10 Symptoms of Rickets
Our skeletons help to give us the support we need to be able to stand and move around. Without them, we would simply slump to the ground under the force of gravity. In addition, our skeletal structure also helps protect delicate organs and soft tissues against damage from impacts.
Our skeletons need the right nutrients which include vitamin D and calcium. If there is not a sufficient supply of these then the skeleton may not be able to grow as it should. One such condition, caused mostly by a lack of vitamin D, is rickets. It causes the bones to be softer than usual and also causes the skeleton to become deformed. Although easily treated, deformities caused by it are permanent and may require extensive surgery to correct.
Symptom #1: Muscle Cramps
Overuse your muscles and you are likely to know about it. Tired or overworked muscles can cramp up, potentially causing us significant discomfort. It is fairly common among athletes that are not in peak condition. Muscle cramps can also be caused by other factors such as vitamin and mineral deficiencies.
With the skeleton not in a natural shape, some muscles can be placed under unnecessary pressure, causing cramps to arise. What’s more is that the vitamin and mineral deficiencies causing rickets can also cause the patient to experience cramps. If you are experiencing cramps regularly for no apparent reason then you should arrange to speak with a doctor.

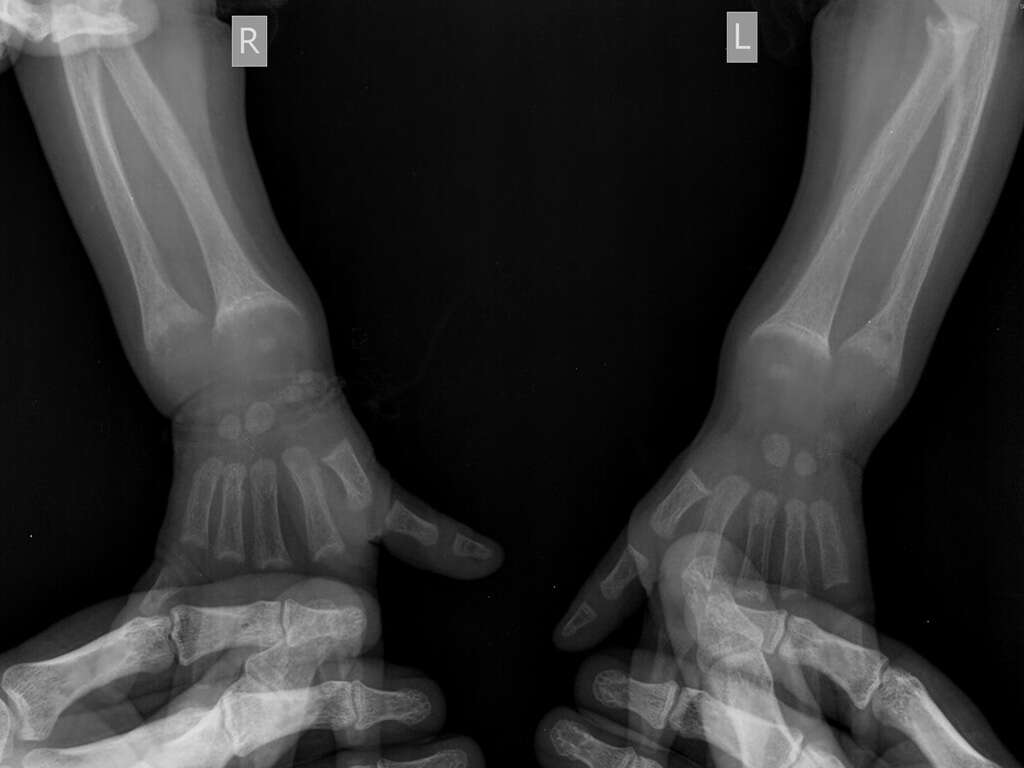
Symptom #2: Stunted Growth
Our skeletons are essential for our growth. If the skeleton is not able to grow as it should, then our overall growth can also be stunted, leaving us shorter and generally smaller than we should be.
This is particularly problematic in children that still have plenty of growing to do. It can also be difficult to spot quickly as growth tends to happen over a long period of time. If you do think that your child is not developing physically as they should be, speak with a doctor as soon as possible.

Symptom #3: Bone Pain
We tend not to feel much sensation in our bones. They are generally protected by the rest of our bodies so we only usually feel pain in the case of a physical impact. When we do feel sensation in our bones, however, it can be quite unbearable.
Patients with rickets are likely to find that their bones can be quite sore and painful. It tends to be more noticeable in bones that take a lot of weight, such as the legs, pelvis and spine. The pain makes it difficult for them to walk, causing them to have an unusual gait such as waddling.
