10 Cat Scratch Fever Symptoms
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. ’Cat Scratch Disease (Bartonella henselae infection).’ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/healthypets/diseases/cat-scratch.html
- 2. ’Cat-Scratch Disease.’ American Academy of Family Physicians. https://familydoctor.org/condition/cat-scratch-disease
- 3. ’Cat Scratch Disease.’ MedlinePlus. https://medlineplus.gov/catscratchdisease.html
- 4. ’Cat Scratch Disease.’ Johns Hopkins Medicine. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/cat-scratch-disease
- 5. Giladi M; Maman E; Paran D; Bickels J et al. ‘Cat Scratch Disease Associated arthropathy. ’Arthritis and Rheumatism Nov 2005. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16255053
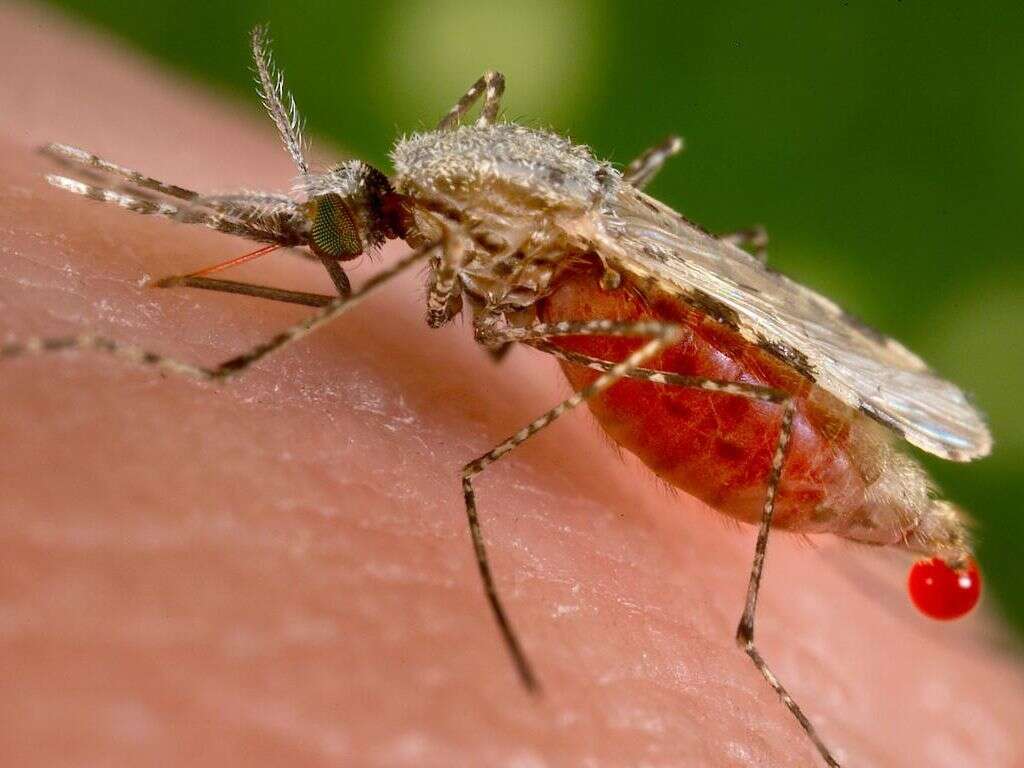
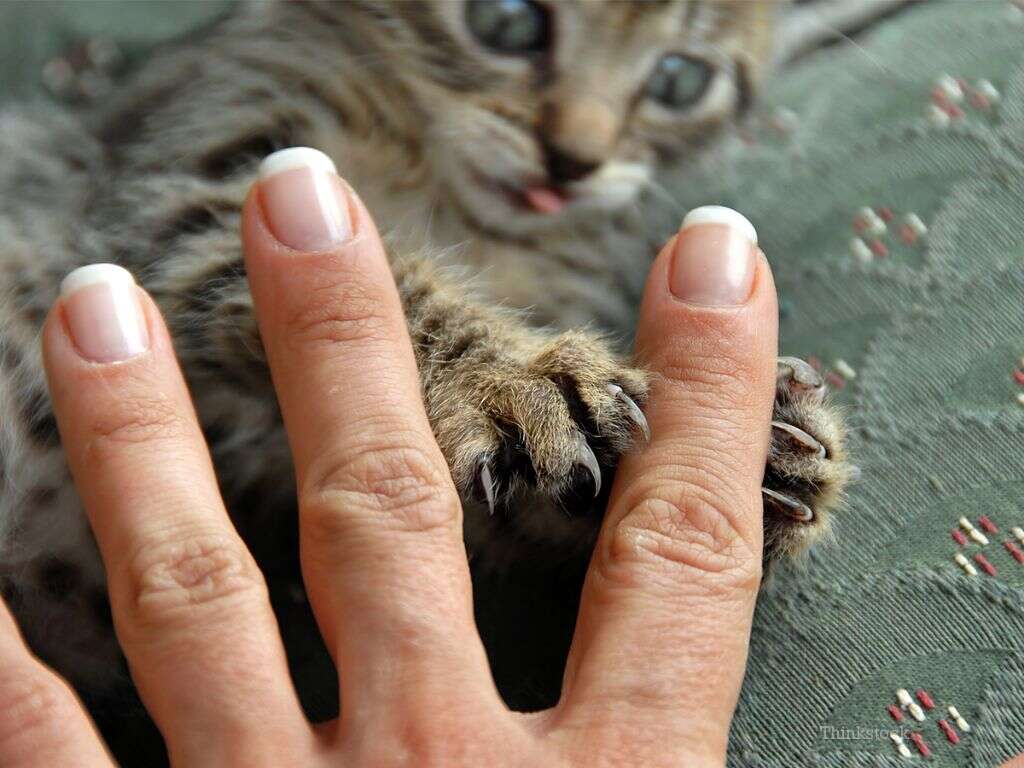
Cat Scratch Fever, also called Cat Scratch Disease or CSD, is an infection passed to humans by a bite or scratch from a cat infected with Bartonella henselae bacteria. Cats bite and scratch at the fleas that carry the bacteria and transfer it to their claws and teeth. Open wounds can be infected by a cat licking them.
