MRSA Causes, Symptoms & Treatments
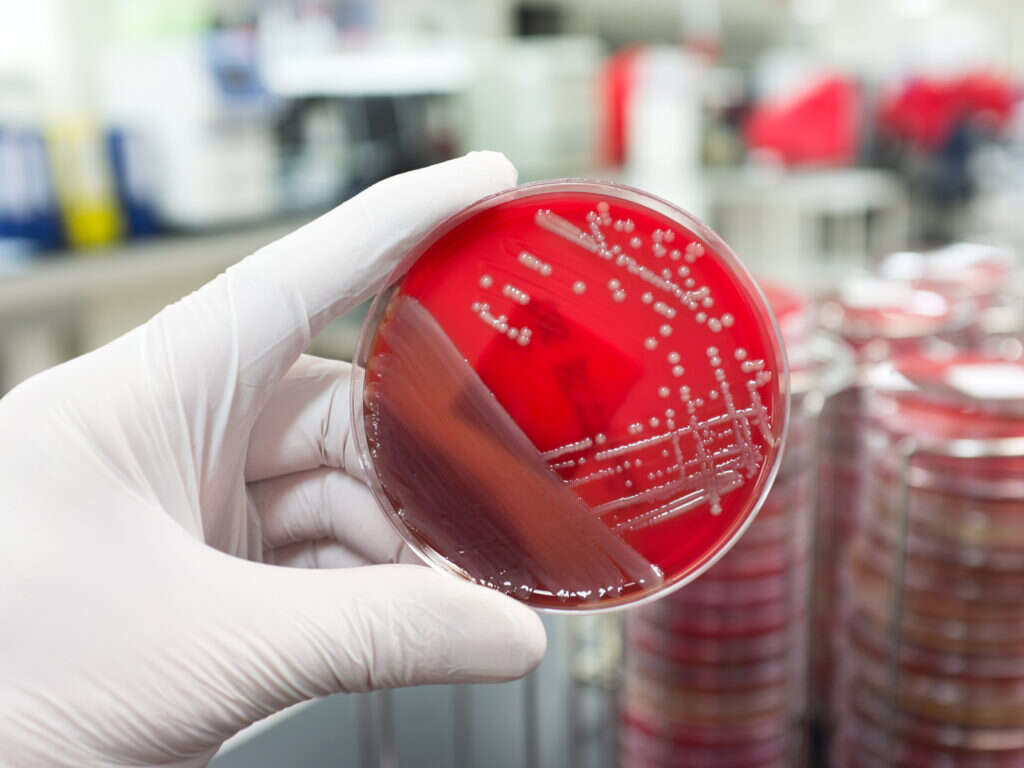
MRSA stands for methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus, a type of bacteria that has become resistant to several types of antibiotics which are being used to treat ordinary staph infections. It also means that it is tougher to treat compared to other strains of staphylococcus.
MRSA most commonly causes skin infections and can sometimes cause pneumonia and other issues. However, the symptoms largely depend on which part of the body is affected. Untreated, MRSA can become severe leading to sepsis. MRSA infections are usually seen in individuals who were previously or currently in hospitals or other health care facilities such as dialysis centers or nursing homes. Many professionals are alarmed by the spread of MRSA as due to its resistance to many types of medication, it is becoming known as a “super bug”.

Cause #1: Resistance
MRSA has resulted from many decades of antibiotic use. Previously, antibiotics were prescribed for all diseases, even diseases such as colds and influenza that do not respond to these drugs. Even now when antibiotics are being used for bacterial infections, they still contribute to resistance as antibiotics do not typically destroy all the germs.
Since bacteria are able to evolve rapidly, the bacteria that survives the antibiotic treatment will learn how to survive and resist that particular antibiotic. This is how resistance develops.
