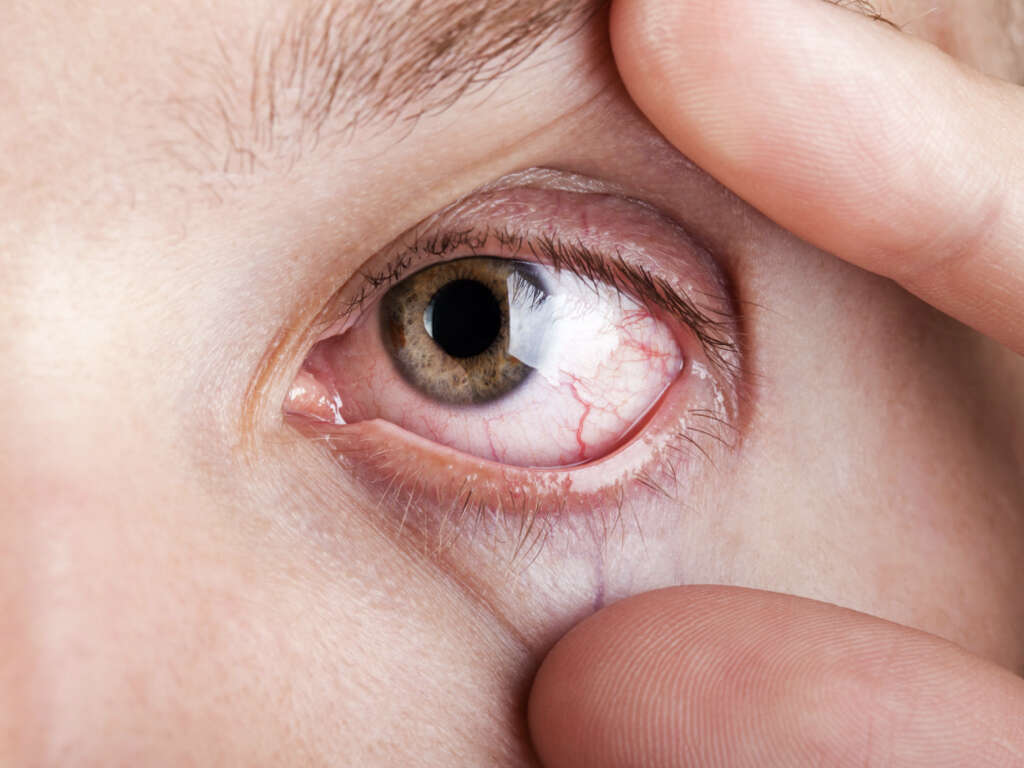
10 Causes of Swollen Eyelids
A swollen eyelid occurs when there is an inflammation of the connective tissue that surrounds the eye, as well as when there is an accumulation of fluid. It can affect both the upper and the lower eyelids. Sometimes it can be painful and sometimes not. The severity of the swelling may vary, and sometimes it is so severe that it interferes with a person’s ability to see. In these cases, it is more than just a cosmetic problem.
Luckily, most causes of swollen eyelids are harmless and resolve on their own or with the right treatment within a couple of days. However, you should remember that even minor problems can be quite serious. If you have a swollen eyelid, especially if it tends to get worse or does not resolve within a couple of days, you should seek professional medical help. What are the most common causes of swollen eyelids?
