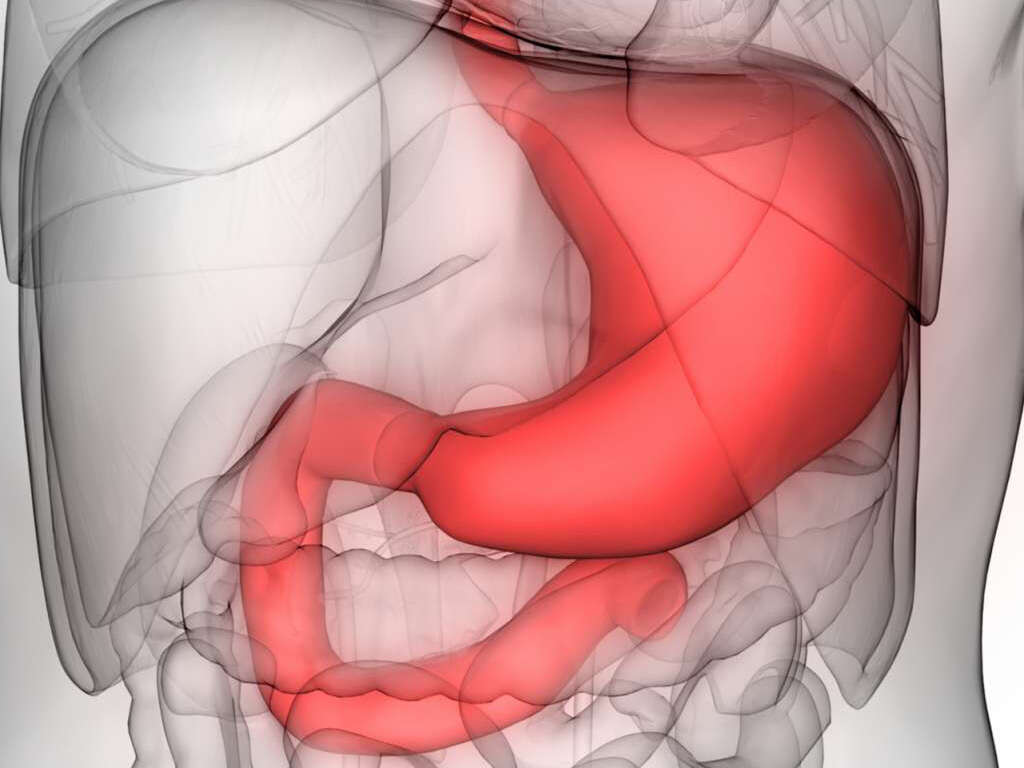
10 Gastritis Symptoms
Gastritis is a condition where the lining of the stomach becomes inflamed. The lining contains glands that function to produce stomach acid (hydrochloric acid) and an enzyme known as pepsin. The acid helps to break down foods while pepsin digests protein. Since the hydrochloric acid is corrosive, the lining of the stomach is coated with a layer of mucus to help prevent the acid from breaking down the lining. When gastritis occurs, the stomach produces less acid, enzymes, and protective mucus.
Gastritis can be acute (starts suddenly and only lasts for a short time) or chronic (lasts for a long time, possibly years or even throughout life). In erosive gastritis, the stomach lining wears away causing ulcers or deep sores. Non-erosive gastritis does not cause ulcers but leads to inflammation of the stomach lining. Gastritis can be caused by a Helicobacter pylori infection, if there is damage to lining (due to alcohol, medication, or drugs) causing reactive gastritis, or an autoimmune disorder.

Symptom #1: Pain
The commonest symptom of gastritis is abdominal pain that can range from moderate to severe. Due to the innervations and location of the stomach in the body, the pain is usually located in the upper part of the abdomen, in the midline. The pain can usually be described as a gnawing, dull, and aching pain while some have also reported sharp and shooting pain. The pain is not relieved with change of position. It can be aggravated by certain foods especially acidic foods. Antacids are usually effective in relieving the pain, even if not completely.
Symptom #2: Bloating
Those who have experienced gastritis also report bloating as a common symptom. It is not a specific symptom of gastritis.
In many cases, it can take a while before the affected individual realizes that their symptoms are due to gastritis. However, if you notice a pattern such as bloating after acidic based foods, it might be gastritis.

Symptom #3: Nausea
Another common symptom of gastritis is nausea. Even the sight, smell, or thought of food can be repulsive. In severe cases, they are unable to retain the food they consumed. While some nausea may lead to bouts of retching and vomiting, others may not have vomiting.
Anti-emetics (anti-vomiting) medication can help to relieve the feeling of nausea but only works as a short-term measure. It is recommended that you stay hydrated by drinking clear fluids. You can then progress to soups or any soft foods that are easier to digest. It is important to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment.

Symptom #4: Vomiting
Since the lining of the stomach is inflamed and irritated, someone who suffers from gastritis may not be able to retain the food they ingested. It does not happen in mild to moderate cases but can be distressing in severe cases of gastritis.
Anti emetic medications can be used to help retain some food and reduce the frequency of vomiting. Since the stomach is sensitive, it is recommended that you start with a soft diet and small meals to help your stomach get used to food again. Avoid oily foods, spicy foods, and acidic foods until you feel better.