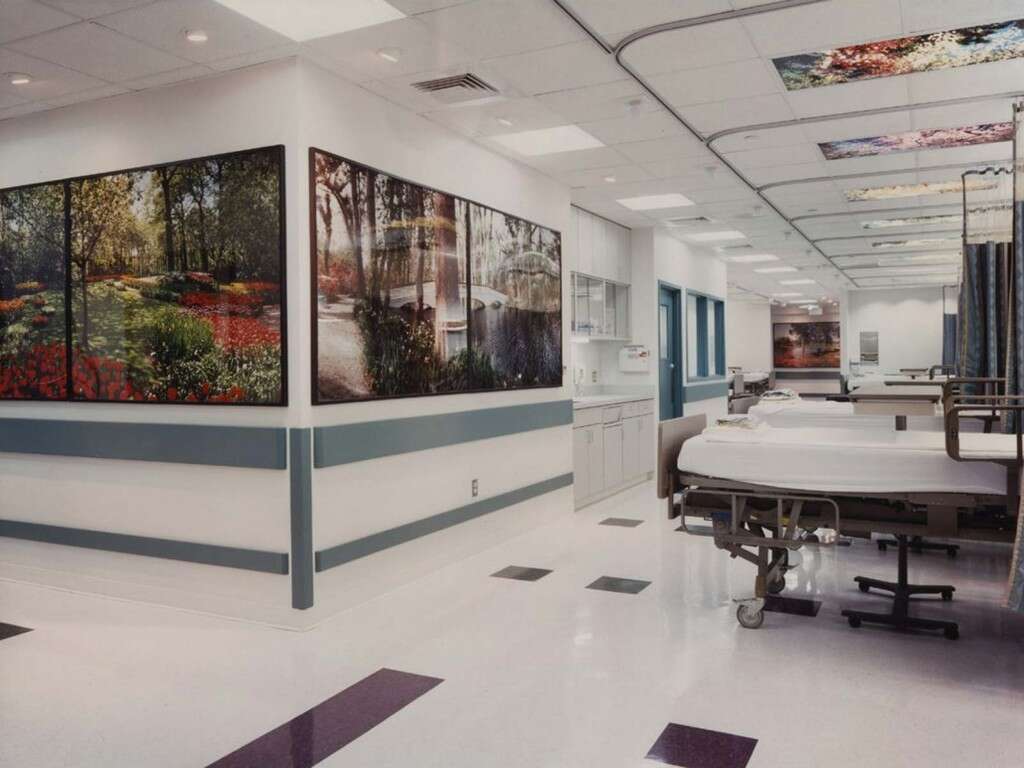
Cause #2: Healthcare Facilities
Both a risk factor and cause, healthcare associated MRSA or HA-MRSA are MRSA strains that usually affect individuals who are associated with healthcare settings such as hospitals, dialysis centers or nursing homes.
It can also be spread through medical devices (such as catheters, intravenous lines, artificial joints) and invasive procedures such as surgeries. MRSA carriers can spread it even if they have no symptoms.
Cause #3: Contact
Another risk factor and cause, community associated MRSA (CA-MRSA) is spread through skin to skin contact. Therefore, CA-MRSA usually affects those who are involved in high school contact sports, people in crowded conditions, military camps, prisons, child care workers, and more.
Cuts and abrasions allow the bacterium to invade and cause significant issues.