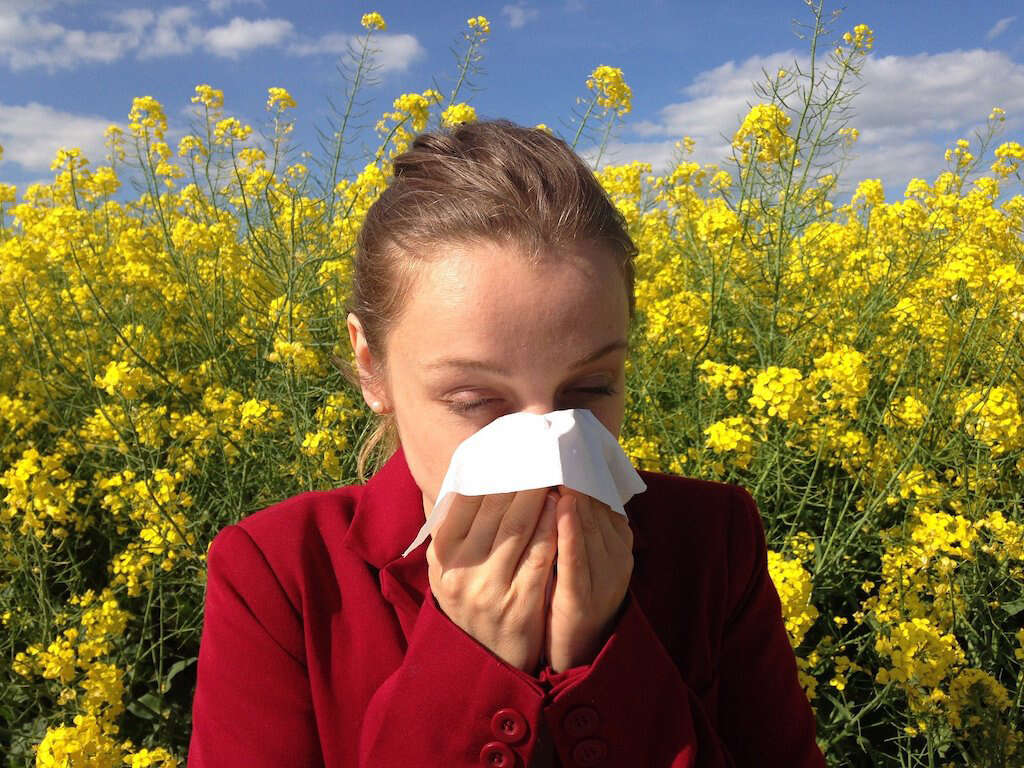
Cause #1: Allergy
Allergy is a possible cause of swollen eyelids, especially in cases when the affected eye is red, itchy, and watery. Common allergens are pollen, dust, and mites, which irritate the eyes and trigger an allergic reaction. Even though eye allergies are rarely dangerous, they are quite annoying.
The best treatment when it comes to swollen eyelids because of an allergy is avoiding the possible allergen that triggers the allergic reaction. Your doctor may prescribe eye drops and antihistamines to improve your symptoms.
Cause #2: Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis, otherwise known as pink eye, is an inflammation of the conjunctiva, the clear thin tissue that lines the eyelid and the eyeball. Pink eyeballs, itchiness, pain, and swollen eyelids are common symptoms that those affected by conjunctivitis experience.
In most cases, conjunctivitis is a viral infection that tends to resolve on its own within 7 to 10 days. However, bacterial conjunctivitis is also possible. Allergens and irritants are another possible cause of conjunctivitis.