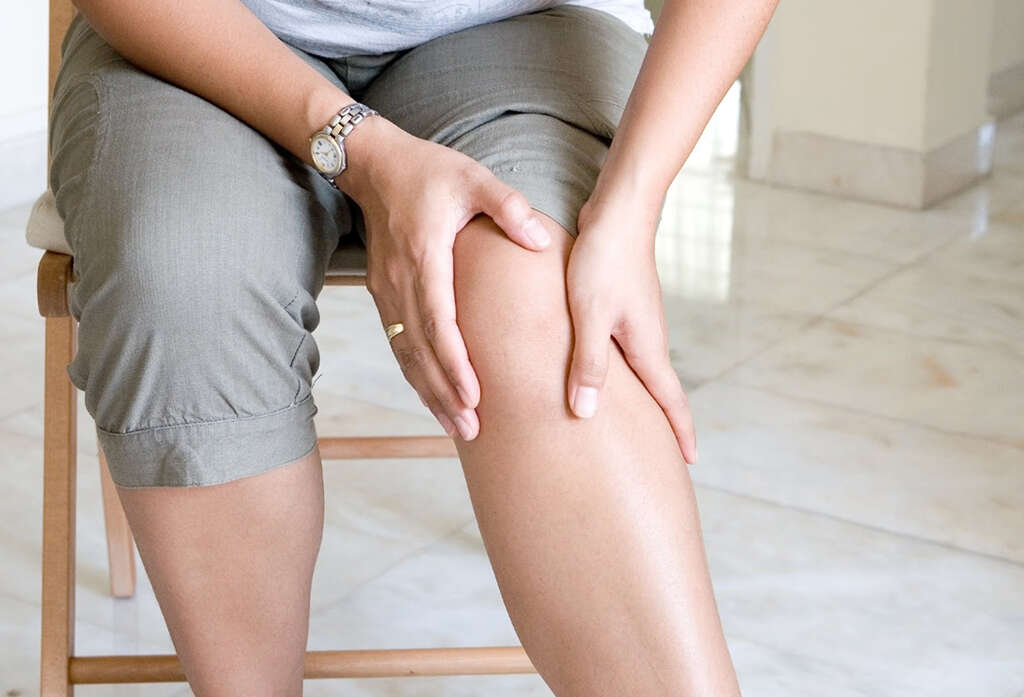
Symptom #4: Regular Fractures
Our bones are made from tough stuff, meaning they are not easy to break. It would usually take a considerable impact to break one of our bones, although smaller bones are more likely to break than others. If all is not right with the bones, though, then fractures are more likely to occur.
A lack of vitamins can lead to the bones becoming weaker, making them easier to break. What’s more is that deformed bones are less able to absorb impacts than others, again meaning they are more likely to be broken. In addition to causing considerable pain for the patient, broken bones will also increase the chances of infections.
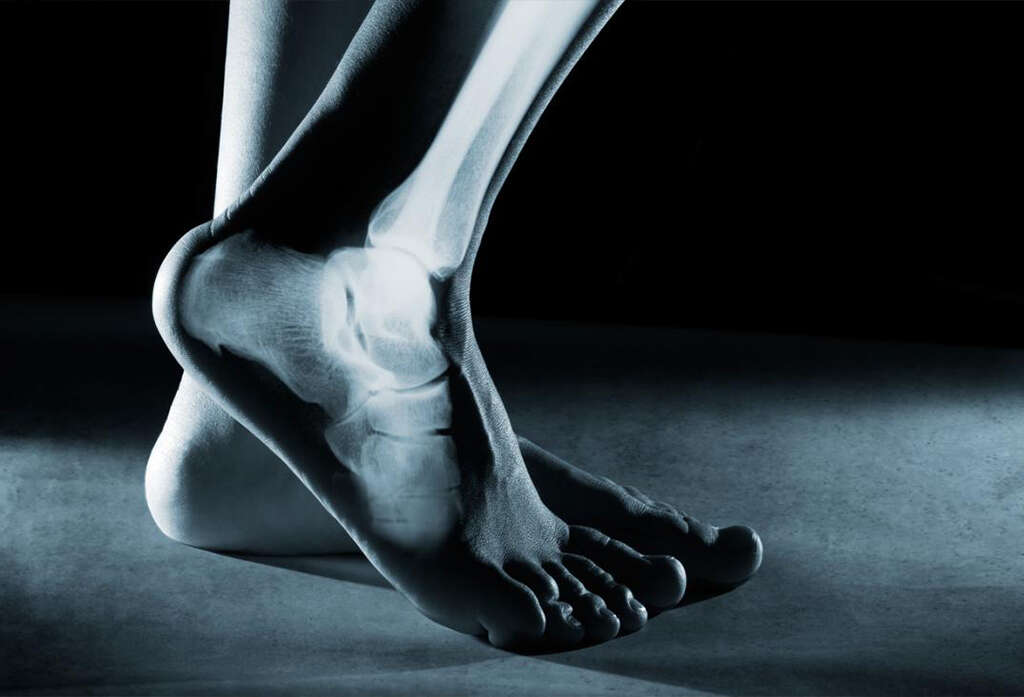
Symptom #5: Deformed Tooth Structure
Our teeth are made largely of the same stuff that our bones are made of. This means that if our bones are suffering from a lack of required nutrients, our teeth are likely to suffer also. Just like with the skeleton, the teeth are also likely to grow irregularly in cases of rickets.