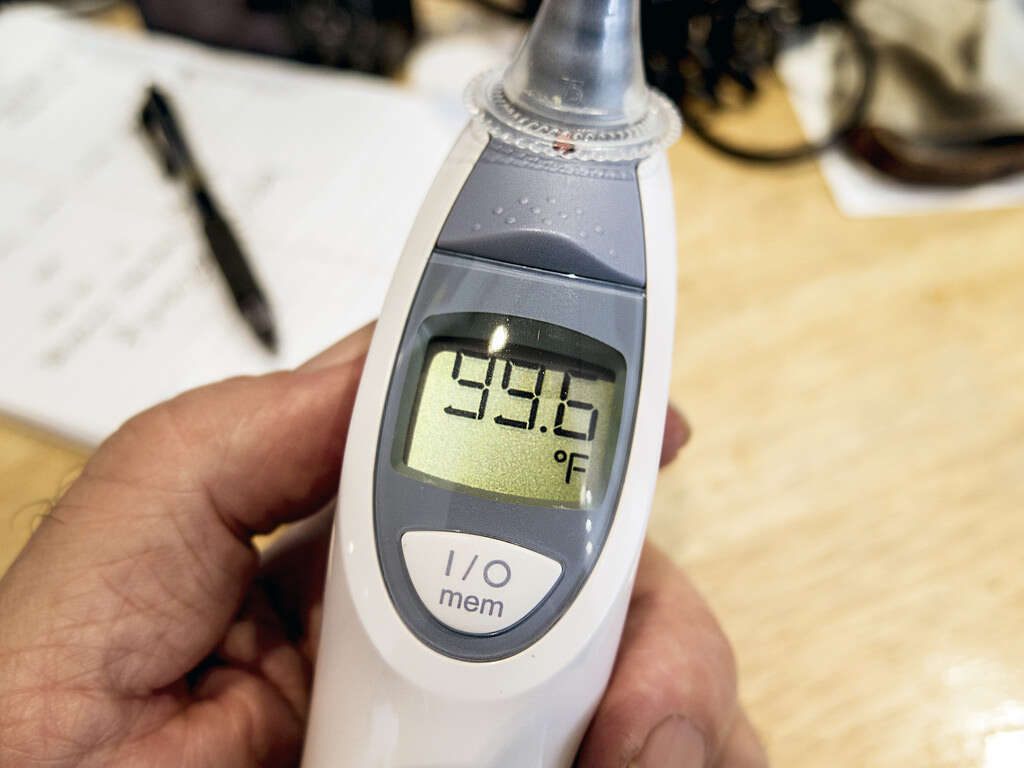
Symptom #1: Fever and Chills
Like any other infection, MRSA infections can cause a fever. Fevers occur when the body’s temperature is above 37 degrees Centigrade or above 98 to 100 degrees Fahrenheit. The body increases the set point of temperature as a higher body temperature helps the immune system to fight the infection.
In some cases where the fever is too high, it can lead to complications. If the fever is too high, you can try an over the counter anti-pyretic that helps to bring down the fever. Children with a high fever should seek medical attention if it persists. Chills describe a feeling of coldness that happens due to the release of cytokines and prostaglandins during fever. Shivering may also be present as it helps to produce heat to reach the new set point of body temperature.
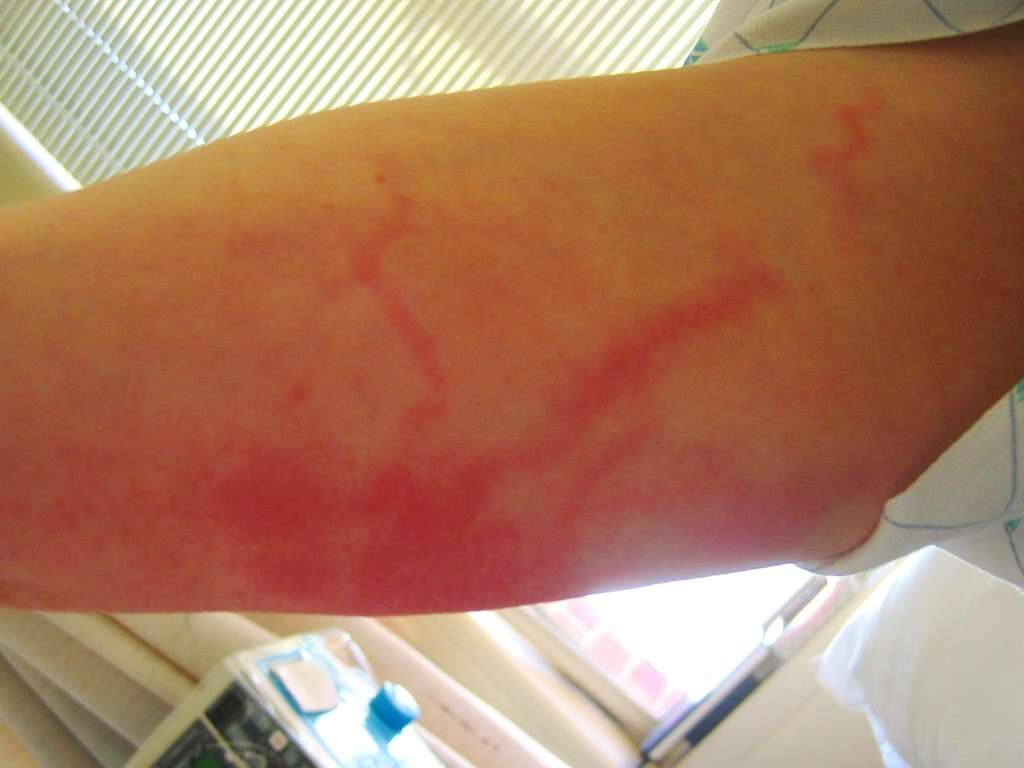
Symptom #2: Cellulitis
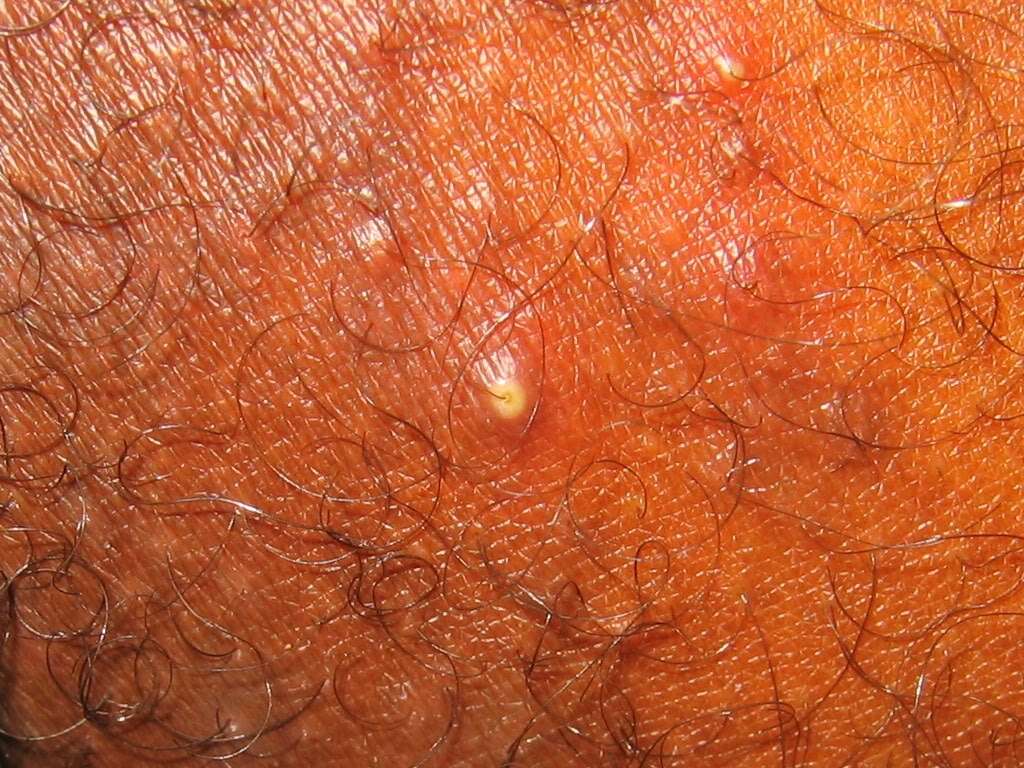
Cellulitis is an infection of the skin and deeper layers of the skin, the dermis and subcutaneous tissue. It usually begins as small red bumps on the skin which feel tender and swollen. The affected area is warm and looks red. As the infection of the skin spreads, other symptoms such as fever, chills, and swollen lymph nodes may appear around the area of the infected skin.
If you have a compromised immune system, it is important for you to seek medical attention as soon as possible as this infection can spread much more rapidly compared to others. If in doubt, always consult a healthcare professional.
Symptom #3: Pus
The area affected by a MRSA infection can sometimes be full of pus or other types of drainage. Pus is the formation of an exudate which is usually yellowish in color that forms at the infected area. If pus collects in an enclosed tissue space, it is known as an abscess. It contains dead white blood cells generated from the body’s immune response.
Bacterium that causes pus are known as pyogenic bacteria. During an infection, macrophages release cytokines that attract neutrophils. The neutrophils then release granules that destroy the bacteria and in response the bacteria releases toxins. The neutrophils that die are destroyed by macrophages forming pus.