Symptom #5: Appetite loss
Naturally, with symptoms such as nausea and vomiting, it is not surprising if there is loss of appetite as well. Since food may be associated with more pain, bloating, and vomiting, there is a psychological contribution that causes the affected individual to be afraid to eat. In severe cases, the smell of food itself can be repulsive.
The loss of appetite is temporary, and your appetite will eventually return to normal with time. Start with foods that appeal to you. Avoid foods that aggravate your gastritis.

Symptom #6: Change in Stool
If you have gastritis, you should pay attention to any changes in the color and appearance of your stool. In some cases, the stool can have a tar-like appearance and become darker than usual (remember to compare it with your normal stool).
If this occurs, it usually means that there is bleeding in the upper gastrointestinal tract (due to erosion causing ulcer). If you notice this, you should seek medical attention as soon as possible.
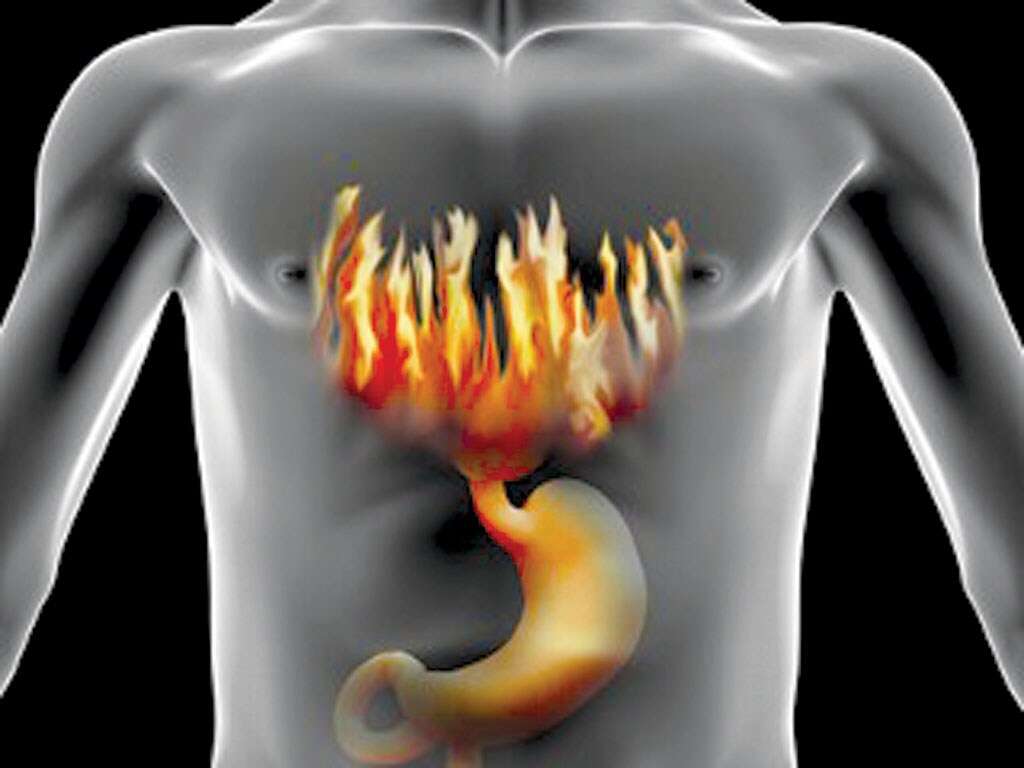
Symptom #7: Belching
Belching and burping are not specific symptoms of gastritis. However, if you notice that you have been burping more frequently, you should observe if you have other symptoms of gastritis. The burps from those afflicted with gastritis usually occur after meals.
Belching occurs due to indigestion that happens as there is inflammation of the stomach lining. If in doubt, always consult your doctor to prevent the condition from worsening.

Symptom #8: Indigestion
There are many causes of indigestion, ranging from mild to severe causes. Indigestion can cause a burning sensation in the upper abdomen and sometimes up the chest. Indigestion is also known as heartburn and can occur after big and heavy meals.
Antacid may be helpful and should be able to provide relief within 20 to 30 minutes. If there is no relief, make sure that you seek medical attention to rule out any harmful conditions (a heart attack can be mistaken as indigestion!).

Symptom #9: Diarrhea
Diarrhea occurs when there is loose stool that occurs three or more times a day. Acute gastritis can be caused by bacterial infection, viral infection, stress, alcohol, medication, and more. Since the stomach lining is inflamed affecting the digesting capabilities, the foods that are ingested may not be able to be broken down properly.
This may result in diarrhea. If there is no fever, you may take anti-diarrheal medication such as loperamide. However, it is best to consult with your doctor before taking it as it may interact with any existing medications you are currently taking.

Symptom #10: Loss of Weight
This is another symptom that is not specific to gastritis. However, since there can be loss of appetite, nausea, and/or vomiting, loss of weight is not a surprising consequence. While the stomach takes time to heal, soft foods that are easily digested are recommended. Oily and spicy foods should also be avoided.
Since there are restrictions on the type of food the affected individual can take, there may not be enough calories that are ingested throughout the day. It may take about three to seven days for the stomach to start accepting normal foods again. Meanwhile, some weight loss is considered to be normal. If you notice that the weight loss continues without any reason (after your normal diet has resumed for a while, not trying to lose weight, and not starting a new exercise routine), you should make an appointment with your doctor to rule out harmful causes of weight loss.