About 40% of cats, especially kittens, carry the Bartonella bacteria.1’Cat Scratch Disease (Bartonella henselae infection).’ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/healthypets/diseases/cat-scratch.html Rough play increases the chance that infection will happen. Outward symptoms of Cat Scratch Fever appear about three to 14 days after exposure. The infection in humans is typically mild, but it can cause serious complications.
Symptoms at the Site of the Cat Scratch or Bite
The early symptoms of Cat Scratch Fever appear at the site of the wound, which may appear swollen and red with raised bumps, sores or blisters. These symptoms generally appear within three to 10 days after the scratching incident. The lesion on the skin may take a long time to heal, even after other symptoms are gone.2’Cat-Scratch Disease.’ American Academy of Family Physicians. https://familydoctor.org/condition/cat-scratch-disease
Secondary infections can be caused by other bacteria or viruses entering the open wound. To prevent secondary infection, it's important to keep the wound clean and dry. Treatment may include antibiotics, although most cases are mild and resolve without treatment.

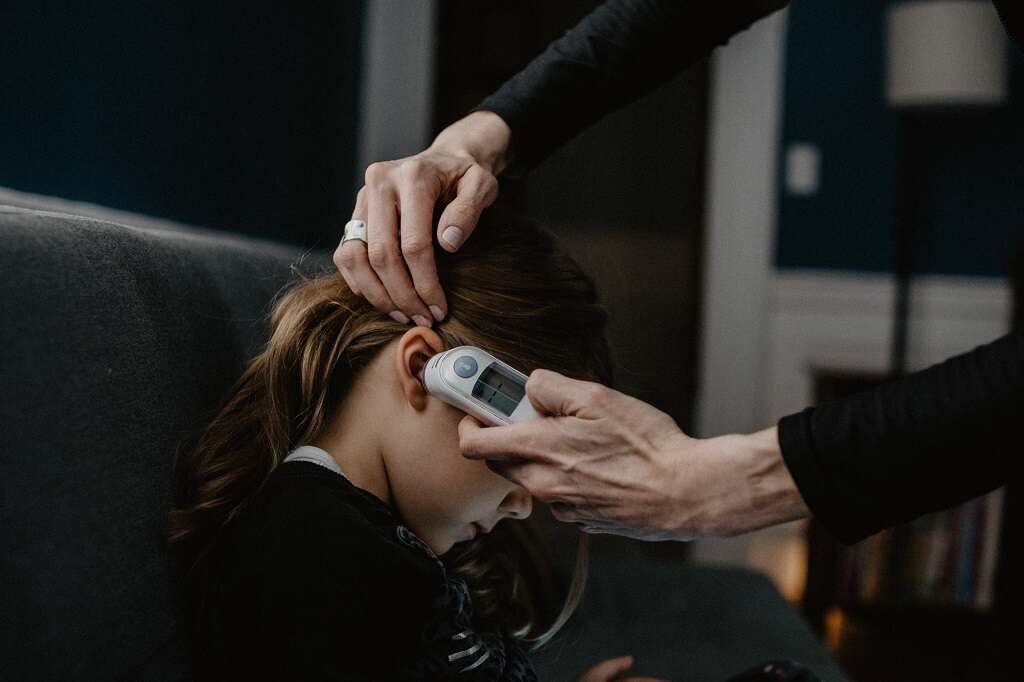
Other Cat Scratch Fever Symptoms
A fever less than 102 degrees is typical in CSD. If it rises, the infection may be more serious or a secondary infection may have developed. Headaches, poor appetite and exhaustion may appear, as well.