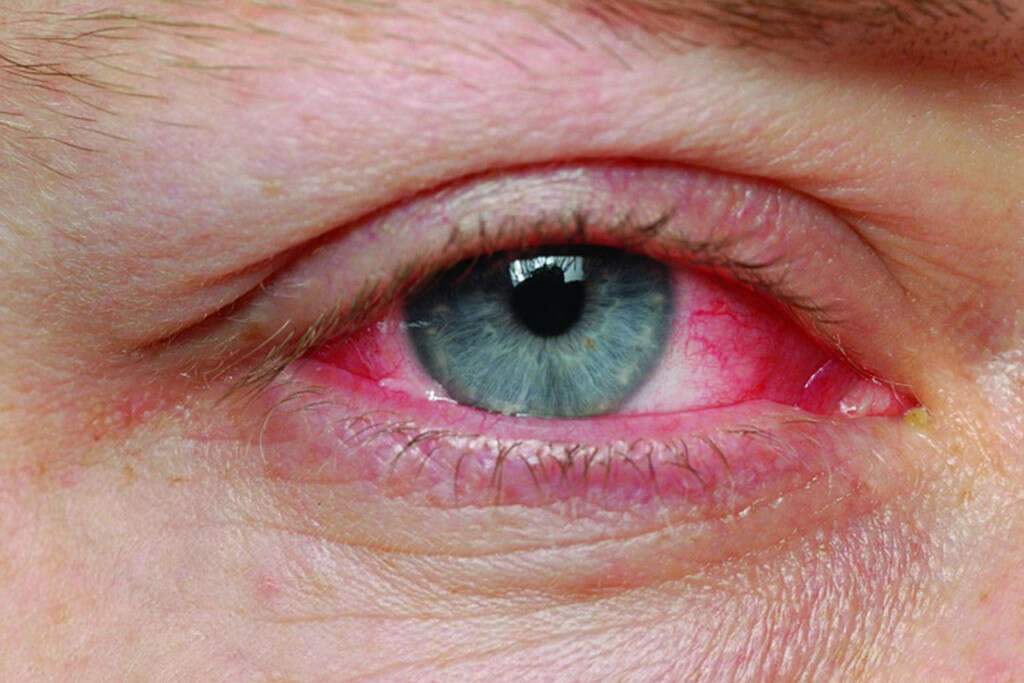
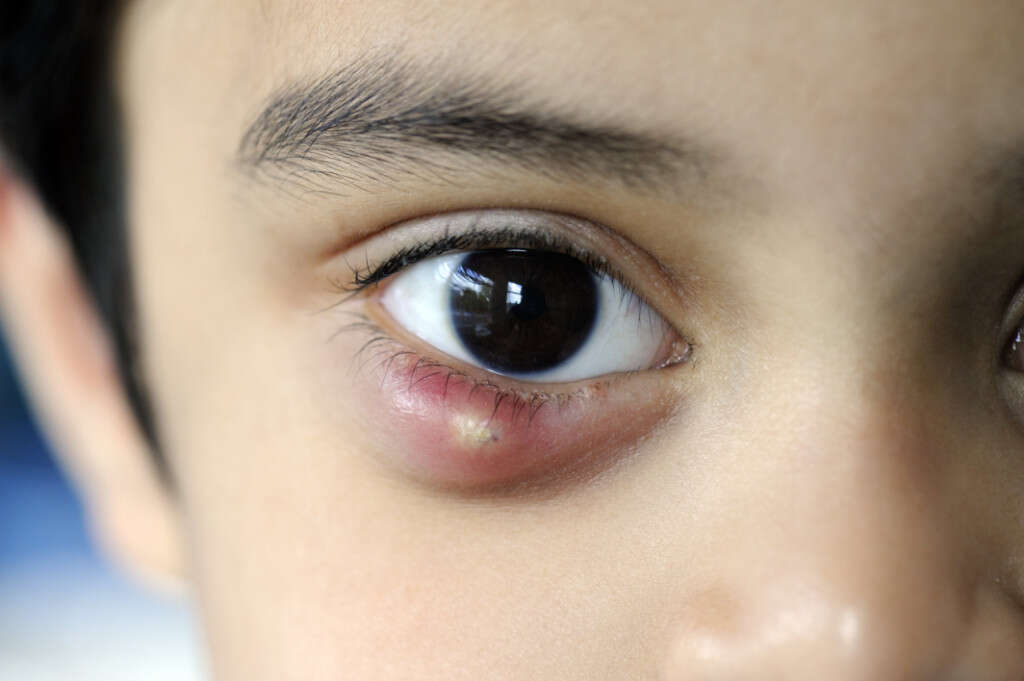
Cause #3: Styes
A stye, otherwise known as a hordeolum, is a local infection of glands that are located in the eyelid. The glands that produce oily substances (i.e. glands of Zeis) are the ones that are most commonly affected. A stye is characterized by the presence of a red, swollen, and painful lump in the eyelid. It can occur in either the upper or the lower eyelid, but very rarely on both of the eyelids at the same time.
