What Is Urethritis?
The urethra is a tube that passes from the bladder to our genitals where it ends in an opening the allows fluids to pass out of the body. In men, this tube also allows for semen to pass out of the body from the testicles. The tube is barely even noticed much of the time, but it can become very noticeable should we develop certain medical conditions.
The urethra is made of delicate tissues that can be easily irritated. This irritation can cause the tissues to become inflamed, in a condition known as urethritis. It is usually a very treatable condition, but it can also be very uncomfortable.
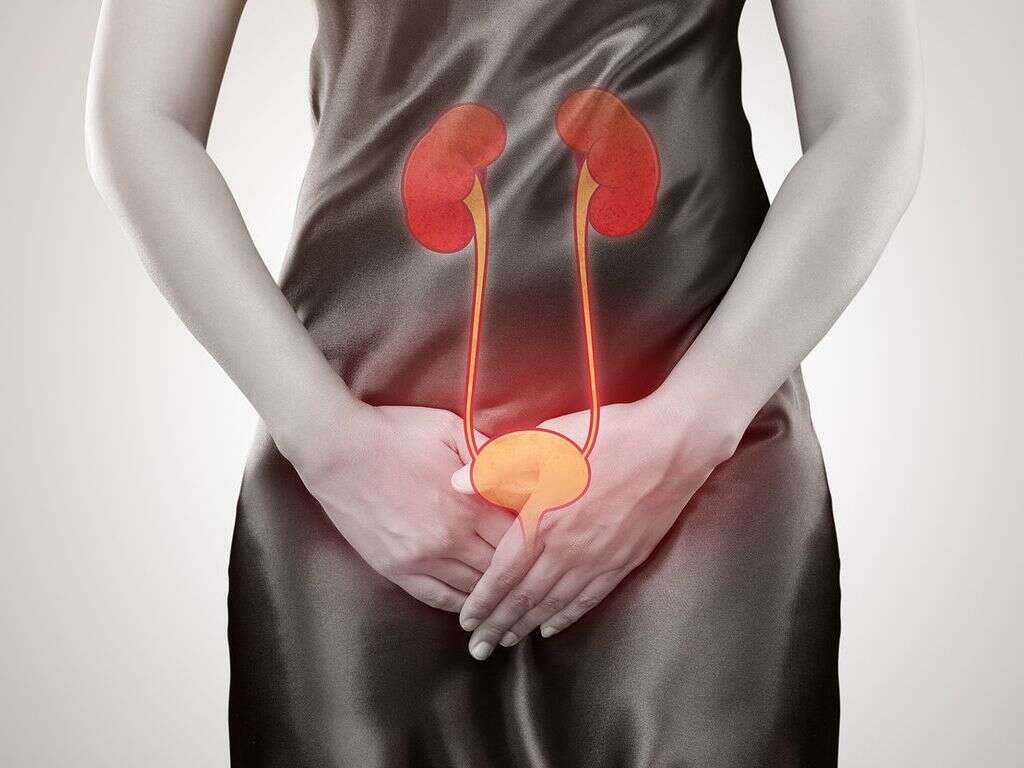
1. Urethritis?
Some medical conditions can cause the urethra to become inflamed in a condition known as urethritis. It can affect both men and women, and it can also happen in people of all ages. It is more likely to develop in women than it is in men, however.
Urethritis has similar symptoms to a urinary tract infection and it will often be mistaken for a UTI. The two are quite different, however, and the two require different treatments. Urethritis is not usually a dangerous condition in itself and can be treated. It will result in potentially serious complications in a small number of cases, however.