There may be swollen, painful lymph nodes near the wound site. If the scratch or bite is on the arm, the lymph nodes in the armpit or inside the elbow may swell. If the scratch is to the face or neck, head and neck nodes swell and become tender.3’Cat Scratch Disease.’ MedlinePlus. https://medlineplus.gov/catscratchdisease.html

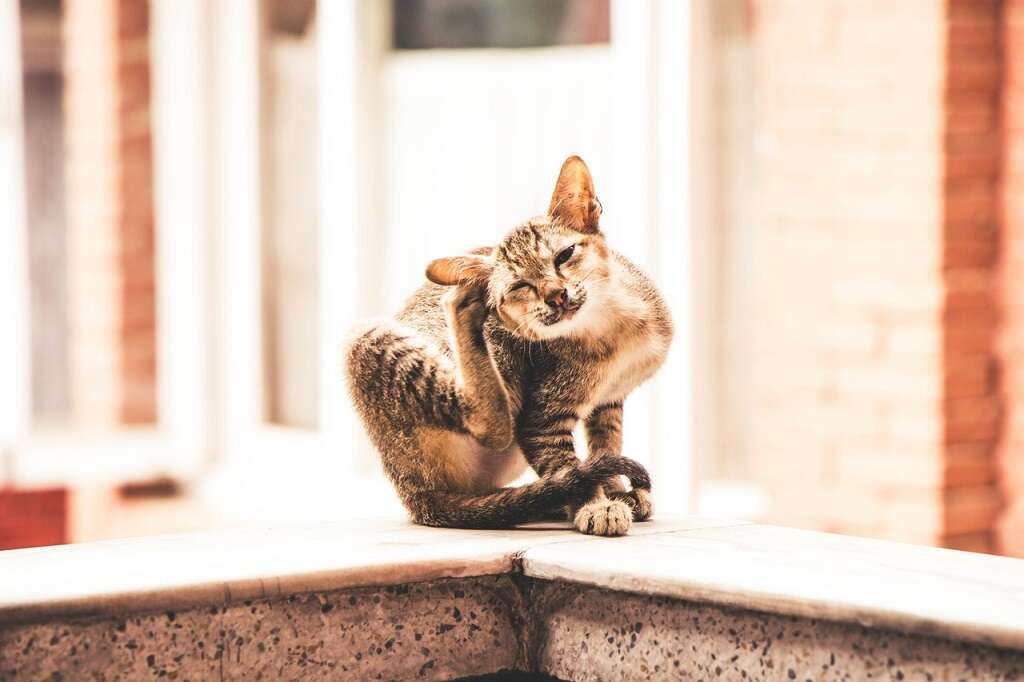
Bartonella Symptoms in the Cat
Cats typically show no signs of illness, but the presence of fleas and flea bites on a cat or kitten means the chances are good that they have become infected. If cats experience symptoms, they usually have fever, swollen glands and muscle aches.
On rare occasions, Bartonella henselae bacteria can cause complications within the cat's body. These may include heart inflammation that leads to labored breathing. The disease may also develop in a cat's eyes, mouth or urinary system. Antibiotics help treat these complications.1’Cat Scratch Disease (Bartonella henselae infection).’ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/healthypets/diseases/cat-scratch.html

Complications of Cat Scratch Fever
Cat Scratch Fever rarely causes complications, but they can be serious and require medical attention if they arise. Organs involved include the brain, eyes and heart. Symptoms include severe headaches, pain, blindness and difficulty breathing because of heart problems. Bone infections, or osteomyelitis, can also develop.
People who have weakened immune systems and children five to 14 years old are those most likely to have complications.1’Cat Scratch Disease (Bartonella henselae infection).’ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/healthypets/diseases/cat-scratch.html Weakened immune systems are associated with diabetes, cancer, chemotherapy, HIV or AIDS and other chronic illnesses.

