What Is Rickets?
The human skeleton is designed to offer support and provide structure to the rest of the body. In healthy individuals, it is made up of hard, strong bones. However, some people develop soft and weak bones: a condition called rickets or, when it manifests in adults, osteomalacia.
Rickets can also affect bone development in some children. While once a relatively common occurrence, improved nutrition and medical care have made a diagnosis of rickets much less common. It can only be diagnosed by a medical professional.
1. What Causes Rickets?
Rickets occurs when the body is unable to absorb enough calcium to maintain bone structure. The most common cause of that is a lack of vitamin D, which the body needs to absorb and utilize calcium. Along with phosphorous, it enables the absorption of calcium from food. However, when vitamin D levels are low, the body cannot access that calcium, resulting in soft and weak bones. They may also become deformed and break more easily than usual.
A lack of vitamin D isn’t the only reason a child’s body might not absorb enough calcium. Certain medical conditions, such as cystic fibrosis, celiac disease, irritable bowel disease and some kidney problems, can also cause poor calcium absorption.
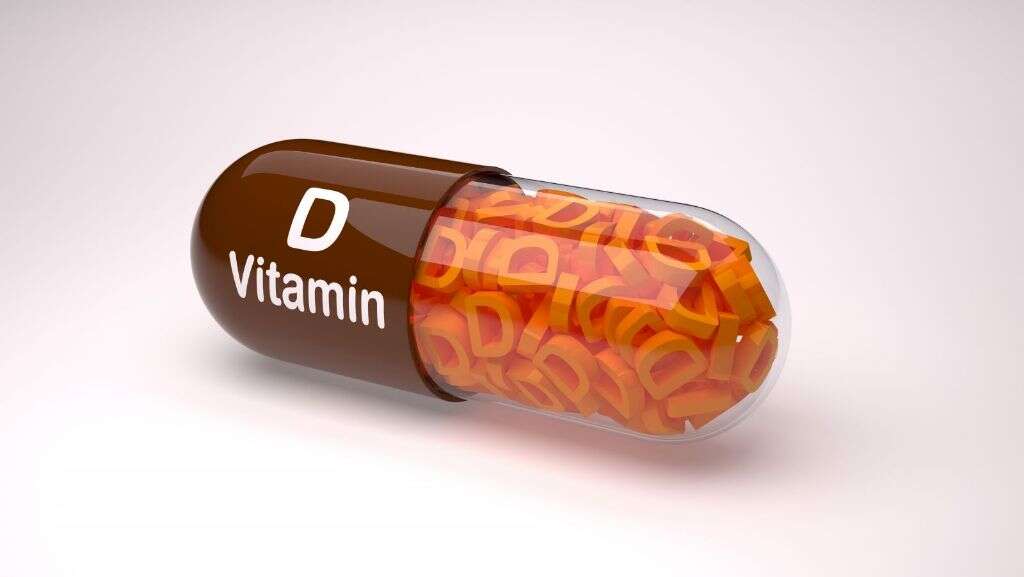
2. How Much Vitamin D Is Enough?
The recommended daily allowance of vitamin D is 600 international units per day for most children and adults. Infants under 12 months of age require slightly less, or about 400 IU. This is sufficient to maintain strong, healthy bones. It is present in some fortified foods like milk and cereals and can also be administered as a dietary supplement.
The skin also produces vitamin D during sun exposure. This is widely regarded as the best and most efficient way to maintain adequate vitamin D levels. Most people can make enough to meet the recommended amounts with about 15 minutes of sun exposure each day. Several factors, such as skin color, location, time of year and whether you use sunscreen, can impact the amount you produce.

3. Who Is at Risk of Developing Rickets?
There are many risk factors for rickets. It is most common in children between six and 36 months of age. Babies who are breastfed exclusively or young children who eat a vegetarian diet without fish, eggs and milk are also more likely to develop the condition. There also appears to be a genetic component, as rickets is more common in some families over others.
Children with darker skin do not produce as much vitamin D in their skin. This puts children from African, Pacific Islander and Middle Eastern families at a higher risk of developing rickets than those with fair skin. Similarly, children who are not exposed to the sun regularly may not produce adequate amounts of vitamin D to keep bones strong and healthy.

4. How Is Rickets Diagnosed?
A diagnosis of rickets is relatively straightforward. It may be suspected if bones appear visibly misshapen or if there is a history of repeated fractures in a small child.
However, it is most commonly diagnosed after a thorough physical examination notes tenderness or soreness when pressure is applied to bones.

