What Is Glaucoma?
Glaucoma is an eye condition that causes damage to the optic nerve. The condition develops as a result of increased pressure within the eye, also called intraocular pressure. The increased pressure damages the optic nerve, which is responsible for transmitting images from the retina to the brain for processing. The condition normally appears in people over 40 years old. It seems to have hereditary properties and is linked to diseases like diabetes.
There are two main types of glaucoma: open-angle glaucoma and closed-angle glaucoma. The disease has no early signs or symptoms. Yet, if left untreated, it can lead to permanent blindness in a few years. For this reason, it is called the silent thief of sight. According to the Glaucoma Research Foundation, up to 12 percent of all cases of blindness can be attributed to glaucoma. This is why people with family history of glaucoma, and those with diabetes and other chronic diseases, should undergo regular eye examinations.

1. Symptoms of Glaucoma
Most people who develop glaucoma have no disease-specific symptoms. Still, there are signs that may indicate that the condition could be developing. The first such signs include poor side or peripheral vision.
Sudden eye pain, blurred vision, appearance of halos around lights, and headache may also develop. Other symptoms of glaucoma include eye redness, narrowed vision, nausea, and vomiting.

2. Causes of Glaucoma
In normal conditions, the fluid inside the eyeball known as aqueous humor stays within a certain pressure range, thanks to a mesh-like channel through which the fluid moves in and out.
If this fluid movement is compromised by a blockage in the channel, pressure can build up within the eyeball.
3. Intraocular Pressure Buildup
It is not clear why the blockage or the buildup happens. However, studies suggest that there are hereditary causes. Other causes include trauma or chemical injury to the eye, inflammation, blockage of blood vessels in the eye, and infection. A medical procedure such as eye surgery can also lead to glaucoma.
In most cases, glaucoma affects both eyes, although it is usually worse in one eye.

4. Glaucoma and Other Associated Diseases
Although glaucoma affects the eyes, some experts say that it may be connected to other conditions. The disease, which affects about 60 million people globally, develops slowly and, generally, painlessly and is usually diagnosed when it has already caused significant damage.
The most common type of glaucoma called primary open-angle glaucoma, POAG in short, often occurs in people with high blood pressure and/or diabetes. A 2010 study comparing the medical records of 75,000 people with POAG, and 230,000 people without POAG, found that over half of those with POAG also had high blood pressure, while 30 percent had diabetes. Glaucoma is also associated with other diseases like coronary heart disease and high cholesterol.
5. Complications of Glaucoma
The most obvious complication of glaucoma is loss of vision or blindness. This can be partial or total depending on the stage at which a patient seeks intervention.
The loss of vision cannot be undone, but further damage can be averted. Other complications of glaucoma include the inability to drive or operate machinery safely, and complications that may result from treatment or surgical procedures such as allergic reactions and infection.

6. Disease Process
As mentioned earlier, glaucoma develops over time and usually without any early signs or symptoms. For this reason, it is difficult for a patient to know that they are getting glaucoma without undergoing tests by a doctor. As the disease progresses, it causes damage to the optic nerve in the back of the eye.
This leads to deterioration of vision, especially peripheral vision. The patient might not notice this change, and therefore might not consult a doctor. This can mean that glaucoma continues damaging the optic nerve until vision is greatly compromised at which point a patient might seek medical care. However, while the patient can get help so that the damage does not progress any further, at this state, the damage already done is irreversible.

7. Diet and Lifestyle to Ease Glaucoma
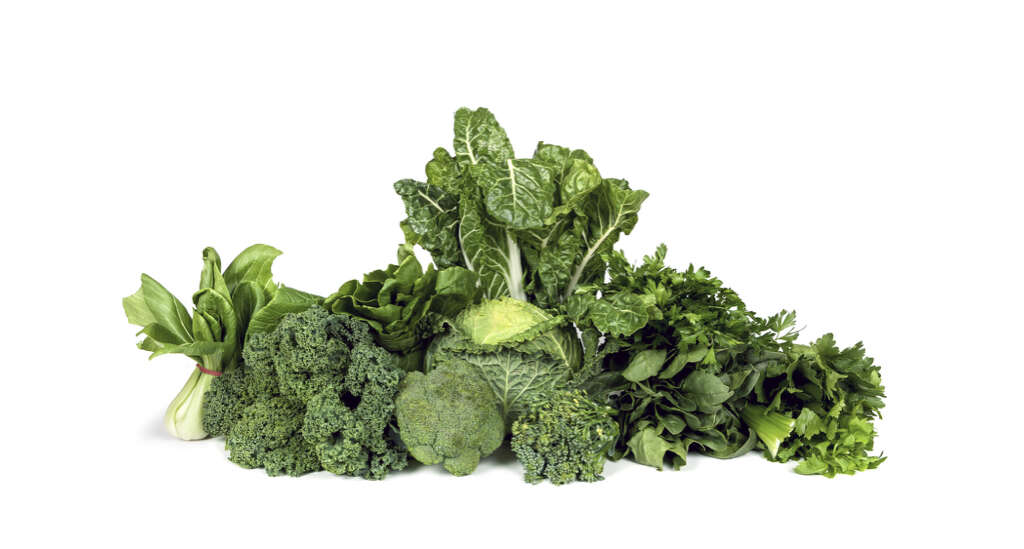
It is generally believed that glaucoma cannot be prevented. However, there are studies that suggest that eating certain types of foods regularly can lower the risk of getting the disease. According to the Glaucoma Research Foundation, including high amounts of leafy green vegetables and fruits in the diet can lower the risk of glaucoma.
Recommended are foods rich in vitamins A and C, and antioxidants. Such foods include carrots, spinach, kale, collard greens, cabbage, celery, beets, Brussels sprouts, and radishes. Others include pomegranate, cranberries, green and black tea, tomatoes, acai berries, bilberries, and dark chocolate. These foods should be included in a healthy and balanced diet. Physical exercise is also recommended.

8. Diagnosis
To diagnose glaucoma, the doctor will apply an eye drop to dilate the pupils of the eyes. This way, it is easy to examine the inside of your eyes. The doctor will examine the optic nerve for signs of glaucoma-related damage.
They will also carry out a tonometry test to determine the pressure inside your eyes. They will also test your vision and visual field to find out if you have a good peripheral vision. These tests take a short time and are not invasive. It is, therefore, sensible to have your eyes tested regularly to protect your sight.

9. Treatment
Treatment for glaucoma is generally aimed at controlling intraocular pressure and to maintain it at a healthy level. Available treatments include eye drops, microsurgery, and laser surgery. If eye drops are used, they work by increasing fluid outflow or reducing the collection of fluid in the eye. Typical eyedrops used to treat glaucoma include prostaglandin analogues, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, cholinergic agents, and beta blockers.
When microsurgery is performed, it creates a new channel for draining fluid from the eye to ease intraocular pressure. A tiny tube might be inserted for this purpose. Similar to microsurgery, laser surgery opens up the blocked drainage to allow outflow of fluid so as to reduce intraocular pressure.

10. Long-Term Outlook
If glaucoma is not treated in its early stages, chances are that its victim will ultimately go blind. This is the reason why it is important to undergo a regular eye checkup after the age of 40.
This helps to detect any increase in intraocular pressure so that it is controlled from early on. When this is done, a person with glaucoma can preserve their vision and lead a relatively normal life.