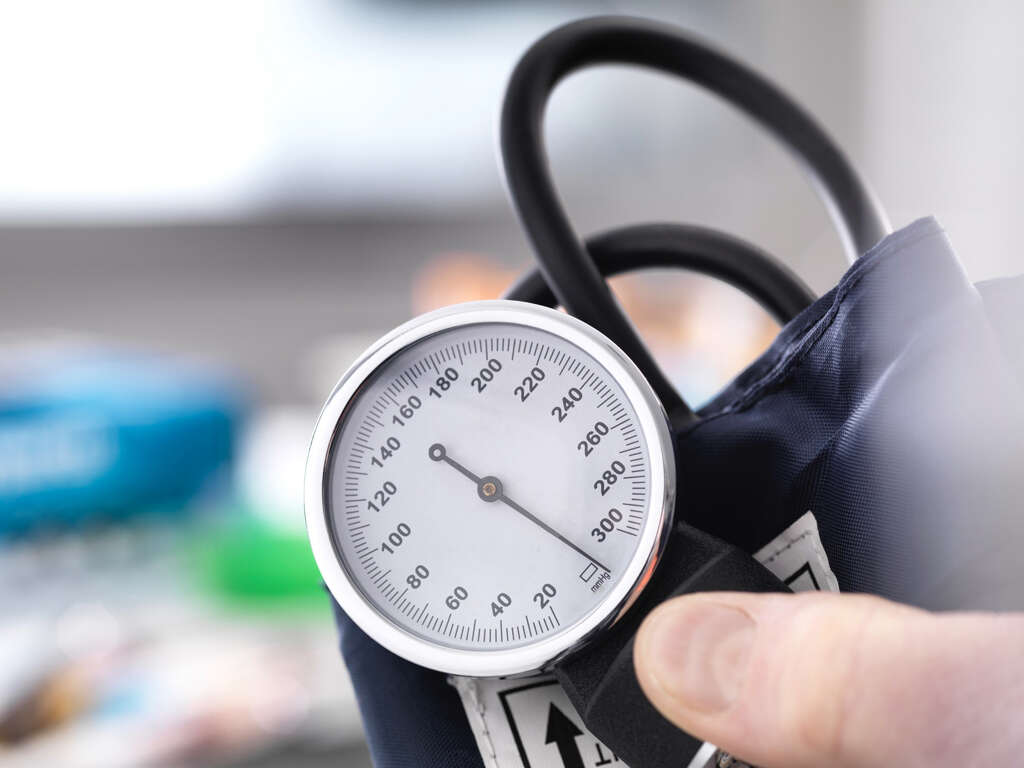
10 Lower Blood Pressure Symptoms
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. 'Clammy Skin.' Nicklaus Children's Hospital, www.nicklauschildrens.org/symptoms/clammy-skin
- 2. 'Self-help Tips to Fight Tiredness.' Nhs.uk, 3 Oct. 2018, www.nhs.uk/live-well/sleep-and-tiredness/self-help-tips-to-fight-fatigue
- 3. 'Dizziness - Symptoms and Causes.' Mayo Clinic, 15 Apr. 2020, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/dizziness/symptoms-causes/syc-20371787
- 4. 'Water: How Much Should You Drink Every Day?' Mayo Clinic, 6 Sept. 2017, www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/in-depth/water/art-20044256
- 5. 'Orthostatic Hypotension.' NORD (National Organization for Rare Disorders), 20 July 2017, rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/orthostatic-hypotension
- 6. 'Depression Statistics.' Depression and Bipolar Support Alliance, 12 July 2019, www.dbsalliance.org/education/depression/statistics
Blurry Vision
Lower blood pressure can cause some people to have blurry vision. Individuals with blurred vision may have a diminished field of view or have difficulty making out the details of their environment. Problems with vision may occur in people with hypotension shortly before fainting.
Laying down with the head slightly elevated can help restore vision and normalize blood pressure. If blurry vision persists, it could indicate a secondary health problem aside from hypotension, including high blood pressure, stroke or injury to the brain.
Advertisement