5. What Tests Are Used?
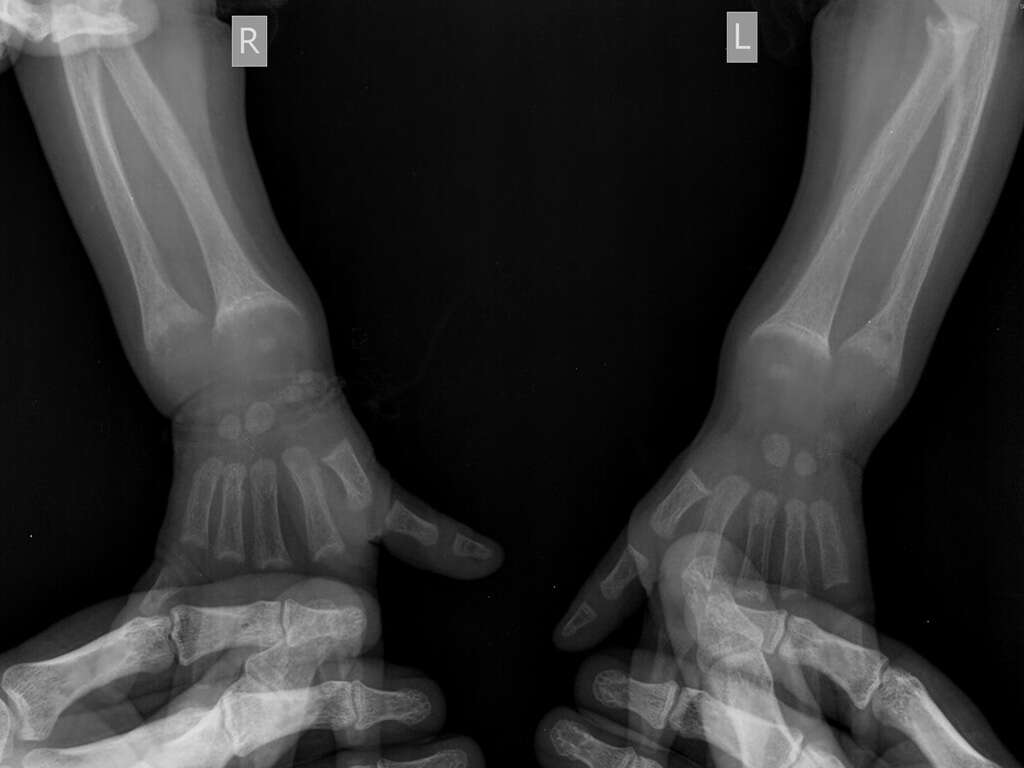
There are two relatively standard tests used to diagnose rickets and monitor the condition. The first is a blood test. It is used to measure the levels of calcium and phosphate in the blood. When levels are low, bones are not able to develop correctly. Bone X-rays may also be used to check for deformities. They are painless and non-invasive.
For severe cases, a bone biopsy may be performed. During this surgical procedure, a small section of bone is removed. The sample is then sent to a laboratory for complete diagnostics.

6. How Is Rickets Treated?
The most effective way to treat the condition is to increase the amount of calcium available for use in the body. That might mean adding a vitamin D or calcium supplement. In patients who have experienced bone deformities, those may need additional treatment to be corrected.
However, most doctors will also suggest lifestyle modifications. A diet that includes fish, eggs and dairy can help provide additional vitamin D, and so it is likely that patients will be encouraged to increase consumption of these items. Increasing exposure to sunlight is also a very effective way to raise vitamin D levels.
7. Can Rickets Be Prevented?
For most people, preventing rickets is relatively straightforward. A balanced diet with adequate amounts of vitamin D, phosphorous and calcium is a great starting place. Moderate and consistent exposure to sunlight also helps by allowing the body to produce a sufficient amount of vitamin D.
It is essential to monitor vitamin and mineral levels and bone density in people with an underlying illness that prevents or limits vitamin absorption. If irregularities are noted, supplementation can be used to prevent rickets from developing.

8. What Are Common Symptoms of Rickets?
Pain and tenderness in the bones is an early sign of rickets. This most commonly manifests in the spine, legs, arm or pelvis. Stunted or slowed growth is another indicator of insufficient calcium levels. Frequent bone fractures and muscle cramps are also common in individuals with rickets.
Sometimes rickets is diagnosed after deformities are noticed. Malformed bones such as severely bowed legs,
excessive spinal curvature, a misshapen skull or protruding pelvis are commonly associated with the condition. Teeth with abnormal enamel growth or that have an excessive amount of cavities may also indicate insufficient calcium absorption.
9. What Type of Doctor Treats Rickets?
Most of the time, diagnosis and treatment can begin with a general practitioner or family doctor. Pediatricians are trained to look for growth abnormalities in children and are uniquely positioned to spot early warning signs. However, severe deformities may need a specialist to be corrected.
An orthopedic specialist or surgeon may be needed to craft braces and casts designed to correct bone growth patterns. If a hormonal imbalance is causing absorption issues, those should be treated by an endocrinologist familiar with your particular disorder. Nutritionists may also be helpful in identifying healthy ways to increase the vitamin and mineral content of your diet.
10. What Questions Should You Ask Your Doctor?
If you have concerns about rickets, you will undoubtedly have a lot of questions for your doctor. While they are all worthwhile, you might want to start with those that will move you closer to uncovering the condition’s cause.
You will likely want to ask about the need for supplements and recommended dosages. While it only takes a few minutes of exposure to produce vitamin D, many people still have concerns about harmful UV rays. So, if you have concerns about sun exposure without sunscreen, be sure to ask about that, too.