In patients with rickets, teeth can grow later than usual, and/or be misaligned when they do grow. The teeth might also have holes in the enamel and have various structural defects. This can be very painful for the patient as well as making it difficult for them to eat and drink.
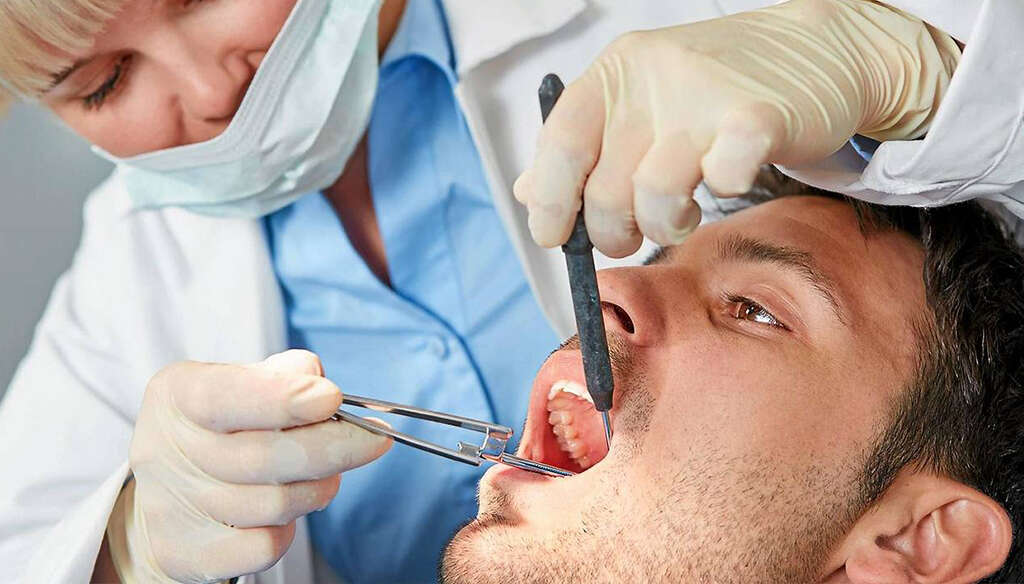
Symptom #6: Deformed Skull
When we are first born, our skulls are soft and supple. This is to allow the baby to fit through the birth canal. This soft skull means that the baby’s head could become deformed if the baby is made to lay in certain positions for too long. The skull will usually harden in time.
Because rickets makes the bones softer than usual, however, then the patient’s skull will be soft for as long as they have the condition. This means that their skull is prone to becoming disfigured.

Symptom #7: Uneven Ribcage
Our upper torsos are home to some of our most essential organs such as the heart and the lungs. These organs are delicate and an injury to them could be very dangerous. The good news is that they are well protected. Our ribs provide a strong protective cage that helps prevent the soft organs and other tissues inside from getting hurt.
Usually, our ribcage will grow quite evenly, providing a visibly smooth surface on the outside. Rickets, however, can cause the rib cage to grow abnormally, resulting in lumps and bumps on the exterior surface. Softer than usual rib bones also increase the chances of a serious injury to the organs inside.
