10 Bladder Infection Symptoms
The bladder is located in your pelvis. It is a muscular organ that functions to store and expel urine. Urine drains from the kidneys via the ureters into the bladder. It is then stored until it reaches a point where it signals you that you need to urinate. The bladder then contracts and passes the urine out via the urethra. The urethra and bladder are therefore part of the lower urinary tract while the ureters and kidneys are part of the upper urinary tract. Bladder infections is also known as cystitis.
Most bladder infections are due to bacteria, but it can also be due to yeast or viral infections and sometimes chemical irritation. Bladder infection can either be complicated (due to factors such as stones, urethral strictures, prostate enlargement, and more that increases the risk of infection and lowers the effectiveness of antibiotic therapy) or uncomplicated (infection in a normal urinary tract, both structurally and functionally).
Symptom #1: Dysuria
Dysuria refers to pain during urination, a burning sensation, or discomfort that occurs most commonly due to a bladder infection caused by bacteria. It is usually accompanied by other symptoms of urinary tract infection such as blood in the urine. It can occur in women after intercourse when infection is present.
There are other causes of dysuria such as pyelonephritis (kidney infection), prostatitis (infection of the prostate), or due to sexually transmitted diseases. If you are experiencing prolonged dysuria, it is best to seek medical attention as the infection could spread upwards to the kidneys and cause more severe symptoms.

Symptom #2: Increase Urinary Frequency
You should be aware of how often you usually need to use the bathroom. If you notice that you have been needing to go to the bathroom to urinate more frequently, you may have a bladder infection. The increased frequency for urination is often accompanied by dysuria (pain, burning sensation, or feeling of discomfort during urination).
The increased frequency may indicate interstitial cystitis where there is inflammation of the bladder muscles causing the frequent need to urinate although the urine produced is small. This should not apply if you are drinking more fluids than usual as it is only natural you are peeing more due to the higher intake of fluids.

Symptom #3: Increased Urgency
If you have a bladder infection, you may experience an increased urgency to urinate. Urinary urgency is defined as the sudden urge to urinate which is a common symptom of cystitis.
Normally you would be able to hold the urge to pee but, in this case, you may find that it is almost impossible to hold it in and barely makes it to the bathroom in time. When you do, you may find that there is a very small amount of urine that is passed. The urge to urinate also starts again even when you have just come out of the bathroom. It can be extremely distressful for the patient.

Symptom #4: Changes in Urine Color
This is one of the most characteristic signs of bladder infection where the changes in color and smell of the urine become significant. The urine color may become darker or cloudy (contain dead skin cells, bacteria, and white blood cells) and, in some cases, it may even become similar to the color of blood. The light pink to dark red urine is indicative that there is blood in the urine.
You will also notice that your urine also has a very repellent odor such as a strong ammonia smell, has a slightly sweet scent, or an unpleasant stench.

Symptom #5: Lethargy
While dysuria and urine color changes are the more obvious signs of a bladder infection, there are also non-specific symptoms such as lethargy. You may feel unusually tired and have lower energy levels. In older women, this may be the only symptom of bladder infection that they experience.
Since there are many other medical conditions that can cause lethargy, it may be hard to achieve the diagnosis of a bladder infection. Many may attribute to increased work load, changes in daily routine, or older women may attribute it to menopause.