Bacillary Angiochromatosis Symptoms
Bacillary angiomatosis is an infection caused by Bartonella quintana or B henselae, the same bacterium responsible for cat scratch fever. It's a skin disorder that causes red, elevated lesions surrounded by a scaly ring, and the lesions bleed easily. It may also affect internal organs, appearing as tumors.
The disorder was originally thought to only affect HIV patients, but it's now known to occur in people with normal and weakened immune systems. This includes people with diabetes, cancer and chemotherapy patients.4’Cat Scratch Disease.’ Johns Hopkins Medicine. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/cat-scratch-disease

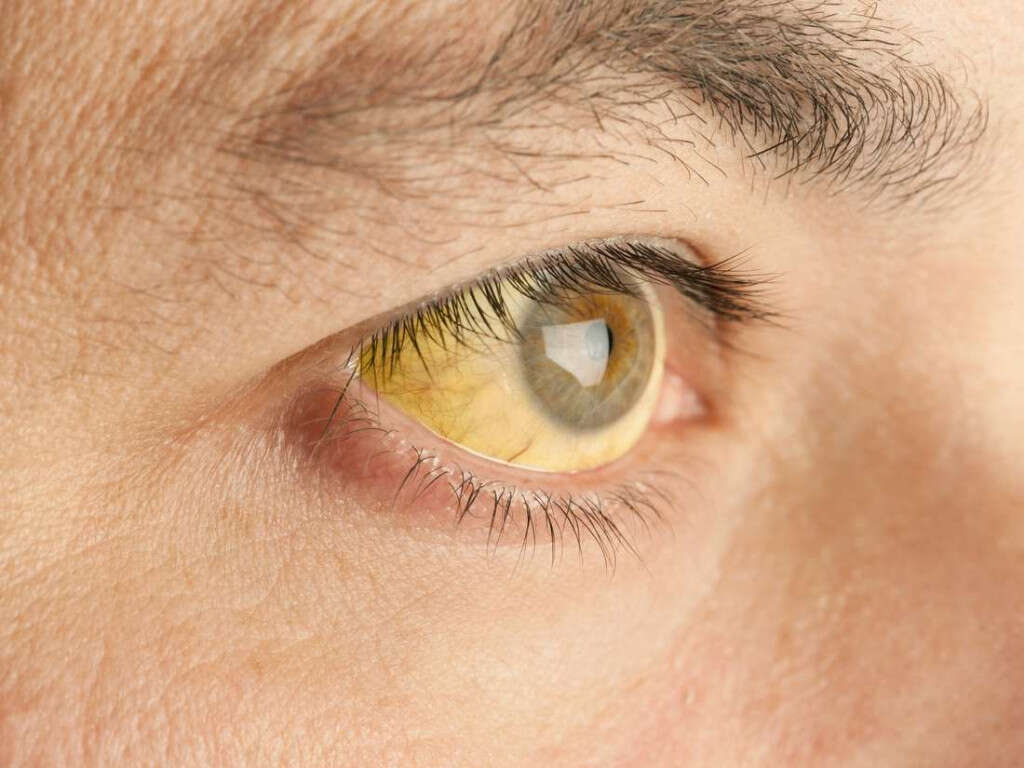
Parinaud's Oculoglandular Syndrome
Parinaud oculoglandular syndrome is a potential complication of Cat Scratch Fever that affects the eyes and lymph glands of the face and neck. The eye itself looks red, much like it does in conjunctivitis or pink eye. It feels irritated and may cause pain. There may be an infection of the retina.