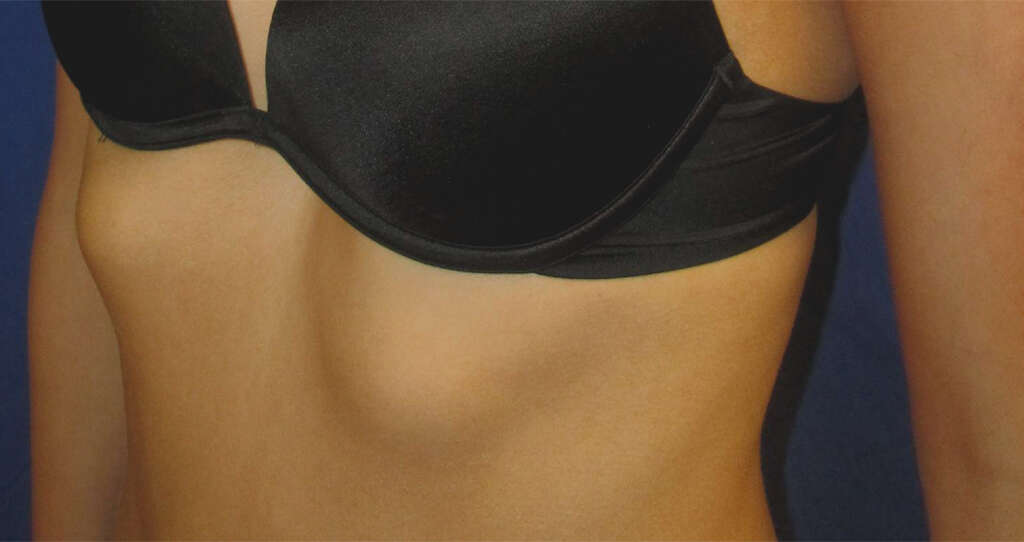
Symptom #8: Protruding Breastbone
Our breastbones also play an important part in the protection of the organs and other tissues within the chest cavity. Known medically as the sternum, the breastbone is attached to the collarbone and holds the ribs firmly in place. Usually, it lays quite flat down the front of the chest, but that is not always the case.
One symptom of rickets is that the breastbone will become deformed and protrude from the front of the chest. Not only is this problematic aesthetically, but it can also increase the chances of harm as well as being quite uncomfortable for the patient.

Symptom #9: Curved Spine
Our spines are one of the most important supporting pillars of our body, essentially providing support for the entire upper torso. In addition, it houses the spinal cord which is an essential part of the central nervous system. Our spines are naturally curved to help it withstand stress, although this is usually not noticeable from the outside.
One common symptom of rickets is a spine that is curved considerably more than usual. This curvature can occur from front to back and from side to side, potentially resulting in a very deformed stature. Extensive surgery may be necessary to treat it.

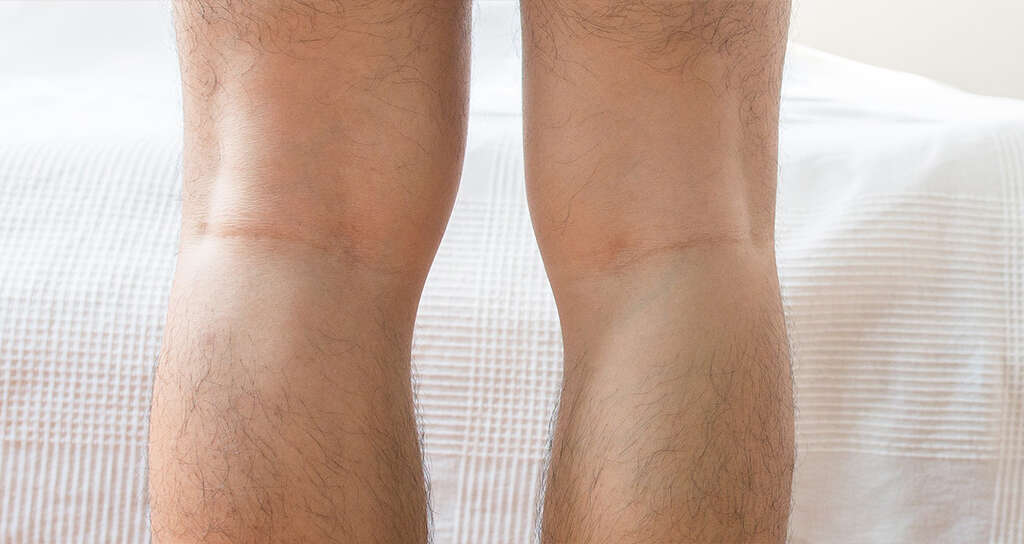
Symptom #10: Bow Legs
The bones in our legs need to be strong enough to withstand the weight of our entire bodies. Despite the forces they endure, they allow us to walk, run and even jump without injuries. Should there be a problem with these bones, though, then our mobility can become severely restricted.
One symptom that is often considered to be synonymous with rickets is bow legs. The legs will bow outwards, resulting in quite an unusual gait. This can be very uncomfortable for the patient while also severely impacting their mobility. Alternatively, rickets can cause knock knees which is when the legs bend inwards.