Treatment #1: Vancomycin
Vancomycin is a type of antibiotic that can be administered intravenously to treat issues such as skin infections, bone infections, septicemia and meningitis caused by MRSA.
Some of the side effects of Vancomycin are indigestion, hives, itching, dizziness, low blood pressure, dry mouth, increased thirst, loss of appetite, and more. You should inform your doctor if you have issues with your kidneys or hearing as Vancomycin may worsen it.

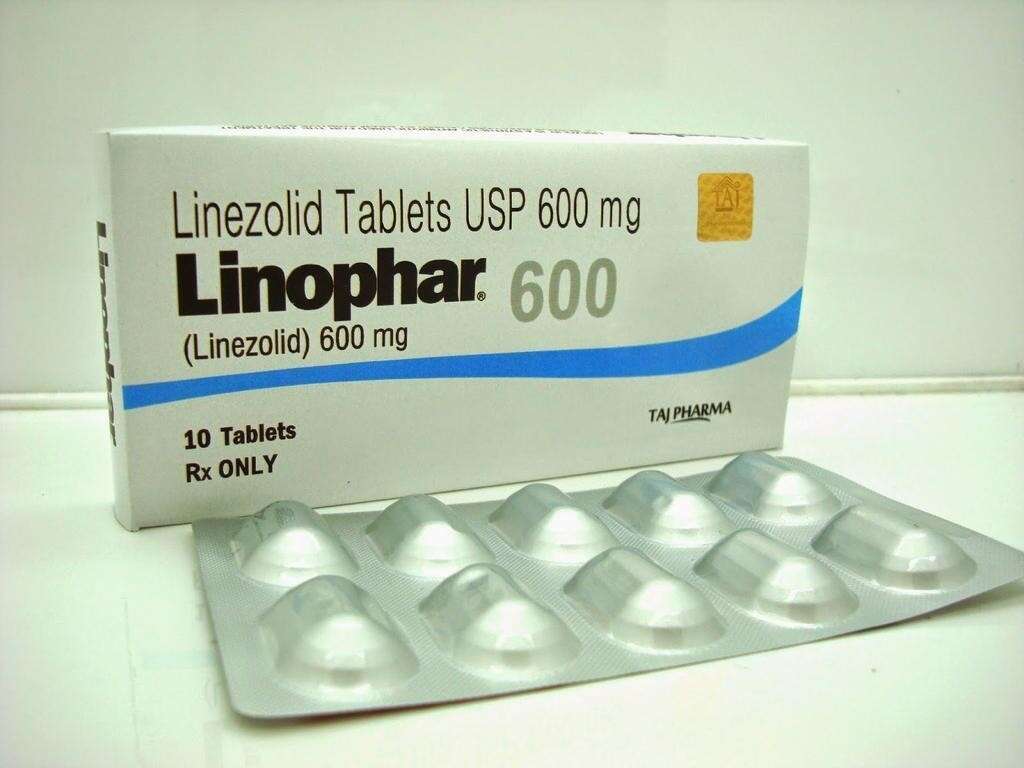
Treatment #2: Linezolid
Linezolid is a type of antibiotic that is effective against gram positive bacteria that do not respond to other antibiotics, such as MRSA. It is mainly used in infections of the skin and pneumonia. It can be administered orally or intravenously. It is suitable for patients of all ages and those who have liver or kidney issues. Some of the side effects are headaches, rash, diarrhea, and nausea.
If used for longer than two weeks, it can cause more serious side effects such as bone marrow suppression, serotonin syndrome, and high blood lactate levels. It can also cause optic nerve damage that can be irreversible.
Treatment #3: Clindamycin
Clindamycin is a type of antibiotic that can be used for the treatment of multiple issues such as pneumonia, endocarditis, bone or joint infections and more. It can be administered orally, topically, or intravenously. Some of the common side effects are rash, nausea, diarrhea, and may increase the likelihood of hospital acquired Clostridium difficile colitis.
It works by stopping the bacteria from making protein. Inform your doctor if you have issues with your liver, kidneys, intestinal diseases, and allergies before taking the medication. It may interact with other medications so remember to tell your doctor about any medications you are currently taking.