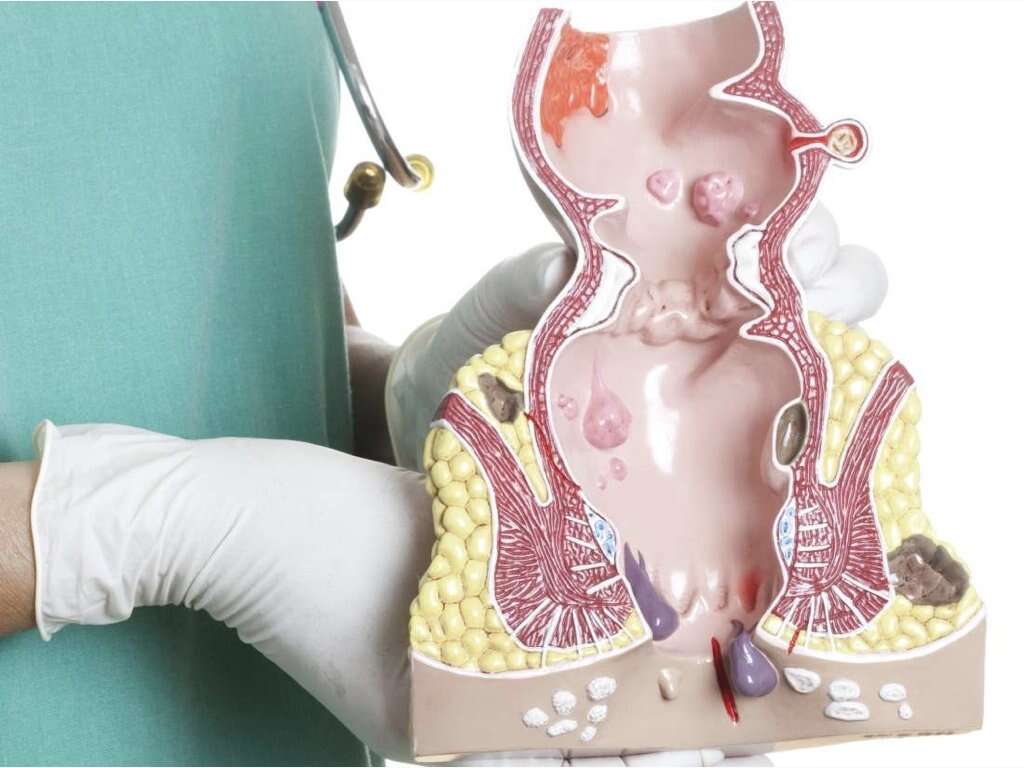
Rectal Prolapse Symptoms, Causes and More
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. ‘Rectal Prolapse Expanded Version.’ ASCRS, fascrs.org/patients/diseases-and-conditions/a-z/rectal-prolapse-expanded-version
- 2. ‘Rectal Prolapse: Treatment, Diagnosis, Causes & Symptoms.’ Cleveland Clinic, my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/14615-rectal-prolapse#:~:text=Is rectal prolapse just another, the anus and lower rectum
- 3. Jan Rakinic, MD. ‘Rectal Prolapse Treatment & Management: Approach Considerations, Nonoperative Management, Surgical Options.’ Medscape, 24 July 2020, emedicine.medscape.com/article/2026460-treatment
- 4. Trompetto, Mario, et al. ‘Altemeier’s Procedure for Complete Rectal Prolapse; Outcome and Function in 43 Consecutive Female Patients.’ BMC Surgery, BioMed Central, 3 Jan. 2019, bmcsurg.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12893-018-0463-7#:~:text=Altemeier’s procedure is one of the pouch of Douglas
Treatment
Very minor cases of rectal prolapse may be treated at home using stool softeners and pushing the prolapsed tissue back into the anus using the hand. However, surgery is necessary in many cases.
The extent of the prolapse, existing health problems, the person's age and the results of a physical exam and tests determine the type of surgery required. The surgeon's experience and preferences may also factor into their choice of surgery type. The most common approaches are abdominal and rectal surgery.
Advertisement