What Is Scalp Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a chronic, complex, and inflammatory disease that involves increased proliferation of keratinocytes in the skin with an increase in the skin cell turnover rate. Psoriasis is thought to be caused by immunological, genetic, and environmental factors. Psoriasis is most commonly observed on the skin of the knees, elbows, glans penis, lower back, scalp, and between the buttocks. About 30% of patients also have joints that are affected.
It is a noncontagious, chronic, and multisystem condition. Psoriasis may wax and wane depending on environmental and systemic factors such as infection and stressful life events. It can negatively affect the quality of life along with a higher risk of depression in patients with psoriasis. Psoriasis can be divided into plaque-type psoriasis, discoid psoriasis, and more.

1. Scalp Psoriasis
Scalp psoriasis is just psoriasis that affects the scalp. It can cause the scalp to appear scaly, reddish, and have raised patches. It can only be a single patch or affect the entire scalp. In some cases, it may affect the back of the neck, behind the ears, and forehead. Just like any other case of psoriasis, it is noncontagious and the cause of it is unclear. The risk of scalp psoriasis increases in those with positive family history. It is estimated that about 50% of 7.5 million Americans with psoriasis have it on their scalp. While some cases are mild and can be unnoticeable, there are also those with severe scalp psoriasis resulting in thick crusted sores. It can also cause itching, leading to sleep deprivation, hair loss, and skin infections.

2. Environmental Factors
There are many factors that have been thought to trigger the exacerbation of psoriasis such as infections (HIV, staphylococcal, and streptococcal), alcohol consumption, cold, trauma, and medications. One study has also demonstrated that there is an increase rate of psoriasis among those with chronic gingivitis.
The appropriate treatment of gingivitis was also found to result in improved psoriasis control. However, this did not affect the long-term incidence, which implies that there are multiple factor that influence psoriasis. Some experts have observed that sunlight, hot weather, and pregnancy may reduce the exacerbations of psoriasis. Many have suggested that psoriasis is a stress-related condition.

3. Genetic Factors
Patients with a positive family history of psoriasis have a higher risk of developing this condition. However, in most cases, the triggering event may be unknown and is likely immunologic. Researchers have reported that psoriasis commonly begins after an upper respiratory tract infection.
Psoriasis has been associated with some human leukocyte antigen (HLA) alleles with the most prominent being the human leukocyte antigen Cw6 (HLA-Cw6). Some cases of psoriasis are also autosomal dominant. Other HLA antigens associated with psoriasis include HLA-B13, HLA-B17, HLA-B27, and HLA-DR7. The deletion of two late cornified envelope (LCE) genes such as LCE3B and LCE3C have also been found to be a common genetic factor that increases the susceptibility to psoriasis.

4. Immunologic Factors
There is some literature suggesting the possibility of psoriasis as an autoimmune disease. These studies have demonstrated that there are high levels of circulating tumor necrosis factor (TNF) alpha. This means that the treatment of psoriasis using TNF-alpha inhibitors has shown success as psoriatic lesions are often due to increased T-cell activity in the underlying skin.
It has also been observed that 2.5% of HIV patients with decreasing CD4 counts (more severe cases of HIV) develop worsening psoriasis. This finding supports the hypothesis that psoriasis is caused by T-cell hyperactivity. Obesity is another potential factor that increases the risk of psoriasis. When there is exacerbation or onset of psoriasis with weight gain, weight loss often results in improvement.

5. Statistics
Based on the National Institutes of Health (NIH), about 2.2% of the population in the United States has psoriasis. Globally, the incidence varies based on the location. In a study involving 26,000 South American Indians, there was no psoriasis case while an incidence of 2.8% of psoriasis was observed in the Faeroe Islands. Overall, about 2% to 3% of the global population are affected by psoriasis.
Although this condition can occur at any age, there is a bimodal peak between the ages of 20 to 30 and 50 to 60 years old. It is estimated that about 10% to 15% of new cases occur in pediatric patients younger than 10. Psoriasis seems to affect women more than men. Some believe that the incidence is dependent on the genetic heritage and climate of the population.
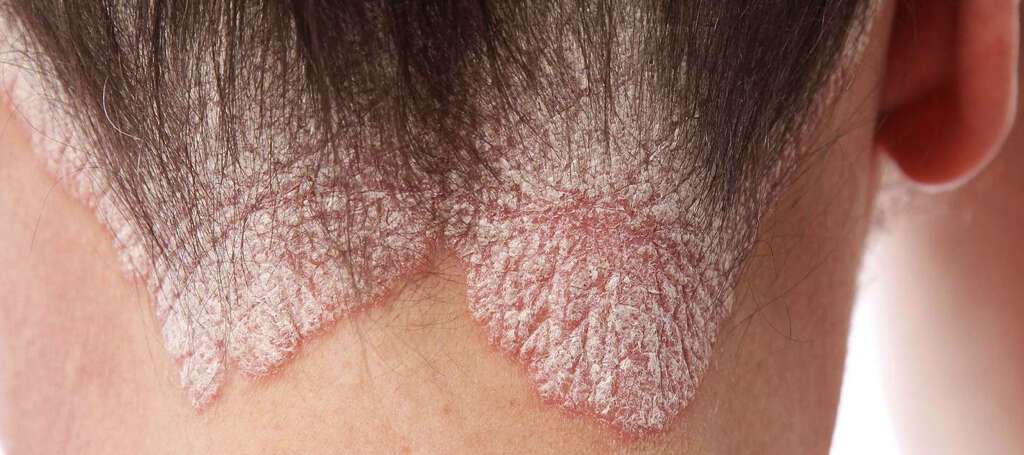
6. Signs and Symptoms
In scalp psoriasis, patients who have mild cases often present with slight and fine scales on the scalp. However, when the symptoms become severe or moderate, the scalp can appear to be red and have bumpy or scaly patches, There may also be silvery white scales or dandruff-like flaking. Patients with scalp psoriasis may complain of having a dry scalp that itches resulting in excoriations and hair loss.
These excoriations can also result in infections , burning, or soreness. It is important to note that scalp psoriasis does not generally result in hair loss but the itching or scratching of the scalp, picking at the scabs and scales, and treatments can result in hair loss. In most cases, the hair usually grows back once the psoriasis resolves.