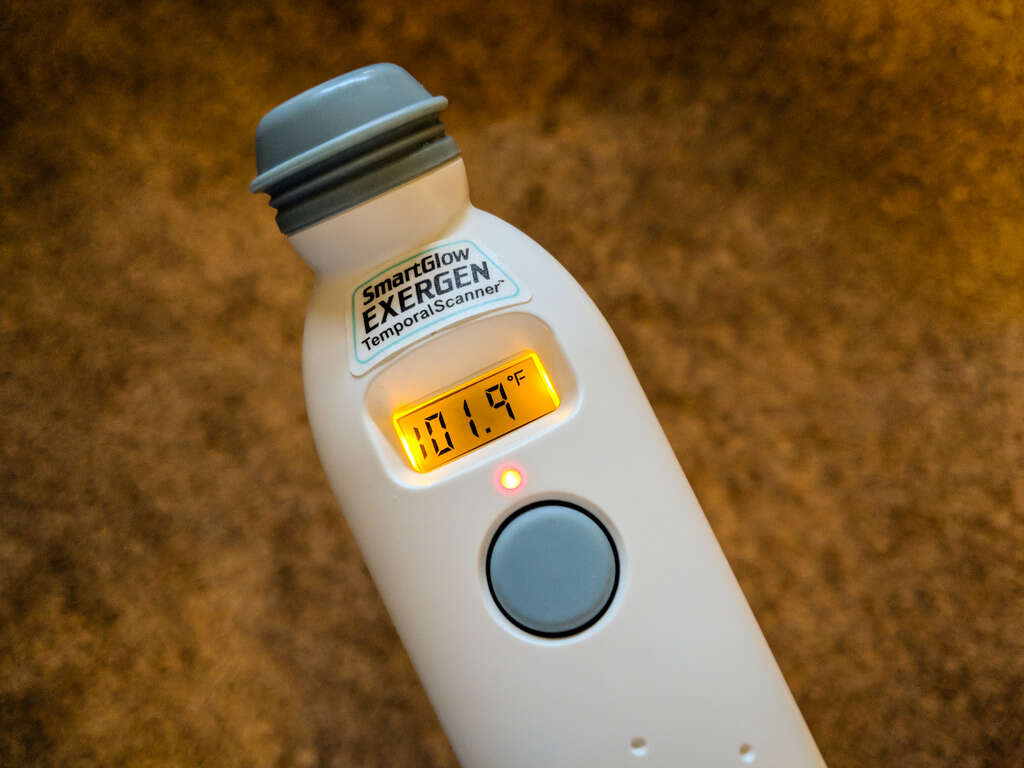
Symptom #6: Fever
Fever is another common symptom that can be caused by any infection. While bladder infections usually do not cause a fever, it may appear in severe cases and children. Since children do not usually experience painful urination or may not notice the change in urine color, fever may be one of the only symptoms that they experience when there is an infection of the bladder.
Children with bladder infections also tend to lose their appetite and may become irritable. If your child is experiencing this symptom, it may be best to seek medical attention to receive proper treatment.

Symptom #7: Nausea & Vomiting
Nausea and vomiting can occur in severe cases of bladder infection where it has spread to the kidneys. If the infection has spread to the kidneys, the patient may also experience fever, chills, lower back pain, nausea and vomiting in addition to the other symptoms of bladder infection.
If this occurs, you should seek medical attention immediately as pyelonephritis can be organ or life threatening that may even lead to scarring in the kidneys.

Symptom #8: Pain in the Lower Abdomen or Back
When the bladder infection spreads upwards towards the kidneys, it can cause pain in the back. The irritation of the bladder due to infection also causes pain in the lower abdomen. Any pressure in the region of your pelvis specifically near the pubic bone can be very uncomfortable.
Unlike muscular pain, this pain is persistent despite the change in position or activity. Kidney infections are much more serious than a bladder infection and require urgent medical care. Pain in the lower abdomen or back can occur together with fever, chills, nausea, and vomiting.

Symptom #9: Abdominal Pain
Cystitis can cause the patient to feel discomfort in their lower abdomen where the bladder is located. This sensation could be mild discomfort or it can be perceived as pain.
It is usual for patients to feel a sensation of bladder fullness that can resemble abdominal pain as well. If you are experiencing this symptom you should seek medical attention for proper diagnosis.

Symptom #10: Confusion
Confusion can occur in a bladder infection but is restricted only to the elderly. It may be the only symptom of bladder infection in this age group. Since the elderly also suffer from other medical conditions such as dementia, the correct diagnosis may take some time before the doctor realizes the cause of confusion or increased confusion in those with dementia.
This confusion is also known as delirium. If you noticed that there is increased confusion, withdrawal, irritability, or agitation in an elderly patient, it may be due to a bladder infection.