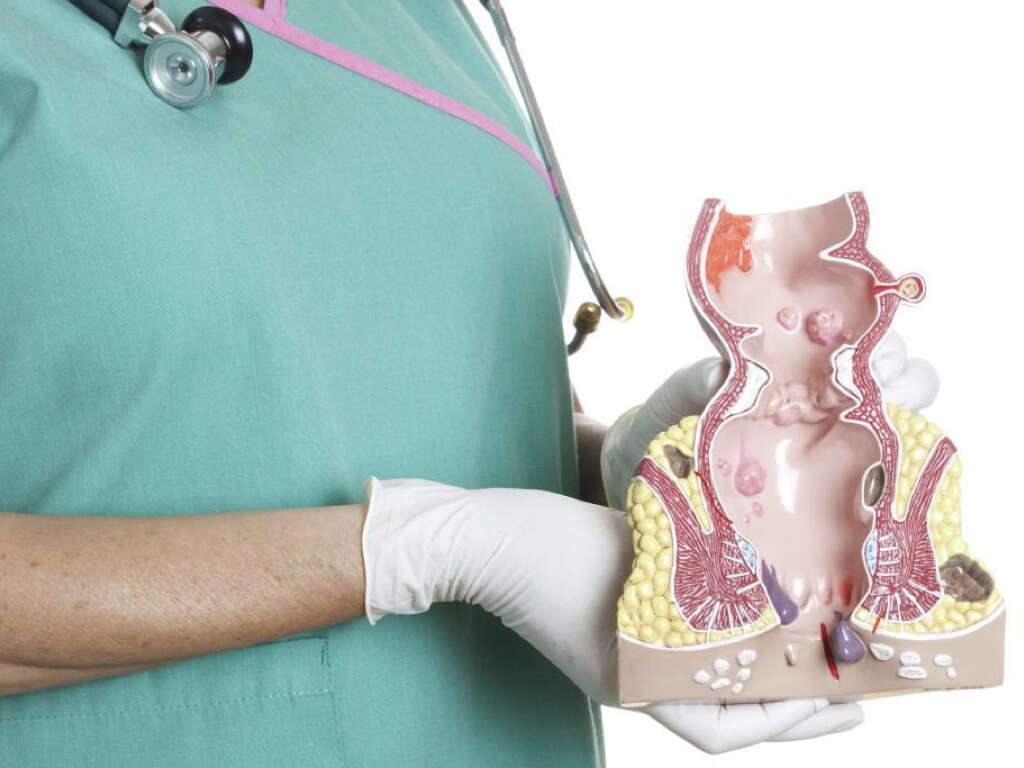
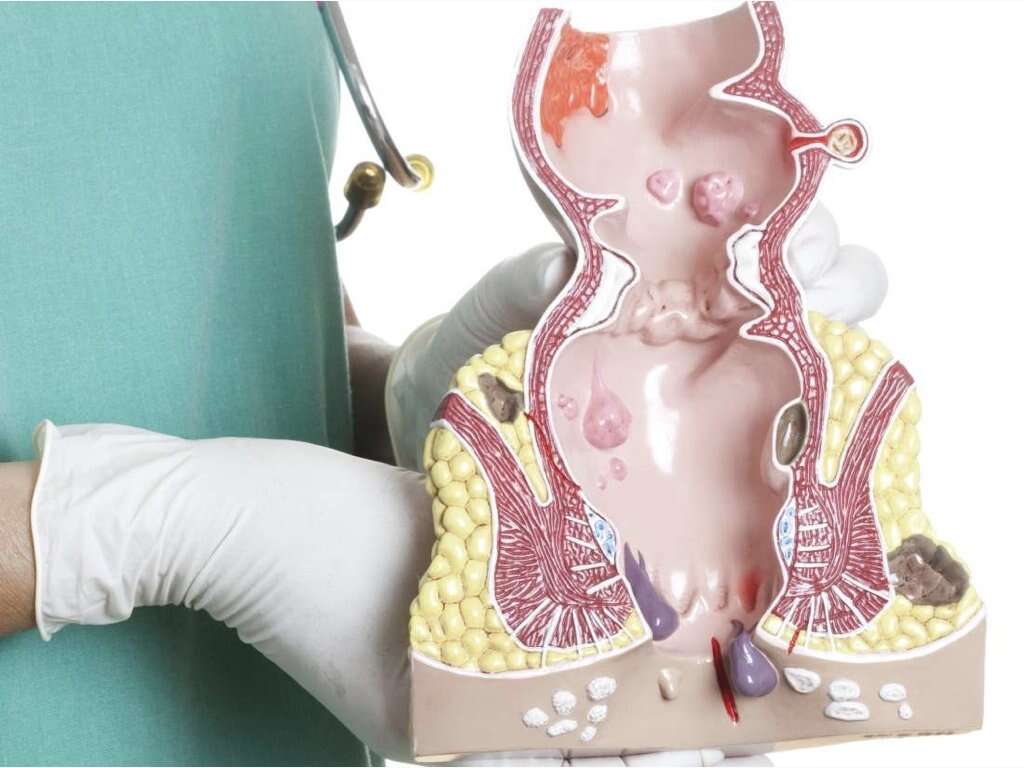
Rectal Prolapse Symptoms, Causes and More
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. ‘Rectal Prolapse Expanded Version.’ ASCRS, fascrs.org/patients/diseases-and-conditions/a-z/rectal-prolapse-expanded-version
- 2. ‘Rectal Prolapse: Treatment, Diagnosis, Causes & Symptoms.’ Cleveland Clinic, my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/14615-rectal-prolapse#:~:text=Is rectal prolapse just another, the anus and lower rectum
- 3. Jan Rakinic, MD. ‘Rectal Prolapse Treatment & Management: Approach Considerations, Nonoperative Management, Surgical Options.’ Medscape, 24 July 2020, emedicine.medscape.com/article/2026460-treatment
- 4. Trompetto, Mario, et al. ‘Altemeier’s Procedure for Complete Rectal Prolapse; Outcome and Function in 43 Consecutive Female Patients.’ BMC Surgery, BioMed Central, 3 Jan. 2019, bmcsurg.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12893-018-0463-7#:~:text=Altemeier’s procedure is one of the pouch of Douglas
Diagnosis
Diagnosis begins with a doctor reviewing a person's medical history and asking them to describe their symptoms. The doctor may also undertake a complete physical examination, in which the patient may be asked to squat and strain as if they're passing stool.
The doctor observes the anus and may place a gloved finger inside to assess the strength and health of the anal sphincter and rectum. The patient may also undergo a colonoscopy to determine whether any polyps are present in the large intestine.
Advertisement