One thing you should keep in mind is that you should never try to pop the lump on your own as it can just make the infection worse and spread it further or lead to serious eye damage. Instead, you should try to keep your eye as clean as possible, avoid wearing makeup, avoid rubbing of the eyes, and using warm compresses on the affected eye as it will help ease the pain and discomfort. Antibiotics are sometimes prescribed as well.
Cause #4: Chalazion
In cases when a gland that produces oily substances in the eyelid becomes obstructed, chalazia (plural of chalazion) develop. Even though it looks very similar to a stye, it is not the same thing. A stye is a local infection of a sebaceous gland of the eyelids that can be painful and tender.
Conversely, a chalazion is usually painless and it is the result of an obstructed sebaceous gland. However, in chalazia, there is inflammation without infection. Furthermore, a chalazion tends to recur every now and then. They also can grow big in size.
Cause #5: Blepharitis
Blepharitis is a chronic condition characterized by an inflammation of the eyelids. It is more common in people with bacterial colonization of the eyelids or the presence of bacteria on the eyelids that are not causing disease in the person. This colonization can lead to bacterial invasion of the eyelids and result in blepharitis. Furthermore, bacterial colonization of the eyelids can be facilitated by dysfunction of sebaceous glands (oily glands) and seborrheic dermatitis.
Luckily, blepharitis signs and symptoms can be managed with treatment, even though it can’t be completely cured. First of all, good hygiene of the eyes, especially of the eyelid margin, is very important. Warm compresses may help ease the pain and discomfort, while antibiotic ointments (if prescribed by your doctor), when applied topically, can help resolve its signs and symptoms faster.
Cause #6: Ocular Herpes
One of the causes of swollen eyelids is ocular herpes. Herpes is an infection with the herpes simplex virus (HSV) which can affect the eyes as well. Ocular herpes leads to inflammation of the cornea and in more severe cases, even scarring of the cornea. Besides swollen eyelids, itchiness, tearing, sensitivity to light, redness, and even painful sores on the eyelids are possible. Visual disturbances can also occur due to a cloudy cornea (i.e. blurry vision) and swelling of the eyelids.
In severe cases of ocular herpes, severe and permanent eye damage is possible leading to corneal transplant and even blindness.

Cause #7: Grave’s Disease
Grave’s disease is an autoimmune condition that is characterized by an overactive thyroid gland. This condition can lead to the release of certain antibodies that attack the host’s tissue (TSH receptor in the thyroid). In about 30% of cases, those suffering from Grave’s disease will have ocular signs and symptoms, otherwise known as Grave’s ophthalmopathy.
In Grave’s ophthalmopathy, cells of the immune system (T cells) can become activated and confuse the thyroid tissue with the tissue behind the eye (retro-orbital space). The T cells that infiltrate the tissue of the eye can stimulate cells known as fibroblasts to produce substances (glycosaminoglycan)that retain fluids. Additionally, some fibroblasts turn into fat cells (adipocytes). Consequently, the tissue in the eye orbit increases in volume, causing several signs and symptoms. Bulging of the eyes (exophthalmos), eye pressure and pain, redness of the eyes, light sensitivity, puffy and retracted eyelids, a gritty sensation in the eyes, double vision, and even vision loss are common signs and symptoms of Grave’s disease when the eyes are involved.
Cause #8: Periorbital Cellulitis
Infections that involve the skin around the eyes are known as periorbital cellulitis. This condition predominantly affects children, but not exclusively. When associated with local trauma (i.e. insect bite), it is mostly caused by bacteria such as Staphyloccocus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes. However, periorbital cellulitis can also be secondary to sinusitis or an infection in the adjacent structures of the eye (i.e. hordeolum, impetigo, conjunctivitis). Moreover, periorbital cellulitis can present with fever and unilateral swelling and redness of the lid. In addition, a sensation of warmth and pain (tenderness) in the area can also be present.