7. Topical Treatment
Topical medication refers to medication that can be applied on a part of the body. In most cases, it is applied to the skin and mucous membranes for the treatment of various diseases. Topical treatments may include foams, gels, creams, ointments, and lotions. For scalp psoriasis, topical treatments generally include creams, gels, medicated shampoos, foams, oils, soaps, and ointments.
Products for psoriasis that are available over the counter include coal tar and salicylic acid. Prescription topical treatment often includes anthralin, antimicrobials, calcipotriene, betamethasone, optical steroids, and tazarotene. These topical treatments have to be applied on the scalp and not just the hair. It can take 8 weeks or more to heal.

8. Other Treatment Options
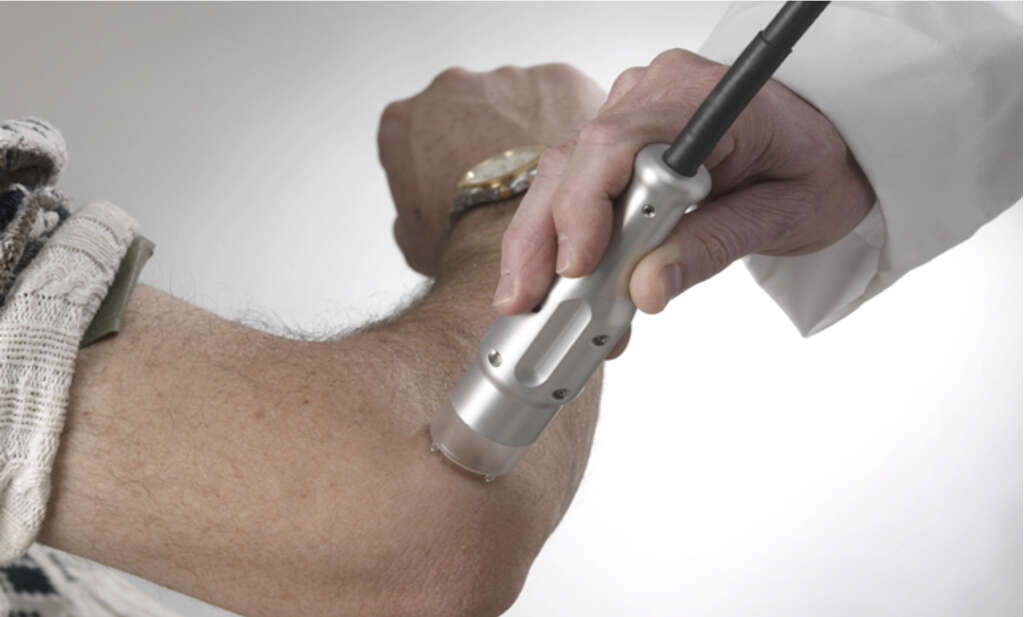
For some patients with mild scalp psoriasis on a few areas, injection of steroids directly into these areas may also be beneficial. Symptoms that don’t improve from topical treatment may benefit from phototherapy with a laser or non-laser light source.
An ultraviolet light comb can also be used for the whole scalp. Individuals with a shaved head or thin hair may be recommended to go out in natural sunlight to help heal the scalp. Some oral medications for scalp psoriasis include cyclosporine, corticosteroids, methotrexate, adalimumab, infliximab, and etanercept. Although there is no cure for scalp psoriasis, patients can often control the flare ups of their symptoms and prevent it from reoccurring. There are also psoriasis support groups that share resources and offer valuable tips.
9. Prognosis
Although benign, psoriasis is a lifelong condition that has remissions and exacerbations. Some cases may be refractory to treatment and cause arthritis in 10% of psoriasis cases. Although mild psoriasis does not increase the risk of death, men with severe cases died 3.5 years earlier while women with severe cases died 4.4 years earlier than their average life expectancy.
A population-based cross-sectional study has also found that those with more extensive psoriatic skin disease have a higher risk of major medical comorbidities such as chronic lung disease, heart disease, blood vessel disease, joint issues, kidney disease, and diabetes. The risk of other serious illness was 11% higher for mild cases, 15% higher for moderate cases, and 35% higher in severe cases.

10. Patient Education and Tips
Patients may try to soften and remove the scales to enable topical medications to work better. Products that contain lactic acid, salicylic acid, zinc pyrithione, urea, and selenium sulfide may help the scales to soften and peel off. Scales can be loosened using a fine comb. Shampooing the scalp can also help remove softened scales.
While the scalp is still damp, thick cream can be applied to help retain the moisture. Petroleum jelly can also be applied using cotton balls and placed into ears to help prevent topical scalp medications from dripping into the ears. Medications should be used sparingly as they can weaken hair shafts and cause skin irritation, leading to temporary hair loss. After the application of topical medication, the scalp can be covered using a shower cap briefly to help the medication work better. All treatments and remedies should be first discussed with a doctor.