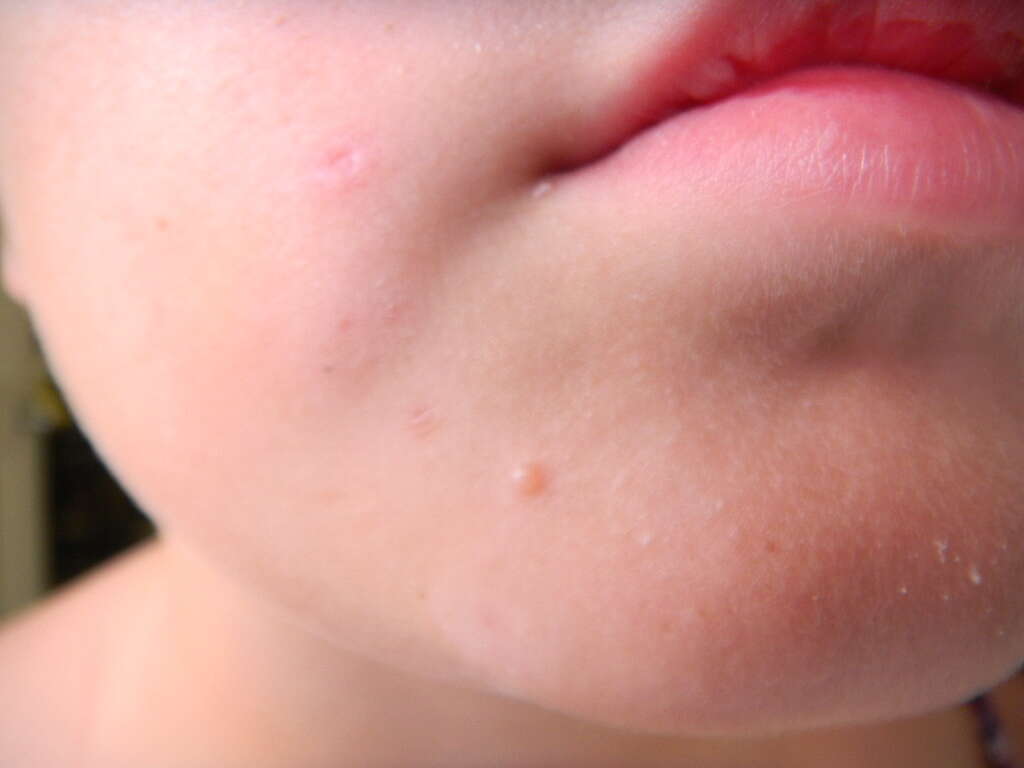
Symptom #3: Flat Warts
Flat warts are usually seen among children and teenagers and are most commonly found on the forehead, face, legs, and arms as these areas have the highest percentage to be scratched (contact). Flat warts are not typically associated with cancer. They appear as raised and flat outgrowths on the skin but are distinctive as they have a darker color.
Since flat warts are smaller than other warts, they can be mistaken for acne or allergies if occurring on the face.
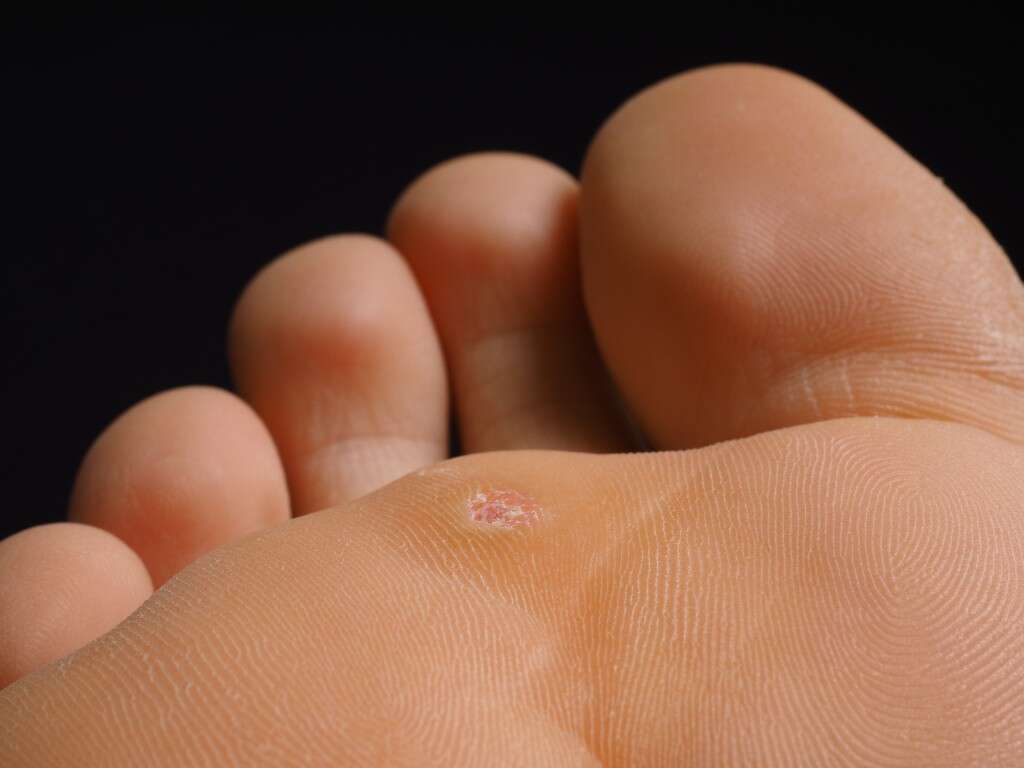
Symptom #4: Plantar Warts
Plantar warts occur on the bottom of the foot or toes (soles). The color of these warts is usually similar to skin color although black dots may occasionally occur on the surface. Patients who are affected often complain of difficulty walking as the pressure from the warts make it feel as if you are walking on a small pebble. A break in the skin is necessary for the infection to occur.
The risk of plantar warts increases if there is use of communal showers and poor immune system. Treatment of plantar warts is only necessary if it is causing issues for the patient. It includes salicylic acid, surgical removal, or cryotherapy. Approximately 33-67% of these cases usually resolve on its own.
Symptom #5: Respiratory Tract Issues
HPV infections can also affect parts of the respiratory tract. This usually occurs in more severe cases and lesions can be found on the tonsils, nose, and larynx. Most of these lesions are usually painful and tender, making it hard for the affected individual to breath and swallow. In infection by HPV strains 6 and 11, it can also cause recurrent laryngeal papillomatosis.
This means that warts form on the larynx and other parts of the respiratory tract. In rare cases, it can progress to cancer. Repeated surgery is therefore recommended to remove the warts.
Symptom #6: Focal Epithelial Hyperplasia
Focal epithelial hyperplasia or Heck’s disease is characterized by white and pink papules that are found in the oral cavity. These papules are diffuse and present as a pale, smooth or rough surfaces. It is caused by the HPV strains 23 and 32.
These papules will resolve on their own without treatment after some time. If necessary, treatment comprises of excisional biopsy for functional or aesthetic concerns.
Symptom #7: Abnormal Bleeding
In women with HPV infection in the genital area, there may be some abnormal bleeding such as intermenstrual bleeding (bleeding in between your menstruation days) and bleeding after intercourse. With bleeding after intercourse, there may also be pain. This can be a sign of early cancerous growth as many cases of cervical cancer often begin with HPV infection.
HPV strains that cause cervical cancer are most commonly high risk types. Eight high risk types of HPV account for 95% of all cervical cancers. Types 16 and 18 account for 70% of all cervical cancers. Your menstruation can also become longer or heavier.