With appropriate follow-up, periorbital cellulitis can be treated in adults with oral antibiotics. However, in most children with this condition intravenous antibiotic treatment in the hospital is warranted, especially during the first days of the infection. Complications of periorbital cellulitis can be quite serious. If not treated promptly, this condition can progress to orbital cellulitis (infection of the soft tissues of the eye’s orbit), which can cause further complications (i.e. abscesses and vision loss).
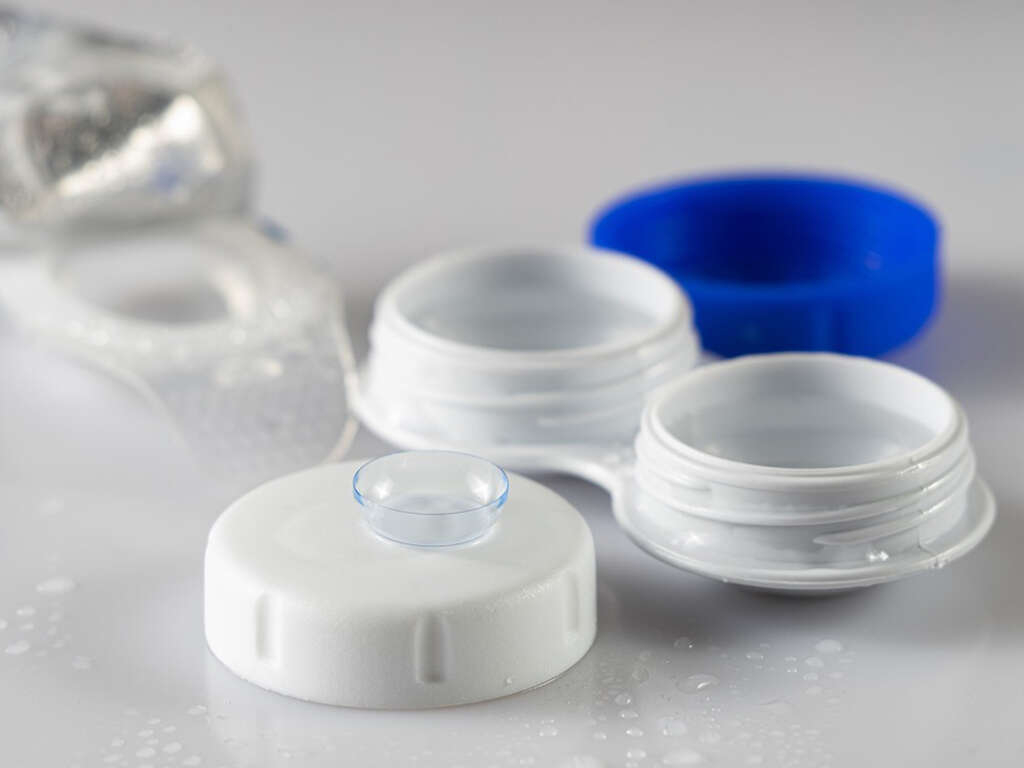
Cause #9: Contact Lenses
Those who have a problem with their vision instead of wearing glasses choose to wear contact lenses. However, wearing contact lenses can sometimes lead to swelling of the eyelids.
This is more likely to occur in cases of improper care, especially when swimming with contact lenses, wearing dirty contact lenses, or storing the lenses in a dirty contact lenses case, which can all lead to an infection of the eye. Using damaged contact lenses can irritate the eyes leading to swelling of the eyelids as well.
Cause #10: Eye Injuries
Any injury of the eye can lead to swollen eyelids besides other vision problems. Ocular trauma is most common among children and young males and it is mostly related to sports, work, traffic accidents, and assaults. Furthermore, it is estimated that roughly half a million people worldwide live with blindness as a result of ocular trauma.
Importantly, this cause of blindness is preventable through several strategies like the use of protective equipment in sports or the implementation of accident prevention training for child caregivers.