2. Different Types
There are two main types of urethritis, each of which will be caused by something different. One type is gonococcal urethritis, which makes up about 20 percent of all cases of urethritis. This variety is caused by the same bacteria that causes gonorrhea, the sexually transmitted disease.
Urethritis cases that are not caused by the gonorrhea bacteria are known as nongonococcal urethritis. There are numerous potential causes of this, one of which is chlamydia. In addition to infections, it is also possible for urethritis to develop because of injury or some other kind of irritation to the urethra. It is also possible for urethritis to be caused by more than one factor simultaneously.
3. Other Causes
In addition to bacteria, urethritis can also be caused by a number of viral infections, although bacteria are usually the culprit. Viruses that can be responsible for the condition include the herpes simplex virus, the cytomegalovirus, and the papillomavirus.
Injuries that can cause the condition include those that can be caused by a catheter damaging the tissues of the urethra. It can also sometimes be caused by soap irritating the delicate tissues, which is more common in young boys. There is also a link to the condition and stress. The cause is not always identified, in which case it is known as non-specific urethritis.
4. Symptoms In Men
Many people with urethritis will barely feel any symptoms, if at all. Men are less likely to have symptoms if the condition is caused by a chlamydia infection. The symptoms can be very uncomfortable if they are present, however. Symptoms of urethritis in men will typically include a discharge from the tip of the penis.
The patient will also often experience a burning or itchiness in the area of the tip, and urinating can cause a burning sensation. There may also sometimes be blood in their urine or semen. These symptoms should encourage the patient to speak with their doctor if they have not done so already.

5. Symptoms In Women
Women are less likely to experience symptoms from urethritis than men are. When there are symptoms, they can range from being mild to being very uncomfortable. Women will typically often experience an irritation at the opening of the urethra that will often be described as a burning sensation.
Women with the condition will also often experience a discharge from the vagina. Some will also complain that they need to urinate more frequently than usual. Urinating can also be very uncomfortable for them. Women should also make sure to see a doctor as soon as they can if they are experiencing these symptoms.

6. Sepsis
Serious complications for urethritis are very unlikely, especially considering the condition is very treatable. If the condition is not treated adequately, however, then serious problems can develop. Any pathogen causing the condition can spread to other parts of the body if left untreated, causing infections elsewhere in the body.
If the infection is severe enough, permanent damage to other organs can result. There is also a chance that the bloodstream will also become infected, potentially resulting in sepsis. Sepsis is a very serious condition indeed that is a result of a severe reaction to the presence of bacteria in the body.
7. Infertility In Women
If the infection were to spread from the urethra and reach the female reproductive system, then it may be able to do permanent damage there. This can result in a number of rather unwelcome conditions including pelvic inflammatory disease. This can cause pain during sex and pain in the pelvis throughout the day.
Untreated urethritis will also result in infertility in some cases. The condition will also make ectopic pregnancies more likely, which can be a threat to the patient’s life. In men the urethra can scar, causing it to become narrower, while the prostate gland can also become infected.

8. Prevention
Practices that will help to encourage a healthy urinary tract are one way to help prevent urethritis from developing. This includes avoiding foods that have a high acid content, and women should avoid using spermicides that irritate their urethra. Urinating after sex is also advised, as is drinking lots of fluids.
The underlying cause of urethritis is usually a sexually transmitted infection. This means that taking precautions against STIs can also help to protect people against urethritis. Using condoms will help to prevent the spread of diseases, while limiting how many sexual partners you have will also reduce your risk.

9. Diagnosis
Your doctor will likely ask about your medical history, and also ask about your symptoms. They may also need to perform a brief exam of the genitals to look for signs of sexually transmitted infections. They are also likely to request a urine sample and/or a swab so that further tests can be carried out.
Tests will help doctors to detect the presence of certain pathogens that would be the cause of urethritis. With the cause detected, the doctor can then prescribe the appropriate medication that will help deal with the underlying problem. The tests can also help to rule out STIs, encouraging them to look for other potential causes instead.
10. Treatment
Treatment for urethritis will depend on the underlying cause of the condition. In most cases it will mean that antibiotics are needed to help clear a bacterial infection. Antiviral medications are needed instead in cases where a virus is the culprit. Patients should always make sure to complete the course of any medication they are prescribed.
It will also be important for the patient to abstain from sexual intercourse until their condition has been cured. If the condition was caused by an STI, then the patient should also inform their sexual partners. Their partners will also need to get checked up and treated if necessary.