Symptom #8: Pelvic Pain
One of the signs of cervical cancer is pain in the pelvis. You should seek medical attention if you start having unexplained pelvic pain. It can be caused by many reasons which include invasive cervical cancer.
This pain may be present during intercourse, and can be accompanied by bleeding, and /or vaginal discharge.

Symptom #9: Rectal Bleeding
Just like cervical cancer and experiencing vaginal bleeding or discharge, rectal bleeding is a sign of rectal cancer. Rectal bleeding can be seen as a discoloration in the stool or bloody discharge when passing motion. The surrounding area can also feel itchy or feel pressured. These feelings are often exacerbated when passing motion or during intercourse.
Other symptoms of anal cancer include other discharge such as pus or mucus, change in bowel habits, having a lump near the anus, or swollen lymph nodes in the anal, groin, or pelvic area. If you have the risk factors for anal cancer, talk to your doctor about getting a yearly examination for screening.

Symptom #10: Difficulties with Speech, Swallowing, and Breathing
In HPV infection especially type 16, some individuals may experience difficulties with breathing, speech, and swallowing. There can be pain and infection in the oropharynx. This may be a sign of HPV positive oropharyngeal cancer. This is a subtype of oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma.
The risk of HPV positive oropharyngeal cancer (HPV + OPC) further increases if there is alcohol and tobacco use. In some cases, some of the earlier symptoms of HPV + OPC also include the presence of lymph nodes in the neck and general symptoms such as loss of weight, weakness, and loss of appetite.