In response to the infection, the lymph nodes on the face in front of the ear typically swell and are tender. Fever may also be a symptom of this infection.4’Cat Scratch Disease.’ Johns Hopkins Medicine. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/cat-scratch-disease

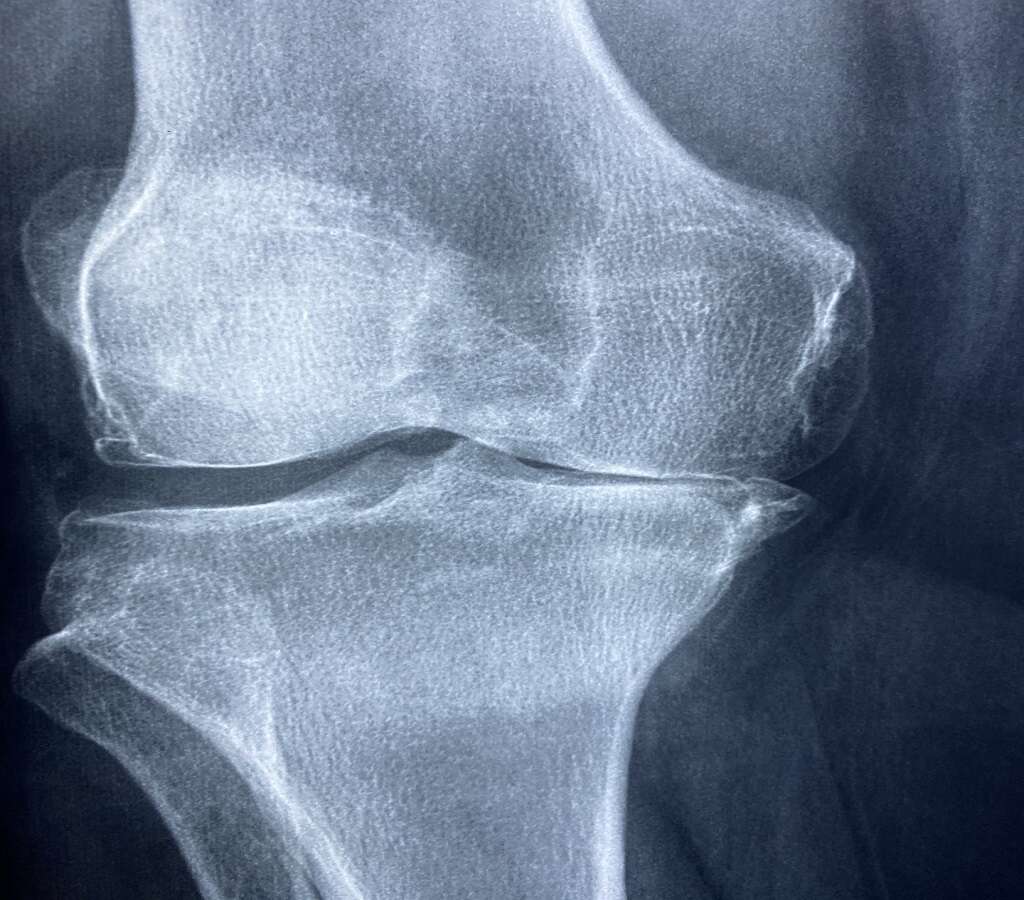
Arthropathy Associated With Cat Scratch Fever
Arthropathy is the medical term for diseases of the joints. Studies have shown that in rare cases, people with CSD may develop arthropathy, especially young and middle-aged women.
Arthropathy causes swelling and pain in the skeletal joints in the body. Like osteoarthritis, symptoms may come and go, but it can be a disabling condition. It may become chronic and last throughout a person's life. Arthropathies usually arise after CSD symptoms have resolved.5Giladi M; Maman E; Paran D; Bickels J et al. ‘Cat Scratch Disease Associated arthropathy. ’Arthritis and Rheumatism Nov 2005. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16255053
Symptoms of Cat Scratch Fever in Elderly Patients
Cat Scratch Disease is typically an ailment of children and young adults. Research has shown that people aged 60 years or older get Cat Scratch Disease but rarely exhibit swollen lymph glands. Elderly are more likely to complain of malaise.
However, CSD endocarditis, an inflammation of the inner lining of the heart, can affect older patients, although this complication is rare. Encephalitis, which is the inflammation of the brain, is also a rare, but a possible complication of Cat Scratch disease in elderly.

When to Call the Doctor
Certain CSD symptoms should prompt a call to a doctor because they can lead to severe complications, including a scratch or bite that doesn't heal or a red, round area that keeps growing.
A high fever that lasts several days or lymph nodes that remain swollen and painful for more than two to three weeks are also cues to call the doctor. Signs of serious infections or complications include bone or joint pain, abdominal pain and excessive fatigue that lasts more than two weeks.2’Cat-Scratch Disease.’ American Academy of Family Physicians. https://familydoctor.org/condition/cat-scratch-disease

Summary
A cat bite or scratch may lead to a skin infection called Cat Scratch Disease. There will be no signs that the cat is infected, but the presence of fleas should raise a red flag.
The disease is generally mild, with a fever of less than 102 degrees and some lymph node swelling, but in some cases, it may progress to complications. Pain and swelling in unexpected places like the joints or eyes indicate possible complications that should be addressed.